Gummy-inspired natural eutectogels with high adhesiveness, toughness and humidity response
Zhiyang Li
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Key Laboratory for Polymeric Composite and Functional Materials of Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhaolin Ge
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Key Laboratory for Polymeric Composite and Functional Materials of Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorQize Chen
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Key Laboratory for Polymeric Composite and Functional Materials of Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorYifei He
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Key Laboratory for Polymeric Composite and Functional Materials of Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorJin Wu
State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies and the Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Display Material and Technology, School of Electronics and Information Technology, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zhuang Xie
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Key Laboratory for Polymeric Composite and Functional Materials of Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Correspondence
Zhuang Xie, School of Materials Science and Engineering and Key Laboratory for Polymeric Composite and Functional Materials of Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorZhiyang Li
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Key Laboratory for Polymeric Composite and Functional Materials of Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhaolin Ge
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Key Laboratory for Polymeric Composite and Functional Materials of Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorQize Chen
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Key Laboratory for Polymeric Composite and Functional Materials of Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorYifei He
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Key Laboratory for Polymeric Composite and Functional Materials of Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorJin Wu
State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies and the Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Display Material and Technology, School of Electronics and Information Technology, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zhuang Xie
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Key Laboratory for Polymeric Composite and Functional Materials of Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Correspondence
Zhuang Xie, School of Materials Science and Engineering and Key Laboratory for Polymeric Composite and Functional Materials of Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorZhiyang Li and Zhaolin Ge contributed equally to the work.
Abstract
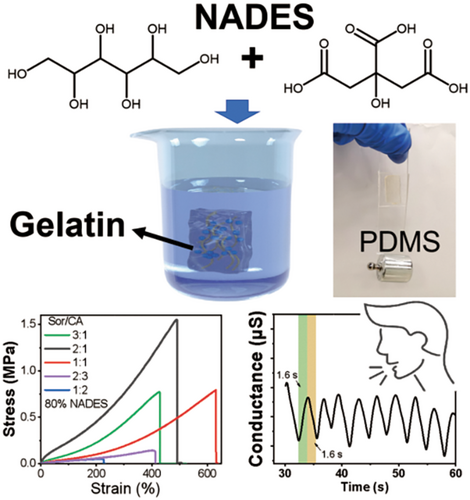
Biogel-based ionic devices have emerged as versatile platforms for broad applications in wearable electronics, healthcare monitoring and bioelectronic interfaces. Electronic functions derived from fully edible natural soft materials are particularly attractive to allow low cost, green, biocompatible and biodegradable devices in biomedical areas as well as smart food package. This work presents a gummy-inspired protein eutectogel by simply soaking gelatin hydrogels into solutions of natural deep eutectic solvent (NADES) consisting of sorbitol and citric acid to allow solvent exchange. Compared with the gelatin hydrogel, this natural eutectogel (NEG) exhibited anti-drying and anti-freezing performance, remarkably improved adhesiveness, room temperature degradability, as well as high mechanical toughness. The soaking conditions were investigated to tune the softness and ionic conductivity of the NEG, which revealed that the water content and acid ratio could significantly impact on the gel properties. Additionally, the eutectogel thin film exhibited good humidity sensing capability with a wide linear detection range (22%–98% RH), in which a soft patch was further demonstrated for breath test to detect various respiration frequencies. Thus, we believe the concept of NEG combining biopolymers and NADES can be explored in a broad range of soft devices for sensing, bio-adhesives, energy supply or drug delivery.
Graphical Abstract
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| pol20240219-sup-0001-supinfo.docxWord 2007 document , 3.2 MB | Figure S1: (A) Photos of NADES (sorbitol/citric acid = 2:3) solutions with varied water contents, showing the difference in viscosity. (B) The soaking results in NADES with varied water contents. Figure S2. Rapid dissolution of the eutectogel in DI water at 37°C. Figure S3. Plots of the breaking strain, breaking stress, elastic Young's modulus and toughness of NEGs with various NADES contents (A), soaking time (B), and Sor/CA ratios (C). Figure S4. (A) Photos of the gel samples before and after soaking in NADES (Sor/CA = 1:2, 60 wt%), showing less volume contraction when adjusting the pH of the NADES to higher level. (B) Comparison of mechanical performance of the NEGs with the 60 wt% NADES treatment before and after the pH adjustment, as well as the NEG through 80 wt% NADES soaking. Figure S5. Stress–strain curves during successive stretching from 50% to 200% strain, with a time interval of ~1 min between two tests. |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1C. Wang, T. Yokota, T. Someya, Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 2109.
- 2C. Yang, Z. Suo, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 125.
- 3J. Xue, Y. Zou, Y. Deng, Z. Li, EcoMat 2022, 4, e12209.
- 4M. Baumgartner, F. Hartmann, M. Drack, D. Preninger, D. Wirthl, R. Gerstmayr, L. Lehner, G. Mao, R. Pruckner, S. Demchyshyn, L. Reiter, M. Strobel, T. Stockinger, D. Schiller, S. Kimeswenger, F. Greibich, G. Buchberger, E. Bradt, S. Hild, S. Bauer, M. Kaltenbrunner, Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 1102.
- 5H. Wang, W. Wang, Z. Xie, J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 2679.
- 6J. W. Zhang, Q. Zhang, X. Liu, S. Xia, Y. Gao, G. H. Gao, J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 2663.
- 7T. Qin, W. C. Liao, L. Yu, J. H. Zhu, M. Wu, Q. Y. Peng, L. B. Han, H. B. Zeng, J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 2607.
- 8Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, Y. Guan, Y. Zhang, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6671.
- 9J. Wu, Z. X. Wu, H. H. Xu, Q. Wu, C. Liu, B. R. Yang, X. C. Gui, X. Xie, K. Tao, Y. Shen, J. M. Miao, L. K. Norford, Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 595.
- 10L. Fang, Z. Cai, Z. Ding, T. Chen, J. Zhang, F. Chen, J. Shen, F. Chen, R. Li, X. Zhou, Z. Xie, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 21895.
- 11Y. Feng, J. Yu, D. Sun, C. Dang, W. Ren, C. Shao, R. Sun, Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107284.
- 12W. Wang, Z. Li, M. Li, L. Fang, F. Chen, S. Han, L. Lan, J. Chen, Q. Chen, H. Wang, C. Liu, Y. Yang, W. Yue, Z. Xie, Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 184.
- 13Y. J. Jo, H. Kim, J. Ok, Y. J. Shin, J. H. Shin, T. H. Kim, Y. Jung, T. i. Kim, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909707.
- 14Y. Liang, Q. Ding, H. Wang, Z. Wu, J. Li, Z. Li, K. Tao, X. Gui, J. Wu, Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 183.
- 15S. Li, Y. Zhang, X. P. Liang, H. M. Wang, H. J. Lu, M. J. Zhu, H. M. Wang, M. C. Zhang, X. P. Qiu, Y. F. Song, Y. Y. Zhang, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5416.
- 16L. Lu, C. Jiang, G. Hu, J. Liu, B. Yang, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2100218.
- 17C. Y. Wang, H. Y. Wang, B. H. Wang, H. Miyata, Y. Wang, M. O. G. Nayeem, J. J. Kim, S. Lee, T. Yokota, H. Onodera, T. Someya, Sci. Adv 2022, 8, eabo1396.
- 18L. Fang, J. Zhang, W. Wang, Y. Zhang, F. Chen, J. Zhou, F. Chen, R. Li, X. Zhou, Z. Xie, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 56393.
- 19Z. Wang, X. Li, Z. Yang, H. Guo, Y. J. Tan, G. J. Susanto, W. Cheng, W. Yang, B. C. K. Tee, EcoMat 2021, 3, e12073.
- 20G. Balakrishnan, A. Bhat, D. Naik, J. S. Kim, S. Marukyan, L. Gido, M. Ritter, A. S. Khair, C. J. Bettinger, Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2211581.
- 21D. Zhou, F. Chen, J. Wang, T. Li, B. Li, J. Zhang, X. Zhou, T. Gan, S. Handschuh-Wang, X. Zhou, J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 7366.
- 22B. B. Hansen, S. Spittle, B. Chen, D. Poe, Y. Zhang, J. M. Klein, A. Horton, L. Adhikari, T. Zelovich, B. W. Doherty, B. Gurkan, E. J. Maginn, A. Ragauskas, M. Dadmun, T. A. Zawodzinski, G. A. Baker, M. E. Tuckerman, R. F. Savinell, J. R. Sangoro, Chem. Rev. 2020, 121, 1232.
- 23D. Yu, Z. Xue, T. Mu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8596.
- 24J. D. Mota-Morales, E. Morales-Narváez, Matter 2021, 4, 2141.
- 25S. Xing, G. Zhang, A. Zhang, Z. Chang, Z. Guo, A. Dong, J. Zhang, J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 62, 925.
10.1002/pol.20230603 Google Scholar
- 26L. Fang, C. Zhang, W. Ge, M. Rong, F. Chen, Z. Chen, X. Wang, Z. Zheng, Q. Huang, Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 478, 147405.
- 27H. Zhang, N. Tang, X. Yu, M. H. Li, J. Hu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2206305.
- 28S. Wu, C. Cai, F. Li, Z. Tan, S. Dong, Angew. Chem. Int. ed. 2020, 59, 11871.
- 29Y. Wu, X.-F. Zhang, M. Li, M. Yu, J. Yao, Langmuir 2024, 40, 5288.
- 30H. Cheng, K. Yang, Y. Zhang, S. Liao, M. Du, J. Li, N. Ma, M. Xue, X. Zhang, Y. Wang, A. C. S. Appl, Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 52402.
- 31C. Lu, X. Wang, Y. Shen, S. Xu, C. Huang, C. Wang, H. Xie, J. Wang, Q. Yong, F. Chu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2311502.
- 32G. Li, Z. Deng, M. Cai, K. Huang, M. Guo, P. Zhang, X. Hou, Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, Y. Wang, X. Wu, C. F. Guo, NPJ Flex. Electron. 2021, 5, 23.
- 33P. Tan, H. Wang, F. Xiao, X. Lu, W. Shang, X. Deng, H. Song, Z. Xu, J. Cao, T. Gan, B. Wang, X. Zhou, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 358.
- 34G. Ge, K. Mandal, R. Haghniaz, M. Li, X. Xiao, L. Carlson, V. Jucaud, M. R. Dokmeci, G. W. Ho, A. Khademhosseini, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2207388.
- 35H. Qin, R. E. Owyeung, S. R. Sonkusale, M. J. Panzer, J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 601.
- 36J. Liu, L. Zhou, P. Zhang, Y. Zhao, H. Wei, Y. Yu, CCS Chem. 2024, 6, 390.
- 37M. L. Picchio, M. S. Orellano, M. A. Motta, C. Huck-Iriart, D. Sánchez-deAlcázar, R. López-Domene, B. Martín-García, A. Larrañaga, A. Beloqui, D. Mecerreyes, M. Calderón, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 35, 2313747.
10.1002/adfm.202313747 Google Scholar
- 38A. Sanchez-Fernandez, M. Basic, J. Y. Xiang, S. Prevost, A. J. Jackson, C. Dicko, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 23657.
- 39Y. Dai, J. van Spronsen, G. J. Witkamp, R. Verpoorte, Y. H. Choi, Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61.
- 40Y. Tian, D.-W. Sun, L. Xu, T.-H. Fan, Z. Zhu, Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 128, 107568.
- 41H. Dai, X. Li, J. Du, L. Ma, Y. Yu, H. Zhou, T. Guo, Y. Zhang, Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105557.
- 42S. Shapardanis, M. Hudpeth, T. Kaya, AIP Adv. 2014, 4, 127132.
10.1063/1.4904724 Google Scholar