Persistence of EEG abnormalities in KCNT1-related DEE in an adult patient
Irfan S. Sheikh is a senior author.
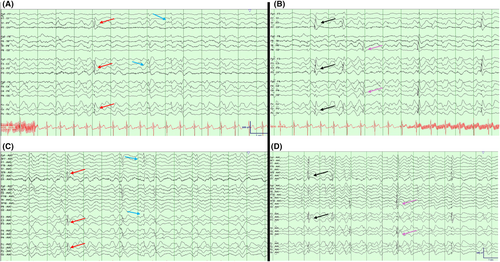
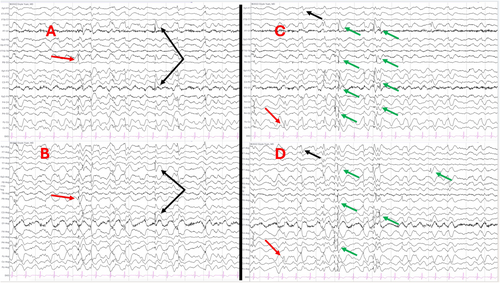
The KCNT1 gene encodes a sodium-activated potassium channel, with variants causing developmental/epileptic encephalopathies (DEEs) and intractable epilepsies.1, 2 EEGs characteristically reveal multi-focal interictal discharges migrating through contiguous cortical regions.3 We demonstrate multi-focal interictal discharges (left parietal, left frontal, right centroparietal, and right parieto-occipital) amidst a disorganized, slow background in a 20-year-old female with a heterozygous likely pathogenic KCNT1 variant (p.L281I; c.841C>A) and DEE (Figures 1 and 2). EEG available at https://hub.eegtalk.com/go/KCNT1. Seizures developed at age 6, followed by developmental regression, precocious puberty, and behavioral/psychiatric disturbances. Cardiac arrhythmias and pulmonary hemorrhage have also been reported.4 Presently, she experiences five to six focal seizures without impaired awareness weekly on lacosamide. Quinidine, thought to control seizures and slow developmental regression in KCNT1-related epilepsies, is no longer recommended and was discontinued.5, 6 A recent trial has not proven its efficacy despite carrying significant risks of arrhythmia.7 Although well-described in children, we demonstrate these EEG findings' persistence into adulthood.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
Irfan S. Sheikh is the assistant program leader for the Epileptic Disorders Journal Internship Program, is an Associate Editor for the journal, and has collaboration with EEGHub. Doyle Yuan has collaboration with EEGHub. Other authors report no disclosures.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in EEGHub at https://hub.eegtalk.com/go/KCNT1.
REFERENCES
Test yourself
-
The KCNT1 gene encodes
- A voltage-gated sodium channel
- A voltage gated potassium channel
- A sodium-activated potassium channel
- A potassium-activated sodium channel
-
EEG characteristically shows
- Focal discharges
- Multifocal discharges
- Temporal discharges
- Bilateral discharges
-
Which of these can be seen in KCNT1-related epilepsy
- Cardiac arrhythmias, precocious puberty, behavioral disturbances, developmental regression
- Cardiomyopathy, precocious puberty, behavioral disturbances, developmental regression
- Cardiac arrhythmias, infertility, behavioral disturbances, developmental regression
- Cardiac arrhythmias, precocious puberty, behavioral disturbances, interstitial lung disease
Answers may be found in the Supporting information.




