Influence of TiC addition on high-temperature oxidation in rich pO2 atmosphere on Cr-rich stainless steel
Abstract
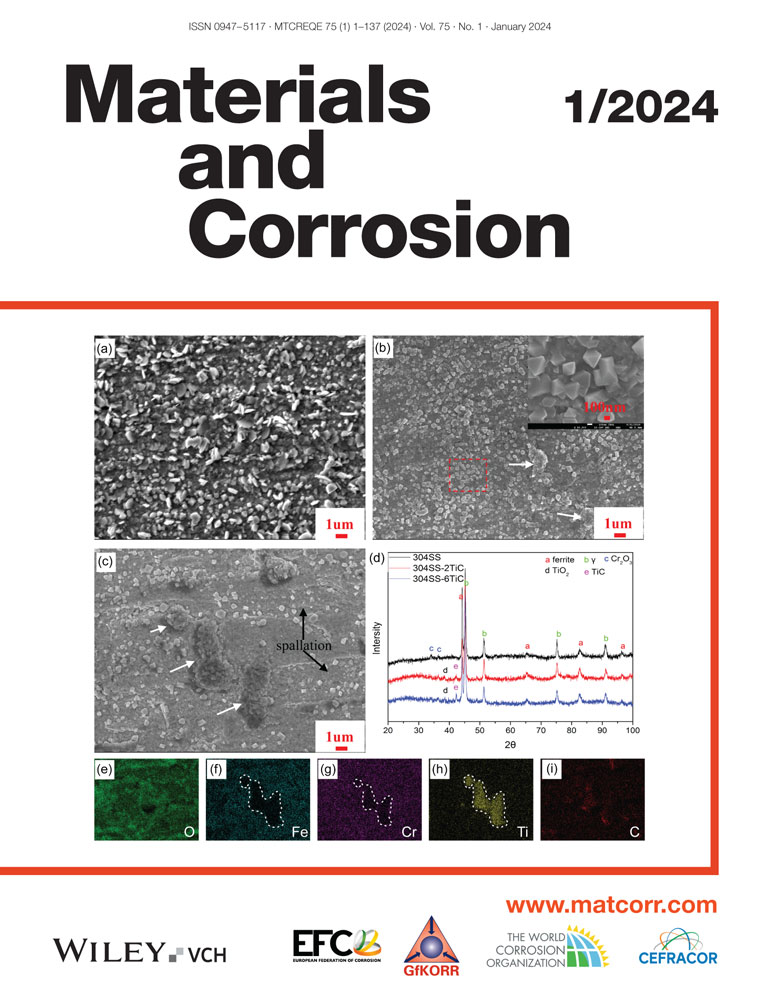
In this study, the effect of TiC on the oxidation resistance of 304 stainless steel (304SS) at 650°C in air was investigated by examining oxidation kinetics and surface and cross-sectional scale microstructures, in comparison with TiC-free alloy. It was found that TiC addition deteriorated the oxidation resistance of 304SS at 650°C, in contrast with its improving effect on oxidation resistance at 850°C reported before. The variation of the TiC effect on the oxidation resistance of 304SS at different temperatures was attributed to the dual effect of TiC where the final results depended on if protective or nonprotective oxide scale formation occurred in TiC-free 304SS materials.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.