Secretory carcinoma of the salivary gland: a multi-institutional clinicopathologic study of 90 cases with emphasis on grading and prognostic factors
Background
Secretory carcinoma (SC) is a rare form of salivary carcinoma that was first described in 2010 and is characterized by ETV6::NTRK3 fusion in most cases. In this large retrospective study, we aimed to identify adverse clinicopathologic factors and propose a prognostically relevant grading scheme for SC.
Methods
A detailed clinicopathologic review was conducted on 90 SCs from the major and minor salivary glands.
Results
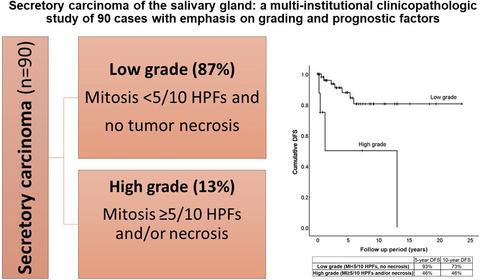
The median age at presentation was 50 years (range: 7–93). Sixty-nine (77%) tumours originated from major salivary glands, whereas the remaining 21 involved minor salivary glands.Six cases (7%) had cervical nodal metastasis. Only lymphovascular invasion (LVI) was associated with a risk of nodal metastasis (P < 0.05). The 5-year disease-specific survival and disease-free survival (DFS) were 98% and 87%, respectively. On univariate survival analysis, adverse prognostic factors associated with decreased DFS included minor salivary gland origin, atypical mitosis, high mitotic index, high-grade transformation (HGT), necrosis, nuclear pleomorphism, infiltrative tumour border, fibrosis at the invasive front, LVI, positive margin, and advanced pT stage (P < 0.05). When adjusted for pT stage and margin status, mitotic index, LVI, nuclear pleomorphism, and HGT remained as independent prognostic factors.
Conclusion
We therefore propose a two-tiered grading system for SC. The low-grade SC is defined as those with <5 mitoses /10 high-power fields and no tumour necrosis, and high-grade SC as those with ≥5 mitoses /10 high-power fields and/or necrosis. This proposed grading system can be useful to risk stratify patients with SC for appropriate clinical management.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interests
No competing financial interests exist for all contributory authors. The research meets the ethics guidelines, including adherence to the legal requirements of the country where the study was performed.
Open Research
Data availability statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.