Humid Bonding with a Water-Soluble Adhesive Inspired by Mussels and Sandcastle Worms
Ailei Li
Key Laboratory of Biobased Materials, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 189 Songling Road, Qingdao, Shandong Province, 266101 PR China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19A Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 PR China
Search for more papers by this authorMingchen Jia
Key Laboratory of Biobased Materials, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 189 Songling Road, Qingdao, Shandong Province, 266101 PR China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19A Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 PR China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Youbing Mu
Key Laboratory of Biobased Materials, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 189 Songling Road, Qingdao, Shandong Province, 266101 PR China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorWei Jiang
National Engineering Research Center for Organic Pollution Control and Resource Reuse, State Key Laboratory of Pollution and Resource Reuse, School of the Environment, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, 210093 PR China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaobo Wan
Key Laboratory of Biobased Materials, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 189 Songling Road, Qingdao, Shandong Province, 266101 PR China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorAilei Li
Key Laboratory of Biobased Materials, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 189 Songling Road, Qingdao, Shandong Province, 266101 PR China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19A Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 PR China
Search for more papers by this authorMingchen Jia
Key Laboratory of Biobased Materials, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 189 Songling Road, Qingdao, Shandong Province, 266101 PR China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19A Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 PR China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Youbing Mu
Key Laboratory of Biobased Materials, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 189 Songling Road, Qingdao, Shandong Province, 266101 PR China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorWei Jiang
National Engineering Research Center for Organic Pollution Control and Resource Reuse, State Key Laboratory of Pollution and Resource Reuse, School of the Environment, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, 210093 PR China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaobo Wan
Key Laboratory of Biobased Materials, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 189 Songling Road, Qingdao, Shandong Province, 266101 PR China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
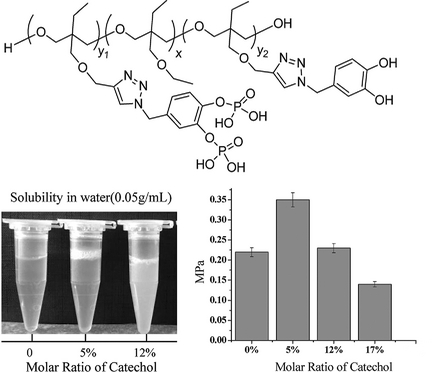
Inspired by mussels and sandcastle worms, a water-soluble adhesive is prepared by grafting catechol and phosphoric acid functionalities to the polyoxetane backbone, which achieves improved adhesion in humid environment. The adhesive is characterized by 1H and 31P NMR spectroscopy and size-exclusive chromatography. The influence of the content ratio of catechol and different phosphoric acid groups and the Fe3+ ions as the crosslinker on the outcome of the adhesive properties is investigated. When the molar ratio of Fe3+ to catechol and PO4 is 1/1 and 0.7/1, respectively, the best bonding strength of 0.35 MPa is achieved for the adhesive containing 5 mol% catechol and 26 mol% bis-phosphoric acid groups under humid conditions. It is found out that Fe3+ interacts not only with the catechol, but also with the bis-phosphoric acid groups, which accounts for its performance in humid conditions.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| macp201400513-sup-0001-S1.pdf935.3 KB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1J. H. Waite, M. L. Tanzer, Science 1981, 212, 1038.
- 2J. H. Waite, Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 1172.
- 3H. Shao, K. N. Bachus, R. J. Stewart, Macromol. Biosci. 2009, 9, 464.
- 4T. H. Anderson, J. Yu, A. Estrada, M. U. Hammer, J. H. Waite, J. N. Israelachvili, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 4196.
- 5Q. Lin, D. Gourdon, C. Sun, N. Holten-Andersen, T. H. Anderson, J. H. Waite, J. N. Israelachvili, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3782.
- 6H. Shao, R. J. Stewart, Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 729.
- 7C. S. Wang, R. J. Stewart, Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1607.
- 8M. Yu, J. Hwang, T. J. Deming, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 5825.
- 9S. A. Burke, M. Ritter-Jones, B. P. Lee, P. B. Messersmith, Biomedical Mater. 2007, 2, 203.
- 10H. Lee, B. P. Lee, P. B. Messersmith, Nature 2007, 448, 338.
- 11M. Mehdizadeh, H. Weng, D. Gyawali, L. Tang, J. Yang, Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7972.
- 12K. Yamada, T. Chen, G. Kumar, O. Vesnovsky, L. D. T. Topoleski, G. F. Payne, Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 252.
- 13J. Wang, C. Liu, X. Lu, M. Yin, Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3456.
- 14J. D. White, J. J. Wilker, Macromolecules 2011, 44, 5085.
- 15C. R. Matos-Perez, J. D. White, J. J. Wilker, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9498.
- 16R. J. Stewart, C. S. Wang, H. Shao, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 167, 85.
- 17B. P. Lee, J. L. Dalsin, P. B. Messersmith, Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1038.
- 18H. Zhao, J. H. Waite, J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26150.
- 19H. Zhao, C. Sun, R. J. Stewart, J. H. Waite, J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 42938.
- 20J. H. Waite, Biochemistry 2001, 40, 2887.
- 21A. V. Anne George, Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 4670.
- 22N. Moszner, F. Zeuner, U. K. Fischer, V. Rheinberger, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1999, 200, 1062.
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3935(19990501)200:5<1062::AID-MACP1062>3.0.CO;2-# CAS Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 23Z. El Asri, K. Chougrani, C. Negrell-Guirao, G. David, B. Boutevin, C. Loubat, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 4794.
- 24S. Monge, B. Canniccioni, A. Graillot, J. J. Robin, Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1973.
- 25S. Kamei, N. Tomita, S. Tamai, K. Kato, Y. Ikada, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 37, 384.
10.1002/(SICI)1097-4636(19971205)37:3<384::AID-JBM9>3.0.CO;2-H CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 26M. Jia, A. Li, Y. Mu, W. Jiang, X. Wan, Polymer 2014, 55, 1160.
- 27G. W. Kenner, N. R. Williams, J. Chem. Soc. 1955, 522.
- 28R. F. Hudson, D. C. Harper, J. Chem. Soc. 1958, 1356.
- 29J. R. Cox, O. B. Ramasay, Chem. Rev. 1964, 64, 317.
- 30C. E. McKenna, M. T. Higa, N. H. Cheung, M. C. McKenna, Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 18, 155.
- 31H. Zhang, L. P. Bre, T. Zhao, Y. Zheng, B. Newland, W. Wang, Biomaterials 2014, 35, 711.
- 32M. J. Sever, J. T. Weisser, J. Monahan, S. Srinivasan, J. J. Wilker, Angew. Chem. 2004, 43, 448.
- 33J. J. Wilker, Angew. Chem. 2010, 49, 8076.
- 34C. Sun, G. E. Fantner, J. Adams, P. K. Hansma, J. H. Waite, J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 1481.
- 35M. Krogsgaard, M. A. Behrens, J. S. Pedersen, H. Birkedal, Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 297.
- 36E. M. White, J. E. Seppala, P. M. Rushworth, B. W. Ritchie, S. Sharma, J. Locklin, Macromolecules 2013, 46, 8882.
- 37P. Sun, J. Wang, X. Yao, Y. Peng, X. Tu, P. Du, Z. Zheng, X. Wang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12495.
- 38D. G. Barrett, D. E. Fullenkamp, L. He, N. Holten-Andersen, K. Y. Lee, P. B. Messersmith, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1111.