Factors in randomly perturbed hypergraphs
Yulin Chang
Data Science Institute, Shandong University, Jinan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jie Han
School of Mathematics and Statistics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China
Correspondence
Jie Han, School of Mathematics and Statistics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorYoshiharu Kohayakawa
Instituto de Matemática e Estatística, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil
Search for more papers by this authorPatrick Morris
Freie Universität Berlin and Berlin Mathematical School, Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorGuilherme Oliveira Mota
Instituto de Matemática e Estatística, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil
Search for more papers by this authorYulin Chang
Data Science Institute, Shandong University, Jinan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jie Han
School of Mathematics and Statistics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China
Correspondence
Jie Han, School of Mathematics and Statistics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorYoshiharu Kohayakawa
Instituto de Matemática e Estatística, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil
Search for more papers by this authorPatrick Morris
Freie Universität Berlin and Berlin Mathematical School, Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorGuilherme Oliveira Mota
Instituto de Matemática e Estatística, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil
Search for more papers by this authorFunding information: The Chinese Scholarship Council; Simons Foundation; CNPq; FAPESP the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) under Germany's Excellence Strategy - The Berlin Mathematics Research Center MATH+; CAPES,#630884;311412/2018-1;423833/2018-9;2018/04876-1;2019/13364-7;EXC-2046/1, 390685689;306620/2020-0;428385/2018-4;2018/04876-1;2019/13364-7;Finance Code 001
Abstract
We determine, up to a multiplicative constant, the optimal number of random edges that need to be added to a k-graph H with minimum vertex degree 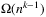 to ensure an F-factor with high probability, for any F that belongs to a certain class
to ensure an F-factor with high probability, for any F that belongs to a certain class 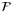 of k-graphs, which includes, for example, all k-partite k-graphs,
of k-graphs, which includes, for example, all k-partite k-graphs, 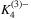 and the Fano plane. In particular, taking F to be a single edge, this settles a problem of Krivelevich, Kwan, and Sudakov. We also address the case in which the host graph H is not dense, indicating that starting from certain such H is essentially the same as starting from an empty graph (namely, the purely random model).
and the Fano plane. In particular, taking F to be a single edge, this settles a problem of Krivelevich, Kwan, and Sudakov. We also address the case in which the host graph H is not dense, indicating that starting from certain such H is essentially the same as starting from an empty graph (namely, the purely random model).
REFERENCES
- 1N. Alon and R. Yuster,
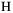 -factors in dense graphs, J. Combin. Theory Ser. B 66 (1996), 269–282 MR1376050.
-factors in dense graphs, J. Combin. Theory Ser. B 66 (1996), 269–282 MR1376050.
- 2S. Antoniuk, A. Dudek, C. Reiher, A. Ruciński, and M. Schacht, High powers of Hamiltonian cycles in randomly augmented graphs, ArXiv e-prints, 2020.
- 3J. Balogh, A. Treglown, and A. Z. Wagner, Tilings in randomly perturbed dense graphs, Combin. Probab. Comput. 28 (2019), 159–176 MR3922775.
- 4W. Bedenknecht, J. Han, Y. Kohayakawa, and G. O. Mota, Powers of tight Hamilton cycles in randomly perturbed hypergraphs, Random Struct. Algorithms 55 (2019), 795–807 MR4025389.
- 5P. Bennett, A. Dudek, and A. Frieze, Adding random edges to create the square of a Hamilton cycle, ArXiv e-prints, 2017.
- 6T. Bohman, A. Frieze, and R. Martin, How many random edges make a dense graph Hamiltonian? Random Struct. Algorithms 22 (2003), 33–42 MR1943857.
- 7J. Böttcher, J. Han, Y. Kohayakawa, R. Montgomery, O. Parczyk, and Y. Person, Universality for bounded degree spanning trees in randomly perturbed graphs, Random Struct. Algorithms 55 (2019), 854–864 MR4025392.
- 8J. Böttcher, R. Montgomery, O. Parczyk, and Y. Person, Embedding spanning bounded degree subgraphs in randomly perturbed graphs, Mathematika 66 (2019), 422–447.
- 9Y. Chang, J. Han, and L. Thoma, On powers of tight Hamilton cycles in randomly perturbed hypergraphs, ArXiv e-prints, 2020.
- 10S. Das, P. Morris, and A. Treglown, Vertex Ramsey properties of randomly perturbed graphs, Random Struct. Algorithms 57 (2020), 983–1006.
- 11S. Das and A. Treglown, Ramsey properties of randomly perturbed graphs: Cliques and cycles, Combin. Probab. Comput. 29 (2020), 830–867.
- 12A. Dudek, C. Reiher, A. Ruciński, and M. Schacht, Powers of Hamiltonian cycles in randomly augmented graphs, Random Struct. Algorithms 56 (2020), 122–141 MR4052848.
- 13P. Erdős and M. Simonovits, Supersaturated graphs and hypergraphs, Combinatorica 3 (1983), 181–192 MR726456.
- 14S. Gerke and A. McDowell, Nonvertex-balanced factors in random graphs, J. Graph Theory 78 (2015), 269–286 MR3312137.
- 15 A. Hajnal and E. Szemerédi, Proof of a conjecture of P. Erdős, in Combinatorial theory and its applications, II (Proc. Colloq., Balatonfüred, 1969), North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1970, 601–623 MR0297607.
- 16J. Han, P. Morris, and A. Treglown, Tilings in randomly perturbed graphs: Bridging the gap between Hajnal–Szemerédi and Johansson–Kahn–Vu, Random Struct. Algorithms 58 (2021), 480–516.
- 17J. Han and Y. Zhao, Hamiltonicity in randomly perturbed hypergraphs, J. Combin. Theory Ser. B 144 (2020), 14–31 MR4115532.
- 18S. Janson, T. Łuczak, and A. Ruciński, Random graphs, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 2000 MR2001k:05180.
10.1002/9781118032718 Google Scholar
- 19A. Johansson, J. Kahn, and V. Van, Factors in random graphs, Random Struct. Algorithms 33 (2008), 1–28 MR2428975.
- 20F. Joos and J. Kim, Spanning trees in randomly perturbed graphs, Random Struct. Algorithms 56 (2020), 169–219 MR4052851.
- 21D. G. Kirkpatrick and P. Hell, On the complexity of general graph factor problems, SIAM J. Comput. 12 (1983), 601–609 MR707416.
- 22 J. Komlós, G. N. Sárközy, and E. Szemerédi, Proof of the Alon-Yuster conjecture, Discrete Math. 235 (2001), 255–269. MR1829855
- 23M. Krivelevich, M. Kwan, and B. Sudakov, Cycles and matchings in randomly perturbed digraphs and hypergraphs, Combin. Probab. Comput. 25 (2016), 909–927 MR3568952.
- 24M. Krivelevich, M. Kwan, and B. Sudakov, Bounded-degree spanning trees in randomly perturbed graphs, SIAM J. Discrete Math. 31 (2017), 155–171 MR3595872.
- 25M. Krivelevich, B. Sudakov, and P. Tetali, On smoothed analysis in dense graphs and formulas, Random Struct. Algorithms 29 (2006), 180–193 MR2245499.
- 26D. Kühn and D. Osthus, Embedding large subgraphs into dense graphs, in Surveys in combinatorics 2009, London Math. Soc. Lecture Note Ser., Vol 365, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 2009, 137–167 MR2588541.
10.1017/CBO9781107325975.007 Google Scholar
- 27D. Kühn and D. Osthus, The minimum degree threshold for perfect graph packings, Combinatorica 29 (2009), 65–107 MR2506388.
- 28A. McDowell and R. Mycroft, Hamilton
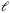 -cycles in randomly perturbed hypergraphs, Electron. J. Combin. 25 (2018), 30 MR3891103.
-cycles in randomly perturbed hypergraphs, Electron. J. Combin. 25 (2018), 30 MR3891103.
- 29R. Montgomery, Embedding bounded degree spanning trees in random graphs, ArXiv e-prints, 2014.
- 30R. Montgomery, Spanning trees in random graphs, Adv. Math. 356 (2019), 106793 MR3998769.
- 31R. Nenadov and Y. Pehova, On a Ramsey–Turán variant of the Hajnal–Szemerédi theorem, SIAM J. Discrete Math. 34 (2020), 1001–1010 MR4080942.
- 32R. Nenadov and M. Trujić, Sprinkling a few random edges doubles the power, ArXiv e-prints, 2018.
- 33E. Powierski, Ramsey properties of randomly perturbed dense graphs, ArXiv e-prints, 2019.
- 34V. Rödl and A. Ruciński, Dirac-type questions for hypergraphs—a survey (or more problems for Endre to solve), in London Math. Soc. Lecture Note Ser. An irregular mind, Bolyai Soc. Math. Stud., Vol 21, János Bolyai Math. Soc., Budapest, 2010, 561–590 MR2815614.
10.1007/978-3-642-14444-8_16 Google Scholar
- 35V. Rödl, A. Ruciński, and E. Szemerédi, A Dirac-type theorem for 3-uniform hypergraphs, Combin. Probab. Comput. 15 (2006), 229–251 MR2195584.
- 36Y. Zhao, Recent advances on Dirac-type problems for hypergraphs, in Recent trends in combinatorics, IMA Vol. Math. Appl., Vol 159, Springer, Cham, 2016, 145–165 MR3526407.
10.1007/978-3-319-24298-9_6 Google Scholar




