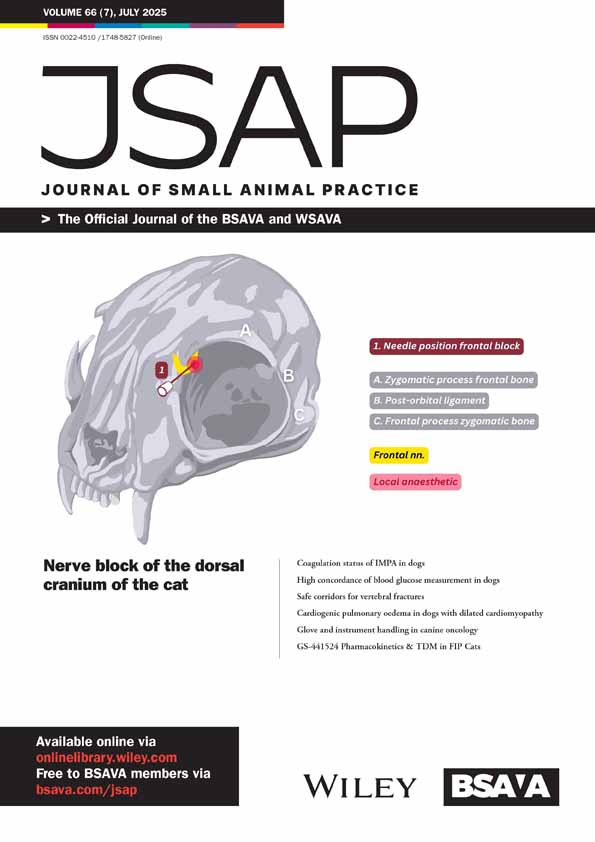
High concordance of blood glucose measurement in dogs between a beta prototype glucometer device and a reference laboratory standard in a clinical setting
Abstract
Objectives
The objective of this study was to confirm the accuracy of a new portable beta prototype glucometer device for monitoring blood glucose levels in dogs.
Materials and Methods
One hundred and three client-owned dogs with dysglycemia or normoglycemia were enrolled. A 3 mL whole blood sample was collected from a peripheral vein from each dog and divided into four aliquots. Blood glucose was measured from three of the aliquots on the beta prototype glucometer in triplicate. The remaining aliquot was used to measure packed cell volume, total solids, and blood glucose via a reference laboratory chemistry analyzer. Accuracy was assessed in accordance with the International Organization for Standardization guidelines.
Results
The analytical performance of the beta prototype met the International Organization for Standardization accuracy requirements, with 95.1% of measurements falling within the International Organization for Standardization accuracy threshold as well as 100% of measurements being within zones A and B of the consensus error grid. Within the full range of glucose concentrations (20 to 750 mg/dL) the mean difference between the AT3 and reference lab analyzer was 2.53 mg/dL (95% limit of agreement: −45.27 to 50.34).
Clinical Significance
The beta prototype glucometer device had a strong correlation with the reference laboratory standard and can be used confidently in clinical patients for the accurate monitoring of blood glucose levels in dogs.
Open Research
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.