Mycophenolate mofetil-induced colitis versus colonic graft-versus-host disease: a comparative histologic study with artificial intelligence model development
Rofyda Elhalaby and Priyadharshini Sivasubramaniam contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Aim
The aim of this study was to compare the histopathologic features of MMF-induced colitis and colonic GVHD and develop a digital tool using deep learning convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to semi-automate the quantification of eosinophils.
Methods
MMF and GVHD colitis cases were retrieved. A cohort of transplant patients who were at risk for developing GVHD and were on MMF at the time of biopsy was also identified. Cases were reviewed for histologic features and a deep learning CNN was trained to quantify lamina propria eosinophils. Clinical history was collected.
Results
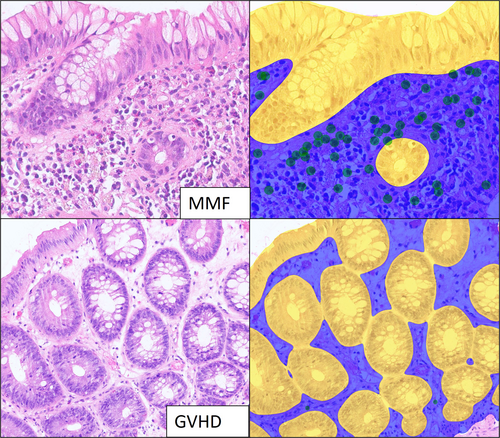
Ninety-five patients were included in the study group: GVHD (n = 37), MMF (n = 25) and GVHD vs. MMF (n = 33). Within the GVHD vs. MMF group, one patient was thought to have definitive MMF colitis and one possible MMF colitis. The GVHD group had a significantly higher apoptotic count compared to the MMF group (median: 7 vs. 2, P = 0.03). Neuroendocrine aggregates were present in the GVHD (N = 12) and GVHD vs. MMF (N = 4) groups while absent in the MMF group. The MMF group had a higher semi-quantitative eosinophil score and a higher automated eosinophil count as detected by the deep learning CNN (median eos/HPF: MMF 19.2, GVHD vs. MMF 3.6, GVHD 3.4, P < 0.001).
Conclusions
Lower eosinophil counts, higher apoptotic counts and neuroendocrine cell aggregates favour the diagnosis of GVHD. AI models for eosinophil quantification may serve as an ancillary tool for assessing this differential diagnosis. Given the rarity of MMF-induced colitis in SCT patients, pathologists should have a high threshold for making this diagnosis in this population.
Graphical Abstract
Mycophenolate-induced colitis and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) colitis have overlapping histology. Lower eosinophil counts, higher apoptotic counts and neuroendocrine cell aggregates are histological features that favour the diagnosis of GVHD. AI models for eosinophil quantification may serve as an ancillary tool for assessing this differential diagnosis.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Open Research
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.