Robust stability and stabilization conditions for uncertain switched positive systems under mode-dependent dwell-time constraints
Funding information: National Natural Science Foundation of China, 61803134; 61873128; 62073111; Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, LY20F030011
Abstract
The article addresses the problems of robust stability and stabilization in exponential sense for uncertain switched positive systems (SPSs) under mode-dependent dwell-time constraints including mode-dependent constant dwell time (MDCDT) constraint, mode-dependent minimum dwell time (MDMDT) constraint, and mode-dependent ranged dwell time (MDRDT) constraint. At first, the mixed time-varying delay case is studied, and sufficient conditions of robust stability and stabilization in exponential sense are provided for uncertain SPSs with MDMDT, MDCDT, and MDRDT constraints, respectively. Next, the robust stability and stabilization issues are also studied for SPSs in delay-free case. With mode-dependent dwell-time constraints, a new discretized linear copositive Lyapunov–Krasovskii functional technique is introduced in this article. Meanwhile, for some specific situations, the proposed conditions of robust stability and stabilization can be degenerated into the ones for SPSs in mode-independent dwell-time constraint case and in non-uncertainty case, respectively. At last, we give five examples to explain the importance and effectiveness of the results.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
There are no conflict of interests for this article.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.



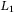 -gain and
-gain and 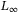 -gain characterization
-gain characterization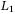 -induced controller synthesis for positive systems with interval uncertainties
-induced controller synthesis for positive systems with interval uncertainties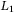 -gain performance of discrete-time singular switched positive systems with time-varying delays
-gain performance of discrete-time singular switched positive systems with time-varying delays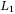 -gain characterization for switched positive systems under dwell-time constraint
-gain characterization for switched positive systems under dwell-time constraint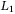 -gain analysis of interval positive switched T-S fuzzy systems with mode-dependent dwell time
-gain analysis of interval positive switched T-S fuzzy systems with mode-dependent dwell time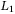 -gain controller design for positive switched systems with mixed time-varying delays
-gain controller design for positive switched systems with mixed time-varying delays