Bildung und Reaktionen silylierter Triphosphane
Abstract
deSilylierte Triphosphane, die als primäre P-Atome P(SiMe3)2-, P(SiMe3)CMe3-, P(SiMe3)Me-Gruppen enthalten und am sekundären P-Atom durch Cl, H, Li, SiMe3 substituiert sind, lassen sich über eine mehrstufige Reaktion gewinnen. Der erste Schritt ist die Reaktion von PCl3 mit P(SiMe3)2R (R = CMe3, Me) unter Me3SiCl-Abspaltung zu R(Me3Si)PPCl2, dem sich die Umsetzung mit LiP(SiMe3)R′ (R′ = SiMe3, Me) anschließt. Als Hauptprodukte entstehen Derivate mit der = PCl-Gruppe am sekundären P-Atom nach
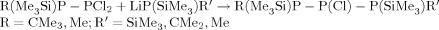
Die PCl-haltigen Derivate sind thermolabil und lassen sich nach ihrer Bildung bei —78°C durch Umsetzung mit LiCMe3 in beständige Derivate überführen. In dieser dritten Stufe ergeben sich folgende Reaktionsmöglichkeiten:
- 1
Substitution an der = PCl-Gruppe zu = PCMe3 und LiCl.
- 2
Ummetallierung unter Bildung von = PLi und Me3CCl.
- 3
Folgereaktionen der Phosphide: Mit Me3CCl-Bildung von = PH, iso-Buten und LiCl bzw. Reaktion der = PLi-Gruppe mit Me3SiCl zu = PSiMe3.
Die sterisch anspruchsvollen Gruppen an den primären P-Atomen begünstigen die Bildung der PH-Gruppe, während Me als Substituent die Substitution am sekundären P-Atom durch SiMe3 oder CMe3 begünstigt. Im Gegensatz zu Triphosphanen mit der PCl-Gruppe sind diejenigen Derivate, die =PH, =PLi, =PCMe3, =PSiMe3 (sekundäres P-Atom) enthalten, isolierbar. Durch Reaktion der =PH-haltigen Derivate mit LiBu in Pentan werden die entsprechenden Li-Phosphide in reiner Form zugänglich. Diese Li-Phosphide unterliegen in polaren Ethern einer Reaktion, die unter Abspaltung von (Me3Si)3P, LiP(SiMe3)2, (Me3C)P(SiMe3)2 in mehreren Stufen zu P-reicheren Verbindungen führt. So bildet sich aus [(Me3Si)2P]2PLi bevorzugt Li3P7, aus (Me3Si)2P—P(Li)—P(SiMe3)CMe3 bevorzugt das Cyclotetraphosphan P4(CMe3)3SiMe3 und aus [(Me3C)(Me3Si)P]2PLi das cyclische Pentaphosphid LiP5(CMe3)4.
Abstract
enFormation and Reactions of Silylated Triphosphanes
Silylated triphosphanes, containing primary P(SiMe3)2, P(SiMe3)CMe3, or P(SiMe3) Me endgroups and secondary =PCl, =PH, =PLi, =PSiMe3, or =PCMe3 groups were prepared by firstly reacting PCl3 with P(SiMe3)2R (R = CMe3, Me) and subsequently by substituting the diphosphanes R(Me3Si)P—PCl2 with LiP(SiMe3)R′ (R′ = SiMe3, CMe3, Me)
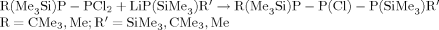
Such triphosphanes, containing both =PCI and =PSiMe3 groups decompose at room temperature. Stable products, however, were isolated after immediately derivating the 2-chloro-triphosphanes at − 78°C with LiCMe3. Among the competing reactions:
- 1
=PC1 substitution yielding the =PCMe, group.
- 2
Cl/Li exchange forming the phosphides =PLi and Ne,CCl,
- 3
consecutive reactions of the phosphides, producing the =PH derivatives -L iso-butene + LiCl with Me3CCI, or the =PSiMe3 derivatives with Me3SiCl, respectively,




