P1264: HEMATOPOIETIC CLONES WITH TP53 MUTATIONS EXPAND IN PATIENTS WITH MCL DURING LENALIDOMIDE-BASED THERAPY
Background: Lenalidomide is widely used to treat mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and multiple myeloma. It is however associated with development of therapy-related leukemia (t-AML/MDS) and the most frequent serious adverse events are hematological toxicities. It is unclear how lenalidomide affects the hematopoietic system in patients with mantle cell lymphoma.
To answer this question, we investigated somatic myeloid mutations, also called clonal hematopoiesis (CH), in sequential blood and bone marrow samples from patients with MCL treated with Lenalidomide-Ibrutinib-Rituximab on the Nordic Lymphoma Group (NLG) Philemon trial (NCT02460276).
Aims: To investigate how a lenalidomide-based therapy impact hematopoietic clones in patients with malignant lymphoproliferative disease.
Methods: A total of 62 sequential blood samples (at pre-treatment and at 6 months treatment follow-up) were analyzed from 31 patients with relapsed/refractory MCL treated in the NLG Philemon trial. Patients received treatment in 28 day cycles with lenalidomide (Len; 15mg days 1-21), ibrutinib (Ibr; 560mg days 1-28), and rituximab (R; 375mg/m2 every 8 weeks). MCL clone-specific minimal residual disease (MRD) in patients bone marrow and blood was measured according to EuroMRD criteria.
DNA from the collected MRD samples were analyzed for somatic mutations with a custom capture-based NGS panel of 31 genes related to CH and t-AML/MDS. MCL tumor mutations were identified with a MCL NGS panel and excluded from CH analyses. Since TP53 mutations occur in both MCL and CH, de novo TP53 variants were considered as of MCL origin if 1) the patient was MRD positive at the same timepoint OR 2) the patient had a relapse in the following six months after the blood sample was taken. Somatic non-MCL mutations (CH) were identified with a variant allele frequency (VAF) down to 0.01.
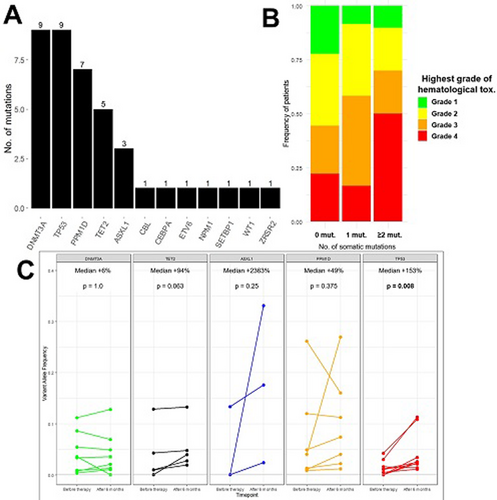
Results: A total of 40 somatic mutations in myeloid related genes, i.e. CH mutations, were identified in 22 patients (71% of cohort) with the majority being in DNMT3A and DNA repair pathway genes (TP53 and PPM1D; Figure 1A). Number of CH mutations were associated with development of Grade 3/4 hematological toxicity during Len-based therapy (Figure 1B). Patients with pre-existing CH mutations tended to more likely develop neutropenia compared to patients without CH (Fischer's exact test p=0.11). CH mutations were not associated with age or number of prior therapies in a linear regression model.
During treatment with Len-Ibr-R there was a significant overall increase in CH clone size (median VAF= +44%, p=0.005), but heterogenous growth patterns of the respective mutated genes was noted (Figure 1C). Mutations in TP53 increased significantly in size (median +153%, p=0.008). Mutations in ASXL1, TET2, and PPM1D had marked median increases (median +2363%, +49%, +94%, respectively) though the increase did not reach statistical significance. On the contrary, mutations in DNMT3A were stable during treatment with Len-Ibr-R (median +6%, p=1.0).
There was no significant difference in overall or progression-free survival with regards to pre-existing clonal hematopoiesis.
Image:
Summary/Conclusion: To our knowledge, we here present the first description of CH evolution during treatment with lenalidomide-based therapy. Pre-treatment presence of somatic mutations were associated with development of grade 3/4 hematological toxicity. Therapy with Len-Ibr-R caused hematopoietic clones with TP53 mutations to significantly expand over time, while clones with DNMT3A mutations were remarkably stable.