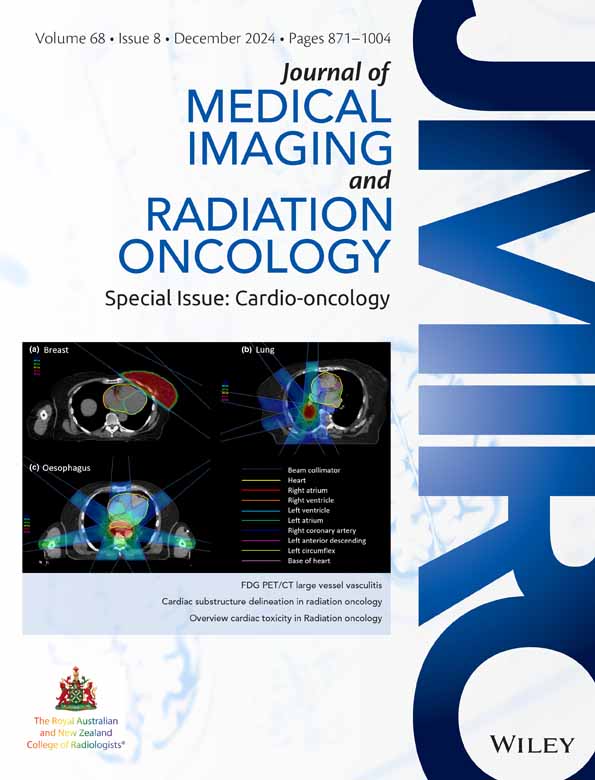
Cardio-oncology and radiation oncology: How collaboration between cardiologists and oncologists can be realised in radiation oncology
S Birch: B App Sci, MBBS (Hons), FRACP (Cardiology); J Otton BA, BSc (Med), MBBS (Hons), MBiomed E PhD, FRACP (Cardiology).
Conflict of interest: James Otton is a special issue Guest Editor for JMIRO and a co-author of this article. To minimise bias, he was excluded from all editorial decision-making related to the acceptance of this article for publication. There are no other conflicts of interest to disclose for either author.
Summary
Increased survivorship, improvements in cancer treatments, and the potential for cardiac side effects from cancer treatments have resulted in increased collaboration between oncologists and cardiologists and the development of cardio-oncology clinics. This collaboration is important given its role in ensuring greater patient satisfaction, aiding teams of clinicians in making complex treatment decision, and ensuring cardiac complications are diagnosed at an early stage. The particularities of implementing this collaboration in the field of radiation oncology and how this setting is different from other areas of cardio-oncology have not been well detailed in the literature. This paper will discuss what is currently understood about the need for and role of cardio-oncology and what a cardio-oncology services involves, with a particular emphasis on patient and clinician needs in the field of radiation oncology. The literature and recent guidelines do advocate for a detailed baseline assessment of cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy, especially patients with treatment or patient risk factors that increase their risk of cancer-therapy related cardiotoxicity. Advancements in cardiac imaging techniques will be discussed as these may help to diagnose cardiac side effects of certain cancer treatments, including radiotherapy, at an early stage. A multi-disciplinary and collaborative approach is well received by patients and such an approach, guided by the aim of maintaining a patient's cancer treatment wherever possible, should be the cornerstone of cardio-oncology clinics regardless of the patient's treatment regime.
Open Research
Data availability statement
Data available on request from the authors. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.