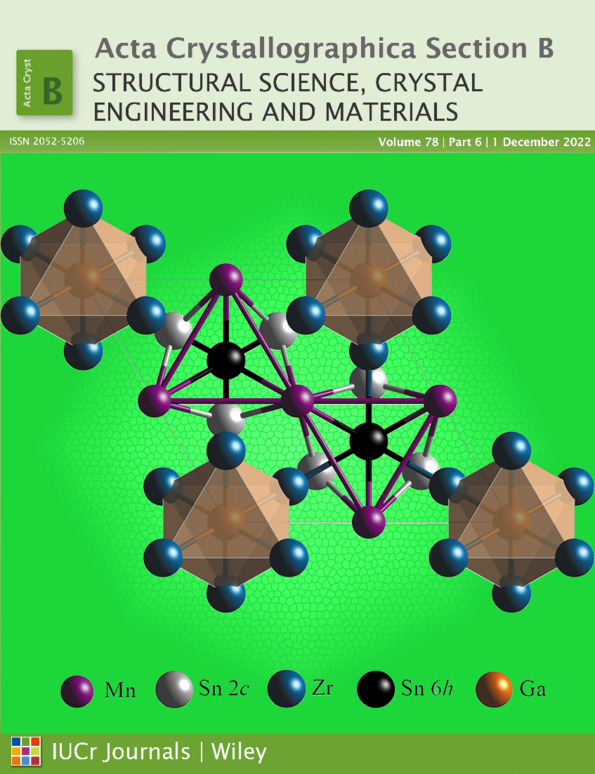
Zr3Mn3Sn4Ga: a new hexagonal Ti6Sn5-type quaternary intermetallic
Abstract
The discovery of a new quaternary intermetallic compound of composition Zr3Mn3Sn4Ga during a survey of the Zr–Mn–Sn–Ga phase diagram is reported. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction reveals that the new compound crystallizes in a hexagonal lattice (space group P63/mmc, No. 194). The analysis of single-crystal X-ray diffraction data indicates that the atomic arrangement is an ordered variant of the high-temperature hexagonal Ti6Sn5 crystal structure. From a simple geometry point of view, the unit cell consists of GaZr3 octahedra chains and Mn chains growing along the sixfold symmetry axis c. The Mn chains are stacked within the ab basal plane in a kagome geometry, with large interatomic distances. The possible slight levels of Sn/Ga and Zr/Mn mixed occupancy based on additional results of electron probe microanalysis and single-crystal neutron diffraction are discussed. It is noteworthy that this compound is the first quaternary intermetallic discovered in this structure and the first Ti6Sn5 derivative bearing a magnetic metal, namely Mn, in the 6g position, which may give rise to interesting physical properties.