Robust H∞ switching control techniques for switched nonlinear systems with application to urban traffic control
Summary
This paper presents robust switching control strategies for switched nonlinear systems with constraints on the control inputs. A quantization technique is used to relax the constraint on continuous control inputs and the L2-gain analysis and H∞ control design problem for switched nonlinear systems are presented. Next, as an alternative method, the switched nonlinear system is approximated by a switched affine system that has autonomous and controlled switching behavior. A robust switching control law is proposed to stabilize the switched affine system. The design procedure involves solving an optimization problem that is nonconvex in a single scalar variable only. Furthermore, we provide the sufficient conditions under which the proposed switching law is able to stabilize the original switched nonlinear system. Finally, the proposed methods are utilized for control of urban traffic networks modeled on a high level. The traffic control objective is translated into a stability and disturbance attenuation problem for the urban network represented by a switched nonlinear system. The switching control approaches are able to reduce congestion in the network and to attenuate the effects of uncertain trip demands. Because the design of the switching laws is performed offline, real-time traffic control is possible with the proposed methods. Copyright © 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.



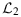 -induced gains of switched linear systems
-induced gains of switched linear systems
