STAGES: the Space Telescope A901/2 Galaxy Evolution Survey
Corresponding Author
Meghan E. Gray
School of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Nottingham, University Park, Nottingham NG7 2RD
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorChristian Wolf
Department of Astrophysics, Denys Wilkinson Building, University of Oxford, Keble Road, Oxford OX1 3RH
Search for more papers by this authorMarco Barden
Institute for Astro- and Particle Physics, University of Innsbruck, Technikerstr. 25/8, A-6020 Innsbruck, Austria
Search for more papers by this authorChien Y. Peng
NRC Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, 5071 West Saanich Road, Victoria, V9E 2E7, Canada
Space Telescope Science Institute, 3700 San Martin Drive, Baltimore, MD 21218, USA
Search for more papers by this authorBoris Häußler
School of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Nottingham, University Park, Nottingham NG7 2RD
Search for more papers by this authorEric F. Bell
Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, D-69117, Heidelberg, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorDaniel H. McIntosh
Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts, 710 North Pleasant Street, Amherst, MA 01003, USA
Department of Physics, 5110 Rockhill Road, University of Missouri-Kansas City, Kansas City, MO 64110, USA
Search for more papers by this authorYicheng Guo
Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts, 710 North Pleasant Street, Amherst, MA 01003, USA
Search for more papers by this authorJohn A. R. Caldwell
University of Texas, McDonald Observatory, Fort Davis, TX 79734, USA
Search for more papers by this authorDavid Bacon
Institute of Cosmology and Gravitation, University of Portsmouth, Hampshire Terrace, Portsmouth PO1 2EG
Search for more papers by this authorMichael Balogh
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University Of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, N2L 3G1, Canada
Search for more papers by this authorFabio D. Barazza
Laboratoire d'Astrophysique, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Observatoire de Sauverny, CH-1290 Versoix, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorAsmus Böhm
Astrophysikalisches Insitut Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, D-14482 Potsdam, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCatherine Heymans
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of British Columbia, 6224 Agricultural Road, Vancouver, V6T 1Z1, Canada
The Scottish Universities Physics Alliance (SUPA), Institute for Astronomy, University of Edinburgh, Blackford Hill, Edinburgh EH9 3HJ
Search for more papers by this authorKnud Jahnke
Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, D-69117, Heidelberg, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorShardha Jogee
Department of Astronomy, University of Texas at Austin, 1 University Station, C1400 Austin, TX 78712-0259, USA
Search for more papers by this authorEelco Van Kampen
Institute for Astro- and Particle Physics, University of Innsbruck, Technikerstr. 25/8, A-6020 Innsbruck, Austria
European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Strasse 2, D-85748 Garching bei Muenchen, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorKyle Lane
School of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Nottingham, University Park, Nottingham NG7 2RD
Search for more papers by this authorKlaus Meisenheimer
Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, D-69117, Heidelberg, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorSebastian F. Sánchez
Centro Hispano Aleman de Calar Alto, C/Jesus Durban Remon 2-2, E-04004 Ameria, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorAndy Taylor
The Scottish Universities Physics Alliance (SUPA), Institute for Astronomy, University of Edinburgh, Blackford Hill, Edinburgh EH9 3HJ
Search for more papers by this authorLutz Wisotzki
Astrophysikalisches Insitut Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, D-14482 Potsdam, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorXianzhong Zheng
Purple Mountain Observatory, National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanjing 210008, PR China
Search for more papers by this authorDavid A. Green
Cavendish Laboratory, 19 J.J. Thomson Avenue, Cambridge CB3 0HE
Search for more papers by this authorR. J. Beswick
Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics, Department of Physics & Astronomy, The University of Manchester, Oxford Road, Manchester M13 9PL
Search for more papers by this authorD. J. Saikia
National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, TIFR, Pune University Campus, Post Bag 3, Pune 411 007, India
Search for more papers by this authorRachel Gilmour
European Southern Observatory, Alonso de Cordova 3107, Vitacura, Casilla 19001, Santiago 19, Chile
Search for more papers by this authorBenjamin D. Johnson
Institute of Astronomy, Madingley Road, Cambridge CB3 0HA
Search for more papers by this authorCasey Papovich
Department of Physics, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77843, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Meghan E. Gray
School of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Nottingham, University Park, Nottingham NG7 2RD
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorChristian Wolf
Department of Astrophysics, Denys Wilkinson Building, University of Oxford, Keble Road, Oxford OX1 3RH
Search for more papers by this authorMarco Barden
Institute for Astro- and Particle Physics, University of Innsbruck, Technikerstr. 25/8, A-6020 Innsbruck, Austria
Search for more papers by this authorChien Y. Peng
NRC Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, 5071 West Saanich Road, Victoria, V9E 2E7, Canada
Space Telescope Science Institute, 3700 San Martin Drive, Baltimore, MD 21218, USA
Search for more papers by this authorBoris Häußler
School of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Nottingham, University Park, Nottingham NG7 2RD
Search for more papers by this authorEric F. Bell
Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, D-69117, Heidelberg, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorDaniel H. McIntosh
Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts, 710 North Pleasant Street, Amherst, MA 01003, USA
Department of Physics, 5110 Rockhill Road, University of Missouri-Kansas City, Kansas City, MO 64110, USA
Search for more papers by this authorYicheng Guo
Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts, 710 North Pleasant Street, Amherst, MA 01003, USA
Search for more papers by this authorJohn A. R. Caldwell
University of Texas, McDonald Observatory, Fort Davis, TX 79734, USA
Search for more papers by this authorDavid Bacon
Institute of Cosmology and Gravitation, University of Portsmouth, Hampshire Terrace, Portsmouth PO1 2EG
Search for more papers by this authorMichael Balogh
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University Of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, N2L 3G1, Canada
Search for more papers by this authorFabio D. Barazza
Laboratoire d'Astrophysique, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Observatoire de Sauverny, CH-1290 Versoix, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorAsmus Böhm
Astrophysikalisches Insitut Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, D-14482 Potsdam, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCatherine Heymans
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of British Columbia, 6224 Agricultural Road, Vancouver, V6T 1Z1, Canada
The Scottish Universities Physics Alliance (SUPA), Institute for Astronomy, University of Edinburgh, Blackford Hill, Edinburgh EH9 3HJ
Search for more papers by this authorKnud Jahnke
Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, D-69117, Heidelberg, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorShardha Jogee
Department of Astronomy, University of Texas at Austin, 1 University Station, C1400 Austin, TX 78712-0259, USA
Search for more papers by this authorEelco Van Kampen
Institute for Astro- and Particle Physics, University of Innsbruck, Technikerstr. 25/8, A-6020 Innsbruck, Austria
European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Strasse 2, D-85748 Garching bei Muenchen, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorKyle Lane
School of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Nottingham, University Park, Nottingham NG7 2RD
Search for more papers by this authorKlaus Meisenheimer
Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, D-69117, Heidelberg, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorSebastian F. Sánchez
Centro Hispano Aleman de Calar Alto, C/Jesus Durban Remon 2-2, E-04004 Ameria, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorAndy Taylor
The Scottish Universities Physics Alliance (SUPA), Institute for Astronomy, University of Edinburgh, Blackford Hill, Edinburgh EH9 3HJ
Search for more papers by this authorLutz Wisotzki
Astrophysikalisches Insitut Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, D-14482 Potsdam, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorXianzhong Zheng
Purple Mountain Observatory, National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanjing 210008, PR China
Search for more papers by this authorDavid A. Green
Cavendish Laboratory, 19 J.J. Thomson Avenue, Cambridge CB3 0HE
Search for more papers by this authorR. J. Beswick
Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics, Department of Physics & Astronomy, The University of Manchester, Oxford Road, Manchester M13 9PL
Search for more papers by this authorD. J. Saikia
National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, TIFR, Pune University Campus, Post Bag 3, Pune 411 007, India
Search for more papers by this authorRachel Gilmour
European Southern Observatory, Alonso de Cordova 3107, Vitacura, Casilla 19001, Santiago 19, Chile
Search for more papers by this authorBenjamin D. Johnson
Institute of Astronomy, Madingley Road, Cambridge CB3 0HA
Search for more papers by this authorCasey Papovich
Department of Physics, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77843, USA
Search for more papers by this authorABSTRACT
We present an overview of the Space Telescope A901/2 Galaxy Evolution Survey (STAGES). STAGES is a multiwavelength project designed to probe physical drivers of galaxy evolution across a wide range of environments and luminosity. A complex multicluster system at z∼ 0.165 has been the subject of an 80-orbit F606W Hubble Space Telescope (HST)/Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) mosaic covering the full 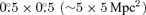 span of the supercluster. Extensive multiwavelength observations with XMM–Newton, GALEX, Spitzer, 2dF, Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope and the 17-band COMBO-17 photometric redshift survey complement the HST imaging. Our survey goals include simultaneously linking galaxy morphology with other observables such as age, star formation rate, nuclear activity and stellar mass. In addition, with the multiwavelength data set and new high-resolution mass maps from gravitational lensing, we are able to disentangle the large-scale structure of the system. By examining all aspects of an environment we will be able to evaluate the relative importance of the dark matter haloes, the local galaxy density and the hot X-ray gas in driving galaxy transformation. This paper describes the HST imaging, data reduction and creation of a master catalogue. We perform the Sérsic fitting on the HST images and conduct associated simulations to quantify completeness. In addition, we present the COMBO-17 photometric redshift catalogue and estimates of stellar masses and star formation rates for this field. We define galaxy and cluster sample selection criteria, which will be the basis for forthcoming science analyses, and present a compilation of notable objects in the field. Finally, we describe the further multiwavelength observations and announce public access to the data and catalogues.
span of the supercluster. Extensive multiwavelength observations with XMM–Newton, GALEX, Spitzer, 2dF, Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope and the 17-band COMBO-17 photometric redshift survey complement the HST imaging. Our survey goals include simultaneously linking galaxy morphology with other observables such as age, star formation rate, nuclear activity and stellar mass. In addition, with the multiwavelength data set and new high-resolution mass maps from gravitational lensing, we are able to disentangle the large-scale structure of the system. By examining all aspects of an environment we will be able to evaluate the relative importance of the dark matter haloes, the local galaxy density and the hot X-ray gas in driving galaxy transformation. This paper describes the HST imaging, data reduction and creation of a master catalogue. We perform the Sérsic fitting on the HST images and conduct associated simulations to quantify completeness. In addition, we present the COMBO-17 photometric redshift catalogue and estimates of stellar masses and star formation rates for this field. We define galaxy and cluster sample selection criteria, which will be the basis for forthcoming science analyses, and present a compilation of notable objects in the field. Finally, we describe the further multiwavelength observations and announce public access to the data and catalogues.
REFERENCES
- Ananthakrishnan S., 2005, in B. S. Acharya et al., eds, Proc. 29th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf., Vol. 10, The Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT): Salient Features and Recent Results. Tata Inst. Fund. Research, Mumbai , p. 125
- Appleton P. N. et al., 2004, ApJS, 154, 147
- Bacon D. J., Goldberg D. M., Rowe B. T. P., Taylor A. N., 2006, MNRAS, 365, 414
- Baldry I. K., Balogh M. L., Bower R. G., Glazebrook K., Nichol R. C., Bamford S. P., Budavari T., 2006, MNRAS, 373, 469
- Balogh M. et al., 2004, MNRAS, 348, 1355
-
Barnes J. E., 1992, ApJ, 393, 484
10.1086/171522 Google Scholar
- Bekki K., 1999, ApJ, 510, L15
- Bell E. F., 2003, ApJ, 586, 794
-
Bell E. F.,
De Jong R. S., 2001, ApJ, 550, 212
10.1086/319728 Google Scholar
- Bell E. F., McIntosh D. H., Katz N., Weinberg M. D., 2003, ApJS, 149, 289
- Bell E. F. et al., 2005, ApJ, 625, 23
- Bell E. F., Zheng X. Z., Papovich C., Borch A., Wolf C., Meisenheimer K., 2007, ApJ, 663, 834
- Bertin E., Arnouts S., 1996, A&AS, 117, 393
- Blakeslee J. P. et al., 2006, ApJ, 644, 30
- Blanton M. R., Eisenstein D., Hogg D. W., Schlegel D. J., Brinkmann J., 2005, ApJ, 629, 143
- Böhringer H. et al., 2004, A&A, 425, 367
- Borch A. et al., 2006, A&A, 453, 869
- Buscombe W., 1998, VizieR Online Data Catalog, 3206, 0
- Caldwell J. A. R. et al., 2008, ApJS, 174, 136
- Calzetti D. et al., 2007, ApJ, 666, 870
- Capak P., Abraham R. G., Ellis R. S., Mobasher B., Scoville N., Sheth K., Koekemoer A., 2007, ApJS, 172, 284
- Carter D. et al., 2002, ApJ, 567, 772
- Carter D. et al., 2008, ApJS, 176, 424
- Chabrier G., 2003, ApJ, 586, L133
- Chary R., Elbaz D., 2001, ApJ, 556, 562
- Coia D. et al., 2005, A&A, 431, 433
-
Colless M.
et al., 2001, MNRAS, 328, 1039
10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04902.x Google Scholar
- Conselice C. J., 2003, ApJS, 147, 1
- Cooper M. C. et al., 2007, MNRAS, 376, 1445
- Dale D. A., Helou G., Contursi A., Silbermann N. A., Kolhatkar S., 2001, ApJ, 549, 215
-
De Lucia G.,
Springel V.,
White S. D. M.,
Croton D.,
Kauffmann G., 2006, MNRAS, 366, 499
10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09879.x Google Scholar
- Desai V. et al., 2007, ApJ, 660, 1151
- Devriendt J. E. G., Guiderdoni B., Sadat R., 1999, A&A, 350, 381
- Dressler A., 1980, ApJ, 236, 351
- Dressler A. et al., 1997, ApJ, 490, 577
- Ebeling H., Voges W., Bohringer H., Edge A. C., Huchra J. P., Briel U. G., 1996, MNRAS, 281, 799
- Elbaz D., Le Floc'h E., Dole H., Marcillac D., 2005, A&A, 434, L1
- Fazio G. G. et al., 2004, ApJS, 154, 10
- Fioc M., Rocca-Volmerange B., 1997, A&A, 326, 950
- Fujita Y., 1998, ApJ, 509, 587
- Gómez P. L. et al., 2003, ApJ, 584, 210
- Gallazzi A. et al., 2009, ApJ, 690, 1883
- Garn T., Green D. A., Hales S. E. G., Riley J. M., Alexander P., 2007, MNRAS, 376, 1251
- Geach J. E. et al., 2006, ApJ, 649, 661
- Gilmour R., Gray M. E., Almaini O., Best P., Wolf C., Meisenheimer K., Papovich C., Bell E., 2007, MNRAS, 380, 1467
- Gordon K. D., Clayton G. C., Witt A. N., Misselt K. A., 2000, ApJ, 533, 236
- Gordon K. D. et al., 2005, PASP, 117, 503
- Goto T., Yamauchi C., Fujita Y., Okamura S., Sekiguchi M., Smail I., Bernardi M., Gomez P. L., 2003, MNRAS, 346, 601
- Goto T. et al., 2005, ApJ, 621, 188
- Gray M. E., Taylor A. N., Meisenheimer K., Dye S., Wolf C., Thommes E., 2002, ApJ, 568, 141
- Gray M. E., Wolf C., Meisenheimer K., Taylor A., Dye S., Borch A., Kleinheinrich M., 2004, MNRAS, 347, L73
- Gunn J. E., Gott J. R. I., 1972, ApJ, 176, 1
- Guzzo L. et al., 2007, ApJS, 172, 254
- Haines C. P., La Barbera F., Mercurio A., Merluzzi P., Busarello G., 2006, ApJ, 647, L21
- Häussler B. et al., 2007, ApJS, 172, 615
-
Helou G.,
Khan I. R.,
Malek L.,
Boehmer L., 1988, ApJS, 68, 151
10.1086/191285 Google Scholar
- Heymans C. et al., 2008, MNRAS, 385, 1431
- Hildebrandt H., Wolf C., Benitez N., 2008, A&A, 480, 703
- Hoffman Y., Ribak E., 1991, ApJ, 380, L5
- Homeier N. L. et al., 2005, ApJ, 621, 651
- Jogee S., Miller S., Penner K., Skelton R. E., Conselice C. J., Somerville R. S., the GEMS Collaboration, 2008, ApJ, submitted
- Kauffmann G., White S. D. M., Heckman T. M., Ménard B., Brinchmann J., Charlot S., Tremonti C., Brinkmann J., 2004, MNRAS, 353, 713
- Kennicutt R. C., Jr, 1998, ARA&A, 36, 189
- Kirkpatrick J. D., Henry T. J., Irwin M. J., 1997, AJ, 113, 1421
- Kodama T., Smail I., Nakata F., Okamura S., Bower R. G., 2001, ApJ, 562, L9
- Koekemoer A. M. et al., 2007, ApJS, 172, 196
-
Kroupa P., 2001, MNRAS, 322, 231
10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04022.x Google Scholar
- Kroupa P., Tout C. A., Gilmore G., 1993, MNRAS, 262, 545
- Lane K. P., Gray M. E., Aragón-Salamanca A., Wolf C., Meisenheimer K., 2007, MNRAS, 378, 716
- Larson R. B., Tinsley B. M., Caldwell C. N., 1980, ApJ, 237, 692
- Le Floc'h E. et al., 2004, ApJS, 154, 170
- Le Floc'h E. et al., 2005, ApJ, 632, 169
- Lewis I. et al., 2002, MNRAS, 334, 673
- Lupton R. H., Gunn J. E., Szalay A. S., 1999, AJ, 118, 1406
- Marinova I. et al., 2008, ApJ, submitted
- Meisenheimer K., Röser H.-J., 1993, Landolt-Börnstein - Group VI, Astronomy and Astrophysics, Instruments, Methods, Solar System. Springer-Verlag, Berlin , p. 29
- Miller N. A., Owen F. N., 2003, AJ, 125, 2427
- Moore B., Lake G., Katz N., 1998, ApJ, 495, 139
- Moran S. M., Ellis R. S., Treu T., Smith G. P., Rich R. M., Smail I., 2007, ApJ, 671, 1503
- Morrissey P. et al., 2007, ApJS, 173, 682
- Papovich C., Bell E. F., 2002, ApJ, 579, L1
- Papovich C. et al., 2004, ApJS, 154, 70
- Peng C. Y., Ho L. C., Impey C. D., Rix H.-W., 2002, AJ, 124, 266
- Poggianti B. M., Bridges T. J., Komiyama Y., Yagi M., Carter D., Mobasher B., Okamura S., Kashikawa N., 2004, ApJ, 601, 197
- Poggianti B. M. et al., 2006, ApJ, 642, 188
- Postman M. et al., 2005, ApJ, 623, 721
- Refregier A., 2003, MNRAS, 338, 35
- Rhodes J. D. et al., 2007, ApJS, 172, 203
- Rix H.-W. et al., 2004, ApJS, 152, 163
- Roussel H., Sauvage M., Vigroux L., Bosma A., 2001, A&A, 372, 427
- Schindler S., 2000, A&AS, 142, 433
- Sérsic J. L., 1968, Atlas de galaxias australes. Observatorio Astronomico, Cordoba , Argentina
- Smith G. P., Treu T., Ellis R. S., Moran S. M., Dressler A., 2005, ApJ, 620, 78
- Smolčić V. et al., 2007, ApJS, 172, 295
- Spinoglio L., Malkan M. A., Rush B., Carrasco L., Recillas-Cruz E., 1995, ApJ, 453, 616
- Taylor A. N. et al., 2004, MNRAS, 353, 1176
-
Treu T.,
Ellis R.,
Dressler A.,
Smail I.,
Czoske O.,
Oemler A.,
Natarajan P., 2003, ApJ, 591, 53
10.1086/375314 Google Scholar
- Voges W. et al., 1999, A&A, 349, 389
- White S. D. M. et al., 2005, A&A, 444, 365
-
Wolf C.,
Meisenheimer K.,
Rix H.-W.,
Borch A.,
Dye S.,
Kleinheinrich M., 2003, A&A, 401, 73
10.1051/0004-6361:20021513 Google Scholar
- Wolf C. et al., 2004, A&A, 421, 913 (W04)
- Wolf C., Gray M. E., Meisenheimer K., 2005, A&A, 443, 435 (WGM05)
- Wolf C., Gray M. E., Aragón-Salamanca A., Lane K. P., Meisenheimer K., 2007, MNRAS, 376, L1
-
Wolf C.
et al., 2009, MNRAS, in press (doi:DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.14204.x) (this issue)
10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.14204.x Google Scholar
- Yan L. et al., 2005, ApJ, 628, 604
- Zabludoff A. I., Zaritsky D., Lin H., Tucker D., Hashimoto Y., Shectman S. A., Oemler A., Kirshner R. P., 1996, ApJ, 466, 104
- Zheng X. Z., Dole H., Bell E. F., Le Floc'h E., Rieke G. H., Rix H.-W., Schiminovich D., 2007, ApJ, 670, 301




