Serum Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer dynamics in patients achieving sustained virologic response for hepatitis C virus
Yu-Ping Chang and Chen-Hua Liu contribute equally to the work.
Abstract
Background and Aim
Understanding the dynamics of serum Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi) remains pivotal for hepatitis C virus (HCV) patients' post-sustained virologic response (SVR12) through direct-acting antivirals (DAAs).
Methods
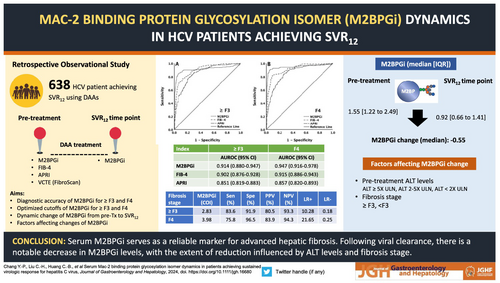
We compared areas under receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROCs) of M2BPGi, FIB-4, and APRI and assess M2BPGi cutoff levels in predicting fibrosis stages of ≥F3 and F4 utilizing transient elastography in 638 patients. Variations in M2BPGi levels from pretreatment to SVR12 and their association with pretreatment alanine transaminase (ALT) levels and fibrosis stage were investigated.
Results
The AUROCs of M2BPGi were comparable to FIB-4 in predicting ≥F3 (0.914 vs 0.902, P = 0.48) and F4 (0.947 vs 0.915, P = 0.05) but were superior to APRI in predicting ≥F3 (0.914 vs 0.851, P = 0.001) and F4 (0.947 vs 0.857, P < 0.001). Using M2BPGi cutoff values of 2.83 and 3.98, fibrosis stages of ≥F3 and F4 were confirmed with a positive likelihood ratio ≥10. The median M2BPGi change was −0.55. Patients with ALT levels ≥5 times ULN or ≥F3 demonstrated more pronounced median decreases in M2BPGi level compared to those with ALT levels 2–5 times ULN and <2 times ULN (−0.97 vs −0.68 and −0.44; P < 0.001) or with < F3 (−1.52 vs −0.44; P < 0.001).
Conclusions
Serum M2BPGi is a reliable marker for advanced hepatic fibrosis. Following viral clearance, there is a notable M2BPGi decrease, with the extent of reduction influenced by ALT levels and fibrosis stage.
Graphical Abstract
Open Research
Data availability statement
Data for this study can be made available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.