Reconstruction of Achiral Polymer for Structural Chirality Using Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Medium and Light-Driven Chiroptic Modulation
Abstract
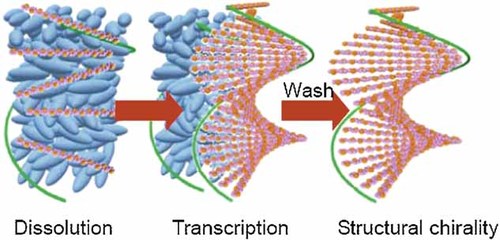
A series of optically inactive polythiophene derivatives bearing the azobenzene moiety are synthesized in an isotropic toluene solution. The polymers are then dissolved in a cholesteric liquid crystal (Ch*LC) medium within the liquid crystal (LC) temperature range. The dissolution process in Ch*LC produces intermolecular π-stacking with structural chirality. Although the polymers thus prepared have no chiral center or axial chirality in the primary structure, they do exhibit consistent chiroptical activity derived from three-dimensional chiral aggregations. Furthermore, photochemical cis–trans isomerization of the substituents allows light-driven chiroptic modulation of the polymer.