Resource allocation for energy efficiency optimization in uplink–downlink decoupled 5G heterogeneous networks
Corresponding Author
Humayun Zubair Khan
Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
Correspondence
Humayun Zubair Khan, Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorMudassar Ali
Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
University of Engineering and Technology, Taxila, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorImran Rashid
Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorAbdul Ghafoor
Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorMuhammad Naeem
COMSATS University, Islamabad Wah Campus, Wah Cantt, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorAdnan Ahmed Khan
Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorAdil Masood Saddiqui
Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Humayun Zubair Khan
Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
Correspondence
Humayun Zubair Khan, Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorMudassar Ali
Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
University of Engineering and Technology, Taxila, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorImran Rashid
Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorAbdul Ghafoor
Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorMuhammad Naeem
COMSATS University, Islamabad Wah Campus, Wah Cantt, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorAdnan Ahmed Khan
Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorAdil Masood Saddiqui
Military College of Signals, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorSummary
Heterogeneous networks (HetNets) are a practical solution for traffic offloading from a high powered base station (HBS) to a low powered base station (LBS). In the HetNets, uplink (UL)–downlink (DL) decoupled access (UDDa) strategy is an optimal solution that ensures cell association, independently, in the UL and DL. This strategy offloads HBS cell edge mobile device (MD) to the nearby LBS in the UL. However, energy-efficient cell association for traffic offloading from HBS to LBS, relay, or device to device (D2D) in the UL employing UDDa strategy has not been explored in the past work. We formulate mathematical models which ensure energy-efficient cell association, power allocation, and traffic offloading employing traditional UL-DL coupled access (UDCa) and UDDa strategies in the HetNets. The formulated problems are concave fractional programming (CFP) problems. The CFP is changed to a concave optimization problem using Charnes–Cooper transformation (CCT). The transformed problems are solved using an outer approximation algorithm to obtain
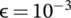 optimal solution. Simulation results show the effectiveness of UDDa strategy over UDCa strategy in terms of MDs association, traffic offloading in the UL and DL, interference mitigation in the UL, data rate, and energy efficiency in the HetNets.
optimal solution. Simulation results show the effectiveness of UDDa strategy over UDCa strategy in terms of MDs association, traffic offloading in the UL and DL, interference mitigation in the UL, data rate, and energy efficiency in the HetNets.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Research data are not shared.
REFERENCES
- 1 C. V. networking Index. Forecast and methodology, 2017-2022, white paper. San Jose, CA, USA 1; 2017.
- 2Andrews JG, Buzzi S, Choi W, Hanly SV, Lozano A, Soong ACK, Zhang JC. What will 5g be? IEEE J Sel Areas Commun. 2014; 32(6): 1065-1082.
- 3Hwang I, Song B, Soliman SS. A holistic view on hyper-dense heterogeneous and small cell networks. IEEE Commun Mag. 2013; 51(6): 20-27.
- 4Panzner B, Zirwas W, Dierks S, Lauridsen M, Mogensen P, Pajukoski K, Miao D. Deployment and implementation strategies for massive mimo in 5g. In: 2014 ieee globecom workshops (gc wkshps); 2014: 346-351.
- 5Rappaport TS, Sun S, Mayzus R, et al. Millimeter wave mobile communications for 5g cellular: it will work!. IEEE Access. 2013; 1: 335-349.
- 6Olsson M, Cavdar C, Frenger P, Tombaz S, Sabella D, Jantti R. 5green: Towards green 5g mobile networks. In: 2013 ieee 9th international conference on wireless and mobile computing, networking and communications (wimob); 2013: 212-216.
- 7Fehske A, Fettweis G, Malmodin J, Biczok G. The global footprint of mobile communications: the ecological and economic perspective. IEEE Commun Mag. 2011; 49(8): 55-62.
- 8Bianzino AP, Chaudet C, Rossi D, Rougier J. A survey of green networking research. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor. 2012; 14(1): 3-20.
- 9Wu J. Green wireless communications: from concept to reality [industry perspectives]. IEEE Wirel Commun. 2012; 19(4): 4-5.
- 10Wu J, Rangan S, Zhang H. Green communications: theoretical fundamentals, algorithms, and applications: CRC press; 2016.
10.1201/b13083 Google Scholar
- 11Wu J, Guo S, Huang H, Liu W, Xiang Y. Information and communications technologies for sustainable development goals: state-of-the-art, needs and perspectives. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor. 2018; 20(3): 2389-2406.
- 12Ali M, Qaisar S, Naeem M, Mumtaz S. Energy efficient resource allocation in d2d-assisted heterogeneous networks with relays. IEEE Access. 2016; 4: 4902-4911.
- 13Khan HZ, Ali M, Rashid I, Ghafoor A, Naeem M. Cell association for energy efficient resource allocation in decoupled 5g heterogeneous networks. In: 2020 ieee 91st vehicular technology conference (vtc2020-spring) IEEE; 2020: 1-5.
- 14Zhuang B, Guo D, Honig ML. Energy-efficient cell activation, user association, and spectrum allocation in heterogeneous networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun. 2016; 34(4): 823-831.
- 15Fabian P, Rachedi A, Guéguen C. Programmable objective function for data transportation in the internet of vehicles. Trans Emerg Telecommun Technol. 2020; 31(5):e3882.
- 16Abar T, Rachedi A, Ben Letaifa A, Fabian P, El Asmi S. Fellowme cache: fog computing approach to enhance (qoe) in internet of vehicles. Future Gener Comput Syst. 2020; 113: 170-182.
- 17Dahlman E, Parkvall S, Skold J. 4g: Lte/lte-advanced for mobile broadband: Academic press; 2013.
- 18Ullah A, Abbas ZH, Muhammad F, Abbas G, Kim S. Uplink performance analysis of user-centric small cell aided dense hcnets with uplink-downlink decoupling. IEEE Access. 2020; 8: 148460-148474.
- 19Abbas ZH, Haroon MS, Muhammad F, Abbas G, Li FY. Enabling soft frequency reuse and stienen's cell partition in two-tier heterogeneous networks: Cell deployment and coverage analysis. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology; 2020.
- 20Haroon MS, Muhammad F, Abbas G, Abbas ZH, Hassan AK, Waqas M, Kim S. Interference management in ultra-dense 5g networks with excessive drone usage. IEEE Access. 2020; 8: 102155-102164.
- 21Muhammad F, Haroon MS, Abbas ZH, Abbas G, Kim S. Uplink interference management for hetnets stressed by clustered wide-band jammers. IEEE access. 2019; 7: 182679-182690.
- 22Haroon MS, Muhammad F, Abbas ZH, Abbas G, Ahmed N, Kim S. Proactive uplink interference management for nonuniform heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Access. 2020; 8: 55501-55512.
- 23Abbas ZH, Haroon MS, Abbas G, Muhammad F. Sir analysis for non-uniform hetnets with joint decoupled association and interference management. Comput Commun. 2020; 155: 48-57.
- 24Boccardi F, Andrews J, Elshaer H, Dohler M, Parkvall S, Popovski P, Singh S. Why to decouple the uplink and downlink in cellular networks and how to do it. IEEE Commun Mag. 2016; 54(3): 110-117.
- 25Elshaer H, Boccardi F, Dohler M, Irmer R. Downlink and uplink decoupling: a disruptive architectural design for 5g networks. In: 2014 ieee global communications conference IEEE; 2014: 1798-1803.
- 26Khan HZ, Ali M, Naeem M, Rashid I, Siddiqui AM, Imran M, Mumtaz S. Resource allocation and throughput maximization in decoupled 5g. In: 2020 ieee wireless communications and networking conference (wcnc); 2020: 1-6.
- 27Khan HZ, Ali M, Naeem M, Rashid I, Imran M. Resource allocation in 5g heterogeneous networks with downlink-uplink decoupled access. Trans Emerg Telecommun Technol. 2020; 31(3):e3831.
- 28Cai S, Che Y, Duan L, Wang J, Zhou S, Zhang R. Green 5g heterogeneous networks through dynamic small-cell operation. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun. 2016; 34(5): 1103-1115.
- 29Wu G, Dong L, Qin Z, Xu Z. Dynamic programming-based pico base station sleep mode control in heterogeneous networks. Int J Commun Syst. 2017; 30(2):e2967.
- 30Zhang L, Feng G, Qin S, Jiang W, Sun Y. Energy efficient sleep strategy for decoupled uplink downlink access in hetnets. In: 2017 ieee wireless communications and networking conference (wcnc); 2017: 1-6.
- 31Khamesi AR, Zorzi M. Energy harvesting and cell zooming in k− tier heterogeneous random cellular networks. IEEE Trans Green Commun Netw. 2018; 2(1): 63-73.
10.1109/TGCN.2017.2752362 Google Scholar
- 32Panahi FH, Panahi FH, Hattab G, Ohtsuki T, Cabric D. Green heterogeneous networks via an intelligent sleep/wake-up mechanism and d2d communications. IEEE Trans Green Commun Netw. 2018; 2(4): 915-931.
10.1109/TGCN.2018.2844301 Google Scholar
- 33Peng J, Hong P, Xue K. Energy-aware cellular deployment strategy under coverage performance constraints. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun. 2015; 14(1): 69-80.
- 34Zhao G, Chen S, Zhao L, Hanzo L. A tele-traffic-aware optimal base-station deployment strategy for energy-efficient large-scale cellular networks. IEEE Access. 2016; 4: 2083-2095.
- 35Yang C, Li J, Anpalagan A, Guizani M. Joint power coordination for spectral-and-energy efficiency in heterogeneous small cell networks: a bargaining game-theoretic perspective. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun. 2016; 15(2): 1364-1376.
- 36Sui X, Zhao Z, Li R, Zhang H. Energy efficiency analysis of heterogeneous cellular networks with downlink and uplink decoupling. In: 2015 ieee global communications conference (globecom); 2015: 1-7.
- 37Luo Y, Shi Z, Bu F, Xiong J. Joint optimization of area spectral efficiency and energy efficiency for two-tier heterogeneous ultra-dense networks. IEEE Access. 2019; 7: 12073-12086.
- 38Gao X, Yang K, Yang N, Wu J. Energy-efficient resource block assignment and power control for underlay device-to-device communications in multi-cell networks. Comput Netw. 2019; 149: 240-251.
- 39Smiljkovikj K, Gavrilovska L, Popovski P. Efficiency analysis of downlink and uplink decoupling in heterogeneous networks. In: 2015 ieee international conference on communication workshop (iccw); 2015: 125-130.
- 40Zhang L, Feng G, Nie W, Qin S. A comparison study of coupled and decoupled uplink-downlink access in heterogeneous cellular networks. In: 2015 ieee global communications conference (globecom); 2015: 1-7.
- 41Yang K, Martin S, Xing C, Wu J, Fan R. Energy-efficient power control for device-to-device communications. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun. 2016; 34(12): 3208-3220.
- 42Yang K, Martin S, Quadri D, Wu J, Feng G. Energy-efficient downlink resource allocation in heterogeneous ofdma networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol. 2016; 66(6): 5086-5098.
- 43Yang K, Martin S, Boukhatem L, Wu J, Bu X. Energy-efficient resource allocation for device-to-device communications overlaying lte networks. In: 2015 ieee 82nd vehicular technology conference (vtc2015-fall) IEEE; 2015: 1-6.
- 44Zhang Y, An J, Yang K, Gao X, Wu J. Energy-efficient user scheduling and power control for multi-cell ofdma networks based on channel distribution information. IEEE Trans Sig Process. 2018; 66(22): 5848-5861.
- 45Gao X, Yang K, Wu J, Zhang Y, An J. Energy-efficient resource allocation and power control for downlink multi-cell ofdma networks. In: Globecom 2017-2017 ieee global communications conference IEEE; 2017: 1-6.
- 46Liao H, Zhou Z, Zhao X, et al. Learning-based context-aware resource allocation for edge-computing-empowered industrial iot. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019; 7(5): 4260-4277.
- 47Zhou Z, Yu H, Mumtaz S, Al-Rubaye S, Tsourdos A, Hu RQ. Power control optimization for large-scale multi-antenna systems. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun. 2020; 19(11): 7339-7352.
- 48Hamdoun S, Rachedi A, Ghamri-Doudane Y. Graph-based radio resource sharing schemes for mtc in d2d-based 5g networks. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2020; 1-19.
- 49Wang A, Chen J, Cai Y, Cai C, Yang W, Cheng Y. Joint subcarrier and power allocation for physical layer security in cooperative ofdma networks. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw. 2013; 2013(1): 193.
- 50Hanif MF, Smith PJ. On the statistics of cognitive radio capacity in shadowing and fast fading environments. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun. 2010; 9(2): 844-852.
- 51Shannon CE. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J. 1948; 27(3): 379-423.
- 52Charnes A, Cooper WW. Programming with linear fractional functionals. Naval Res Logist Q. 1962; 9(3-4): 181-186.
10.1002/nav.3800090303 Google Scholar
- 53Hong M, Luo Z-Q. Distributed linear precoder optimization and base station selection for an uplink heterogeneous network. IEEE Trans Sig Process. 2013; 61(12): 3214-3228.
- 54Duran MA, Grossmann IE. An outer-approximation algorithm for a class of mixed-integer nonlinear programs. Math Program. 1986; 36(3): 307-339.
- 55Fletcher R, Leyffer S. Solving mixed integer nonlinear programs by outer approximation. Math Program. 1994; 66(1-3): 327-349.
- 56Floudas CA, Pardalos PM. Encyclopedia of Optimization, Vol. 1: Springer Science & Business Media; 2001.
10.1007/0-306-48332-7 Google Scholar
- 57Floudas CA. Nonlinear and Mixed-Integer Optimization: Fundamentals and Applications: Oxford University Press; 1995.
10.1093/oso/9780195100563.001.0001 Google Scholar
- 58Van Loan CF, Golub GH. Matrix Computations: Johns Hopkins University Press; 1983.
- 59Khan HZ, Ali M, Naeem M, Rashid I, Siddiqui AM, Imran M, Mumtaz S. Joint admission control, cell association, power allocation and throughput maximization in decoupled 5g heterogeneous networks. Telecommunication Systems, 2020; 1-14.
- 60Bonami P. Basic open-source nonlinear mixed integer programming. Accessed July 31, 2019 http://www.coin-or.org/Bonmin/; 2019.
- 61Lopez-Perez D, Guvenc I, De la Roche G, Kountouris M, Quek TQS, Zhang J. Enhanced intercell interference coordination challenges in heterogeneous networks. IEEE Wirel Commun. 2011; 18(3): 22-30.
- 62Shi Y, Alsusa E, Ebrahim A, Baidas MW. Uplink performance enhancement through adaptive multi-association and decoupling in uhf-mmwave hybrid networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol. 2019; 68(10): 9735-9746.




