Chemie polyfunktioneller Moleküle. 93. Die halogenierende Ringspaltung des As3-Nortricyclans, 4-Methyl-1,2,6-triarsatricyclo[2.2.1.02,6]heptan Darstellung und Eigenschaften von 2,6-Dihalogen-4-methyl-1,2,6-triarsabicyclo[2.2.1]heptanen†
Professor Klaus Brodersen zum 60. Geburtstage am 12. August 1986 gewidmet
Abstract
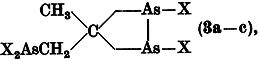
deDas As3-Nortricyclan CH3C(CH2As)3 (1) reagiert mit PCl5, Br2 oder I2 (Molverhältnis jeweils 1:1) zu den neuen 2,6-Dihalogen-4-methyl-1,2,6-triarsabicyclo[2.2.1]heptanen CH3C(CH2As)3X2 (X = Cl, Br, I; 2a–c). Bei Anwendung eines Molverhältnisses von 1:2 erhält man, über die 1H-NMR-spektroskopisch nachweisbaren, aber nicht isolierbaren Tetrahalogendiarsacyclopentan-Derivate
Abstract
enChemistry of Polyfunctional Molecules. 93. Halogenating Ring Cleavage of As3-Nortricyclane 4-Methyl-1,2,6-triarsatricyclo[2.2.1.02,6]heptane. Preparation and Properties of 2,6-Dihalogeno-4-methyl-1,2,6-triarsabicyclo[2.2.1]heptanes
The reaction of the As3-nortricyclane CH3C(CH2As)3 (1) with PCl5, Br2, or I2 in a molar ratio of 1:1 leads to the new 2,6-dihalogeno-4-methyl-1,2,6-triarsabicyclo[2.2.1]heptanes CH3C(CH2As)3X2 (X = Cl, Br, I; 2a–c). Application of a molar ratio of 1:2 results in the formation of 1,1,1-tris(dihalogenoarsinomethyl)ethanes CH3C(CH2AsX2)3 (4a–c) in rather poor yields; 1H-NMR spectroscopic studies suggest that 4a–c are formed via 2a–c and the tetrahalogenodiarsacyclopentane derivatives





