P961: BORTEZOMIB, RITUXIMAB AND DEXAMETHASONE REGIMEN (BDR) IN WALDENSTRÖM MACROGLOBULINEMIA: A RETROSPECTIVE ANALYSIS
Abstract Topic: 14. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background: Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) is a B-cell neoplasm characterized by an immunoglobulin IgM monoclonal gammapathy with bone marrow infiltration by lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. To date WM remains incurable, but whole genome sequencing in WM patients demonstrated a common molecular signature with a mutation of MYD88 L265P downstream the activation of NFκB pathway allowing the development of new therapy approach. Proteasome inhibitor affects NFκB signaling with a synergistic activity with rituximab. A phase II study demonstrated the efficacy of bortezomib rituximab and dexamethasone regimen (BDR) in first-line WM patients with a median progression free survival (PFS) of 43 months and a 7-years overall survival (OS) at 66%.
Aims: We retrospectively analyzed the efficacy of BDR regimen in 33 patients with WM.
Methods: Bortezomib at dose of 1.3 mg/m2 was given subcutaneously, initially twice weekly the first cycle followed by a weekly administration at dose of 1.6 mg/m2 for the next cycles. After the first cycle Rituximab 375 mg/m2 and dexamethasone 40 mg were added and given intravenously once weekly. The clinical symptoms and biological parameters with the IPSS-WM at the initiation of treatment were collected. Mutational status (MYD88 and CXCR4) was also recorded. The response rate was assessed as well as PFS, OS and toxicities.
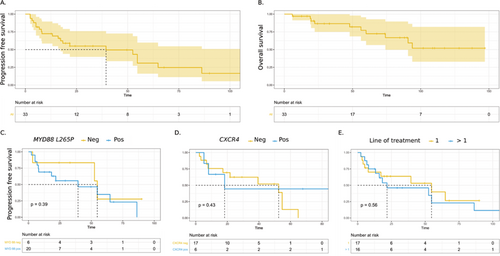
Results: Between January 2010 and June 2021, 33 patients (23 male/10 female) were included. Median age was 65.7 (IQR (59-75)) years. Sixteen patients (48%) were treated in first line and 17 patients (52%) in relapse. Primary reasons for initiating treatment were cytopenia (42%), lymphadenopathy/splenomegaly (33%), hyperviscosity (15%), and cryoglobulinemia (12%). Median serum IgM level was 21 (16-50) g/L. IPSS-WM was low for 5 (15%) patients, intermediate in 10 (33%) and high in 16 (48%). MYD88 L265P mutation was found in 20/26 (77%) patients and CXCR4 mutation in 6/23 (26%) patients. Patients received a median of 5 cycles (range (1-8)) of BDR cycles.
The overall response rate (ORR) was 80 %: two patients (6%) achieved complete response, 7 (22%) very good partial response, 14 (43%) partial response, 2 (6%) minor response, and 1 (3%) stable disease. The median of follow up was 68 months. Median PFS was 39 months and median of OS was not reached. The estimated 5-year PFS was 38%, 51%, and 20% for low, intermediate, and high IPSS-WM respectively, with no statistical significance (p = 0.22). Five-years PFS in patients harboring MYD88L265P mutation was 35% (95% CI: [16-77]) and 28% (95% CI: [5-100]) in MYD88L265P negative patients (p = 0.39). Five-years PFS in patients with CXCR4 mutation was 44% (95% CI: [17-100]) and 13% (95% CI: [2-77]) in patients without CXCR4 mutation (p = 0.43). In patients treated in upfront setting, 5-year PFS was 40% (95 % CI: [19-85]) whereas in patients with relapse was 23% (95 % CI: [7-71]), p = 0.56). Toxicities were reported in 14 (42%) patients with peripheral neurotoxicity of any grade in 10 (33%) (4 with grade ≥ 3) and hematological toxicity in 1 (3%).
Summary/Conclusion: BDR regimen remains an interesting treatment with 80 % ORR and a median of PFS of 39 months. We failed to find difference in patients’ outcome according to IPSS-WM or molecular status probably due to a lack of statistical power. More patients should be included and extensive screening of additional mutations by NGS should be performed in our retrospective analysis to better identify subgroup who may benefit from BDR regimen.
Figure 1. Progression free survival (A) and Overall survival (B). Progression free survival according to the MYD88 mutational status (C), CXCR4 mutational status (D), and the line of treatment (E). Survival curves were plotted with the Kaplan-Meier method. Progression free survival was estimated after a log rank test.
Keywords: Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia, Bortezomib, Mutation status