A Triphenylamine-Based Conjugated Polymer with Donor-π-Acceptor Architecture as Organic Sensitizer for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Wei Zhang
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 4 Engineering Drive 4, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117576, Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorZhen Fang
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 4 Engineering Drive 4, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117576, Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorMingjuan Su
Singapore-MIT Alliance, Chemical and Pharmaceutical Engineering Program, Singapore 117576, Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorMark Saeys
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 4 Engineering Drive 4, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117576, Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Bin Liu
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 4 Engineering Drive 4, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117576, Singapore
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 4 Engineering Drive 4, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117576, Singapore. Fax: 65 6779 1936Search for more papers by this authorWei Zhang
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 4 Engineering Drive 4, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117576, Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorZhen Fang
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 4 Engineering Drive 4, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117576, Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorMingjuan Su
Singapore-MIT Alliance, Chemical and Pharmaceutical Engineering Program, Singapore 117576, Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorMark Saeys
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 4 Engineering Drive 4, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117576, Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Bin Liu
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 4 Engineering Drive 4, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117576, Singapore
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 4 Engineering Drive 4, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117576, Singapore. Fax: 65 6779 1936Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
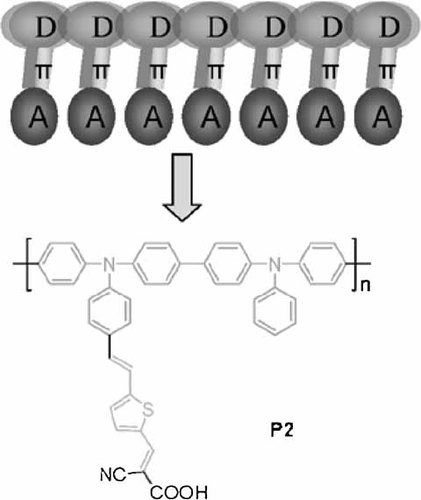
A conjugated polymer containing an electron donating backbone (triphenylamine) and an electron accepting side chain (cyanoacetic acid) with conjugated thiophene units as the linkers has been synthesized. Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) are fabricated utilizing this material as the dye sensitizer, resulting a typical power conversion efficiency of 3.39% under AM 1.5 G illumination, which represents the highest efficiency for polymer dye-sensitized DSSCs reported so far. The results show the good promise of conjugated polymers as sensitizers for DSSC applications.
Supporting Information
Detailed facts of importance to specialist readers are published as ”Supporting Information”. Such documents are peer-reviewed, but not copy-edited or typeset. They are made available as submitted by the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| marc_200900243_sm_supplfigs.pdf17.8 KB | supplfigs |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 B. O'Regan, M. Grätzel, Nature 1991, 353, 737.
- 2 U. Bach, D. Lupo, P. Comte, J. E. Moser, F. Weissörtel, J. Salbeck, H. Spreitzer, M. Grätzel, Nature 1998, 395, 583.
- 3 P. Wang, S. M. Zakeeruddin, J.-E. Moser, R. Humphry-Baker, M. Grätzel, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 7164.
- 4 Y. Bai, Y. Cao, J. Zhang, M. Wang, R. Li, P. Wang, S. M. Zakeeruddin, M. Grätzel, Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 626.
- 5 F. C. Krebs, M. Biancardo, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 2006, 90, 142.
- 6 M. Biancardo, K. West, F. C. Krebs, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 2006, 90, 2575.
- 7 S. Lu, R. Koeppe, S. Günes, N. S. Sariciftci, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 2007, 91, 1081.
- 8 M. Biancardo, K. West, F. C. Krebs, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 2007, 187, 395.
- 9 K. Hara, K. Sayama, Y. Ohga, A. Shinpo, S. Suga, H. Arakawa, Chem. Commun. 2001, 569.
- 10 L. Schmidt-Mende, U. Bach, R. Humphry-Baker, T. Horiuchi, H. Miura, S. Ito, S. Uchida, M. Grätzel, Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 813.
- 11 S. Spiekermann, G. Smestad, J. Kowalik, L. M. Tolbert, M. Grätzel, Synth. Met. 2001, 121, 1603.
- 12 T. J. Savenije, J. M. Warman, A. Goossens, Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 287, 148.
- 13 Y.-G. Kim, J. Walker, L. A. Samuelson, J. Kumar, Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 523.
- 14 G. K. R. Senadeera, K. Nakamura, T. Kitamura, Y. Wada, S. Yanagida, Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 5470.
- 15 S. Yahagida, G. K. R. Senadeera, K. Nakamura, T. Kitamura, Y. Wada, J. Photochem. Photobio. A: Chem. 2004, 166, 75.
- 16 J. K. Mwaura, X. Zhao, H. Jiang, K. S. Schanze, J. R. Reynolds, Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 6109.
- 17 X. Liu, R. Zhu, Y. Zhang, B. Liu, S. Ramakrishna, Chem. Commun. 2008, 3789.
- 18 A. J. Moore, M. R. Bryce, A. S. Batsanov, A. Green, J. A. K. Howard, M. A. Mckervey, P. McGuigan, L. Ledoux, E. Orti, R. Viruela, P. M. Viruela, B. Tarbit, J. Mater. Chem. 1998, 8, 1173.
- 19 T. Kitamura, M. Ikeda, K. Shigaki, T. Inoue, N. A. Anderson, X. Ai, T. Lian, S. Yanagida, Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 1806.
- 20 T. Horiuchi, H. Miura, K. Sumioka, S. Uchida, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12218.
- 21 D. P. Hagberg, J. H. Yum, H. Lee, F. DeAngelis, T. Marinado, K. M. Karlsson, R. Humphry-Baker, L. C. Sun, A. Hagfeldt, M. Grätzel, M. K. Nazeeruddin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6259.
- 22 Z. Chen, F. Li, C. Huang, Curr. Org. Chem. 2007, 11, 1241.
- 23 H. Xiao, B. Leng, H. Tian, Yingyong Huaxue 2006, 23, 140.
- 24 Q. Fang, T. Yamamoto, Macromolecules 2004, 37, 5894.
- 25 A. G. Shilabin, A. A. Entezami, Eur. Polym. J. 2000, 36, 2005.
- 26 A. Hagfeldt, M. Grätzel, Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 49.
- 27 K. Hara, T. Horiguchi, T. Kinoshita, K. Sayama, H. Arakawa, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2001, 70, 151.
- 28 S. Y. Huang, G. Schlichthörl, A. J. Nozik, M. Grätzel, A. J. Frank, J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 2576.