Synthesis of Ferrocene-Branched Chitosan Derivatives: Redox Polysaccharides and their Application to Reagentless Enzyme-Based Biosensors
Weiwei Yang
College of Chemistry, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012, China
Search for more papers by this authorHong Zhou
College of Chemistry, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Changqing Sun
College of Chemistry, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012, China
College of Chemistry, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012, China. Fax: +86 431 8516 7655Search for more papers by this authorWeiwei Yang
College of Chemistry, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012, China
Search for more papers by this authorHong Zhou
College of Chemistry, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Changqing Sun
College of Chemistry, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012, China
College of Chemistry, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012, China. Fax: +86 431 8516 7655Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
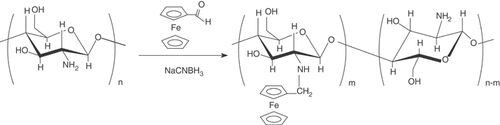
Ferrocene-branched chitosan derivatives (CHIT-Fc) are synthesized by reductive N-alkylation of chitosan with ferrocenecarboxaldehyde. The structures of the products are determined by 1H NMR and FT-IR spectra. CHIT-Fc is used as a functionalized matrix to immobilize GOD on glassy carbon electrodes. Ferrocenyls in CHIT-Fc exhibit an excellent redox activity and establish efficient electrical communication between GOD and the electrodes for the oxidation of glucose. The development of a reagentless glucose biosensor is described.
References
- 1 H. Yi, L.-Q. Wu, W. E. Bentley, R. Ghodssi, G. W. Rubloff, J. N. Culver, G. F. Payne, Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2881.
- 2
- 2a X. Wei, M. G. Zhang, W. Gorski, Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 2060;
- 2b X. Chen, J. B. Jia, S. J. Dong, Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 608;
- 2c
L. T. Ng,
H. Zhao,
Electroanalysis
1998,
10,
1119;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-4109(199811)10:16<1119::AID-ELAN1119>3.0.CO;2-U CAS Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 2d Y. Miao, S. N. Tan, Analyst 2000, 125, 1591.
- 3
- 3a M. Yalpani, L. D. Hall, Macromolecules 1984, 17, 272;
- 3b H. Sashiwa, Y. Makimura, Y. Shigemasa, R. Roy, Chem. Commun. 2000, 909;
- 3c H. Sashiwa, H. Yajima, S.-I. Aiba, Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1244;
- 3d M. Fujioka, H. Okada, Y. Kusaka, S. Nishiyama, H. Noguchi, S. Ishii, Y. Yoshida, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 1776;
- 3e S. S. Silva, R. A. S. Ferreira, L. Fu, L. D. Carlos, J. F. Mano, R. L. Reis, J. Rocha, J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3952;
- 3f M. Bodnar, J. F. Hartmann, J. Borbely, Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2521.
- 4 X. Wei, J. Cruz, W. Gorski, Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5039.
- 5
- 5a B. A. Gregg, A. Heller, Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 258;
- 5b E. J. Calvo, C. Danilowicz, L. Diaz, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1993, 89, 377;
- 5c M. G. Zhang, W. Gorski, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2058;
- 5d M. G. Zhang, W. Gorski, Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 3960.
- 6
- 6a M. J. Green, H. A. O. Hill, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1 1986, 82, 1237;
- 6b C. Bourdillon, C. Demaille, J. Moiroux, J.-M. Savéant, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 2;
- 6c W. Schuhmann, T. J. Ohara, H.-L. Schmidt, A. Heller, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 1394;
- 6d B. I. Willner, A. Riklin, B. Shoham, D. Rivenzon, E. Katz, Adv. Mater. 1993, 5, 912;
- 6e E. J. Calvo, C. Danilowicz, L. Diaz, J. Electroanal. Chem. 1994, 369, 279;
- 6f N. S. Lawrence, R. P. Deo, J. Wang, Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 3735.
- 7
- 7a N. C. Foulds, C. R. Lowe, Anal. Chem. 1988, 60, 2473;
- 7b H. C. Yoon, M.-Y. Hong, H.-S. Kim, Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 4420.
- 8 J. S. Bodenheimer, W. Low, Spectrochim. Acta 1973, 29A, 1733.
- 9 M. D. Hawley, S. V. Tatawadi, S. Piekarski, R. N. Adams, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 447.
- 10 J. G. Voet, J. Coe, J. Epstein, V. Matossian, T. Shipley, Biochemistry 1981, 20, 7182.
- 11 A. E. G. Cass, G. Davis, G. D. Francis, H. A. O. Hill, W. J. Aston, I. J. Higgins, E. V. Plotkin, L. D. L. Scott, A. P. F. Turner, Anal. Chem. 1984, 56, 667.
- 12 E. J. Calvo, R. Etchenique, C. Danilowicz, L. Diaz, Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 4186.
- 13 A. J. Bard, L. R. Faulkner, “ Electrochemical Methods. Fundamentals and Applications”, 1st edition, Wiley, New York 1980, Chapter 5.
- 14 R. J. Forster, J. G. Vos, J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 1991, 1, 67.
- 15 K. Sirkar, M. V. Pishko, Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 2888.
- 16 S. J. Dong, G. L. Che, Y. W. Xie, “ Chemically Modified Electrodes”, 1st edition, Science Press, Beijing 1995, p. 149.
- 17 W. W. Yang, J. X. Wang, S. Zhao, Y. Y. Sun, C. Q. Sun, Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 665.
- 18 S. X. Zhang, W. W. Yang, Y. M. Niu, C. Q. Sun, Sens. Actuators B 2004, 101, 387.
- 19 T. J. Ohara, R. Rajagopalan, A. Heller, Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 2451.
- 20 Y. Liu, M. K. Wang, F. Zhao, Z. A. Xu, S. J. Dong, Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 984.