Stacking faults in β-Ga2O3 crystals observed by X-ray topography
Abstract
Planar defects in 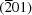 -oriented β-Ga2O3 wafers were studied using X-ray topography. These planar defects were rectangular with dimensions of 50–150 µm, and the X-ray topography analysis revealed that they were stacking faults (SFs) enclosed by a single partial dislocation loop on the
-oriented β-Ga2O3 wafers were studied using X-ray topography. These planar defects were rectangular with dimensions of 50–150 µm, and the X-ray topography analysis revealed that they were stacking faults (SFs) enclosed by a single partial dislocation loop on the 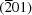 plane. The SF formation was found to be supported by a unique structural feature of the
plane. The SF formation was found to be supported by a unique structural feature of the 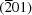 plane as a slip plane; the
plane as a slip plane; the 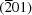 plane consists of close-packed octahedral Ga and O layers, allowing slips to form SFs. Vacancy arrays along the b axis in the octahedral Ga layer reduce the self-energy of the edge component in the partial dislocation extending along the b axis. It is speculated that the SFs occur during the crystal growth process for unknown reasons and then recover owing to elastic instability after initially increasing in size as crystal growth proceeds. Based on this analysis, a structural model for the SFs is proposed.
plane consists of close-packed octahedral Ga and O layers, allowing slips to form SFs. Vacancy arrays along the b axis in the octahedral Ga layer reduce the self-energy of the edge component in the partial dislocation extending along the b axis. It is speculated that the SFs occur during the crystal growth process for unknown reasons and then recover owing to elastic instability after initially increasing in size as crystal growth proceeds. Based on this analysis, a structural model for the SFs is proposed.