Rituximab combined with chemotherapy and acalabrutinib prior to autologous stem cell transplantation in mantle cell lymphoma: The Rectangle Trial
Introduction: In the European MCL Network Triangle study the addition of ibrutinib to frontline rituximab-containing chemotherapy and subsequent maintenance therapy improved failure-free survival in young, fit patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Ibrutinib was administered with R-CHOP, but not with R-DHAP, during the induction phase.
Continuous, uninterrupted Bruton Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) inhibition could maximize the benefit of front-line therapy given that responses develop over time. Acalabrutinib is a second generation BTK inhibitor with less off-target inhibition than ibrutinib. We hypothesize that combining continuous acalabrutinib with R-CHOP may result in a tolerable, outpatient, highly active regimen producing favorable outcomes.
Methods: NCT04566887 is a phase II, non-randomized, single-arm study conducted across 5 academic centres in Canada. Patients ≥18 years of age with previously untreated MCL, ECOG performance status 0–2, adequate organ function and considered fit for autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) were included. Patients received 6 cycles of R-CHOP at standard doses plus acalabrutinib 100 mg twice per day orally. Responding patients proceeded with ASCT and maintenance rituximab and acalabrutinib for a total of 2 years.
The primary endpoint was the complete response (CR) rate after 6 cycles of induction with centrally reviewed PET/CT using the Lugano Criteria. The total sample size is n = 54. We present the results of a preplanned interim analysis when the first 24 subjects completed response assessments after 6 cycles of induction. The study would be terminated if <15/24 patients achieved a CR.
Results: The median age was 60 years (range 38–69), 16 (67%) were male, 23 (96%) had performance status 0–1, 19 (79%) Ann Arbor stage IV, 19 (79%) bone marrow involvement, 4 (17%) high risk MIPI, 3 (13%) blastoid/pleomorphic morphology, 7 (29%) Ki67 ≥30%. All patients completed 6 cycles of induction and proceeded to ASCT. The overall response rate was 100%, and 19 (79%) patients achieved a CR.
-
Baseline high-risk MIPI and Ki67 70%; biopsy at relapse TP53 positive by immunohistochemistry (IHC),
-
Baseline intermediate risk MIPI and Ki67 60%; biopsy at relapse with pleomorphic morphology, TP53 positive by IHC, Ki67 100%,
-
Baseline high risk MIPI, Ki67 ≥30%, and blastoid morphology.
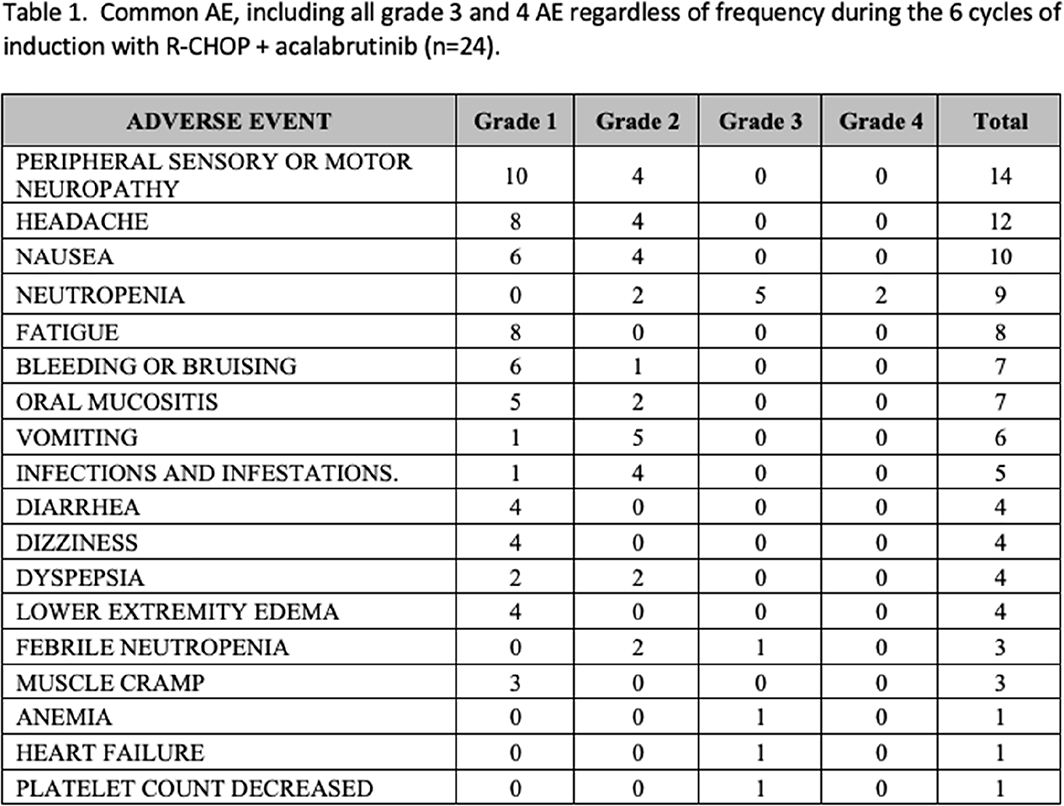
Table 1 lists adverse events (AE) during the 6 cycles of induction. There were no grade 5 AE. Most infections were respiratory including 1 case with mild COVID-19.
Conclusions: Acalabrutinib + R-CHOP is associated with a 79% CR rate with low rates of grade 3–4 AE expected for this combination. The study is ongoing, with expected full accrual by April 2023.
 |
The research was funded by: This investigator-initiated trial was funded by AstraZeneca.
Keywords: combination therapies, indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma, molecular targeted therapies
Conflicts of interests pertinent to the abstract.
D. Villa
Consultant or advisory role: AstraZeneca, Janssen, BeiGene, Kite/Gilead, BMS/Celgene, Merck, Abbvie, Roche
Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Janssen, BeiGene, Kite/Gilead, BMS/Celgene, Merck, Abbvie, Roche
Research funding: AstraZeneca, Roche (research funding to the institution)
D. Scott
Consultant or advisory role: Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Incyte
Research funding: Janssen, Roche
Other remuneration: Patents using gene expression to subtype aggressive lymphoma, including one licensed to Veracyte
J. Kuruvilla
Research funding: AstraZeneca (to the institution)