Highly Water-Soluble Sulfonatopropoxylated Cucurbit[8]urils as Excipients for Drug Solubilization and Bioavailability Enhancement of Remdesivir
Jiabin Xing
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorYong-Sheng Li
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorQihan Lin
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorYue-Yang Liu
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorQian Li
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorQiao-Yan Qi
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Lu, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorHui Wang
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Gang Zhao
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorJiaheng Zhang
Sauvage Laboratory for Smart Materials, Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorDan-Wei Zhang
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wei Zhou
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zhan-Ting Li
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Lu, Shanghai, 200032 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorJiabin Xing
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorYong-Sheng Li
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorQihan Lin
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorYue-Yang Liu
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorQian Li
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorQiao-Yan Qi
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Lu, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorHui Wang
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Gang Zhao
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorJiaheng Zhang
Sauvage Laboratory for Smart Materials, Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorDan-Wei Zhang
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wei Zhou
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zhan-Ting Li
Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2205 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Lu, Shanghai, 200032 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
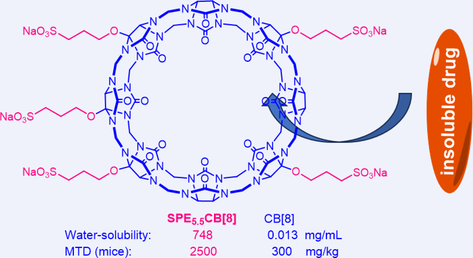
A series of sulfonatopropoxylated cucurbit[8]uril derivatives (SPECB8s) with water-solubility ranging from 344 mmol/L to 360 mmol/L have been prepared. One of the derivatives SPE5.5CB8 bearing an average of 5.5 sulfonatopropoxy side chains has been revealed to display high biocompatibility, with maximum tolerated dose being as high as 2500 mg/kg for mice. Phase solubility diagram investigations illustrate that SPE5.5CB8 can solubilize eighteen poorly soluble drugs and, for fifteen of them including remdesivir, its solubilization efficiency is higher than that of Captisol, the most widely used β-cyclodextrin-derived excipient for drug formulation. Moreover, the improved solubilization for remdesivir, which is formulated by Captisol for clinical use, can lead to important increase of its antiviral activity as compared with Captisol.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202401253-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 2.1 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Williams, H. D.; Trevaskis, N. L.; Charman, S. A.; Shanker, R. M.; Charman, W. N.; Pouton, C. W.; Porter, C. J. H. Strategies to Address Low Drug Solubility in Discovery and Development. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 315–499.
- 2 Abrantes, C. G.; Duarte, D.; Reis, C. P. An Overview of Pharmaceutical Excipients: Safe or Not Safe? J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2019–2026.
- 3 Leuner, C.; Dressman, J. Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 47–60.
- 4 Si, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhou, F.; Bai, X.; Han, L.; Sun, H.; Cha, R. Advances in polysaccharide nanocrystals as pharmaceutical excipients. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 262, 117922.
- 5 Serajuddin, A. T. M. Salt formation to improve drug solubility. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 603–616.
- 6 Stella, V. J.; Nti-Addae, K. W. Prodrug strategies to overcome poor water solubility. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 677–694.
- 7 Kovacs, T.; Nagy, P.; Panyi, G.; Szente, L.; Varga, Z.; Zakany, F. Cyclodextrins: Only Pharmaceutical Excipients or Full-Fledged Drug Candidates? Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2559.
- 8 Saokham, P.; Muankaew, C.; Jansook, P.; Loftsson, T. Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes. Molecules 2018, 23, 1161.
- 9 Stella, V. J.; Rajewski, R. A. Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 583, 119396.
- 10
A, B. Beta-Cyclodextrin as an Excipient In Drug Formulation. Asian J. Pharm. Res. Develop. 2021, 9, 122–127.
10.22270/ajprd.v9i4.1002 Google Scholar
- 11 Rekharsky, M. V.; Inoue, Y. Complexation Thermodynamics of Cyclodextrins. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1875–1918.
- 12
Howes, L. Is this a golden age of small-molecule drug discovery? C&EN 2023, 101, 28–32.
10.1021/cen-10136-cover Google Scholar
- 13 Perinelli, D. R.; Palmieri, G. F.; Cespi, M.; Bonacucina, G. Encapsulation of Flavours and Fragrances into Polymeric Capsules and Cyclodextrins Inclusion Complexes: An Update. Molecules 2020, 25, 5878.
- 14 Cram, D. J. The Design of Molecular Hosts, Guests, and Their Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1988, 27, 1009–1020.
- 15 Gu, A.; Wheate, N. J. Macrocycles as drug-enhancing excipients in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Inclusion Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2021, 100, 55–69.
- 16 Braegelman, A. S.; Webber, M. J. Integrating Stimuli-Responsive Properties in Host-Guest Supramolecular Drug Delivery Systems. Theranostics 2019, 9, 3017–3040.
- 17 Pan, Y.-C.; Hu, X.-Y.; Guo, D.-S. Biomedical Applications of Calixarenes: State of the Art and Perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 2768–2794.
- 18 Español, E. S.; Villamil, M. M. Calixarenes: Generalities and Their Role in Improving the Solubility, Biocompatibility, Stability, Bioavailability, Detection, and Transport of Biomolecules. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 90.
- 19 Zhu, H.; Li, Q.; Khalil-Cruz, L. E.; Khashab, N. M.; Yu, G.; Huang, F. Pillararene-based supramolecular systems for theranostics and bioapplications. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 688–700.
- 20 Das, D.; Assaf, K. I.; Nau, W. M. Applications of Cucurbiturils in Medicinal Chemistry and Chemical Biology. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 619.
- 21 Kuok, K. I.; Li, S.; Wyman, I. W.; Wang, R. Cucurbit[7]uril: an emerging candidate for pharmaceutical excipients. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2017, 1398, 108–119.
- 22 Macartney, D. H. Encapsulation of Drug Molecules by Cucurbiturils: Effects on their Chemical Properties in Aqueous Solution. Isr. J. Chem. 2011, 51, 600–615.
- 23 Ma, D.; Hettiarachchi, G.; Nguyen, D.; Zhang, B.; Wittenberg, J. B.; Zavalij, P. Y.; Briken, V.; Isaacs, L. Acyclic cucurbit[n]uril molecular containers enhance the solubility and bioactivity of poorly soluble pharmaceuticals. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 503–510.
- 24 Lee, J. W.; Samal, S.; Selvapalam, N.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, K. Cucurbituril Homologues and Derivatives: New Opportunities in Supramolecular Chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 621–630.
- 25 Chu, J. J.; Apps, M. G.; Wheate, N. J. Chemical factors affecting cucurbit[n]uril formulation into ocular dosage forms: excipient binding, solubility, corneal permeability and antibiotic encapsulation. Supramol. Chem. 2014, 26, 648–656.
- 26 Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Niu, Y.; Chen, X.; Lee, S. M. Y.; Wang, R. Influence of supramolecular encapsulation of camptothecin by cucurbit[7]uril: reduced toxicity and preserved anti-cancer activity. MedChemComm 2016, 7, 1392–1397.
- 27 Li, S.; Chan, J. Y.; Li, Y.; Bardelang, D.; Zheng, J.; Yew, W. W.; Chan, D. P.; Lee, S. M.; Wang, R. Complexation of clofazimine by macrocyclic cucurbit[7]uril reduced its cardiotoxicity without affecting the antimycobacterial efficacy. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 7563–7569.
- 28 Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Luo, J.; Yi, S.; Guo, T.; Liao, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhang, X. Cucurbit[7]uril-based host–guest complexes for improving bioavailability and reducing side effects of piroxicam. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 660, 124351.
- 29 Kwong, C. H. T.; Mu, J.; Li, S.; Fang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Kam, H.; Lee, S. M. Y.; Chen, Y.; Deng, F.; Zhou, X.; Wang, R. Reviving chloroquine for anti-SARS-CoV-2 treatment with cucurbit[7]uril-based supramolecular formulation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3019–3022.
- 30 Lagona, J.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Chakrabarti, S.; Isaacs, L. The Cucurbit[n]uril Family. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4844–4870.
- 31 Lazar, A. I.; Biedermann, F.; Mustafina, K. R.; Assaf, K. I.; Hennig, A.; Nau, W. M. Nanomolar Binding of Steroids to Cucurbit[n]urils: Selectivity and Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 13022–13029.
- 32 Zhou, H.; Meng, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Y. Supramolecular Combination Chemotherapy: Cucurbit[8]uril Complex Enhanced Platinum Drug Infiltration and Modified Nanomechanical Property of Colorectal Cancer Cells. Langmuir 2022, 38, 14326–14334.
- 33 Mao, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.-T.; Ma, D. Cucurbit[n]uril-based nanostructure construction and modification. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 109363.
- 34 Konda, S. K.; Maliki, R.; McGrath, S.; Parker, B. S.; Robinson, T.; Spurling, A.; Cheong, A.; Lock, P.; Pigram, P. J.; Phillips, D. R.; Wallace, L.; Day, A. I.; Collins, J. G.; Cutts, S. M. Encapsulation of Mitoxantrone within Cucurbit[8]uril Decreases Toxicity and Enhances Survival in a Mouse Model of Cancer. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 538–542.
- 35 Kim, J.; Jung, I.-S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, E.; Kang, J.-K.; Sakamoto, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kim, K. New Cucurbituril Homologues: Syntheses, Isolation, Characterization, and X-ray Crystal Structures of Cucurbit[n]uril (n = 5, 7, and 8). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 540–541.
- 36 Uzunova, V. D.; Cullinane, C.; Brix, K.; Nau, W. M.; Day, A. I. Toxicity of cucurbit[7]uril and cucurbit[8]uril: an exploratory in vitro and in vivo study. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 2037–2042.
- 37 Assaf, K. I.; Nau, W. M. Cucurbiturils: from synthesis to high-affinity binding and catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 394–418.
- 38
Wang, X.-X.; Tian, F.-Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Zhu, Q.-J.; Tao, Z. A water soluble tetramethyl-substituted cucurbit[8]uril obtained from larger intermediates? Tetrahedron 2019, 75, 130488.
10.1016/j.tet.2019.130488 Google Scholar
- 39 Liu, H.-K.; Lin, F.; Yu, S.-B.; Wu, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Qi, Q.-Y.; Cao, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.-W.; Li, Z.-T.; Ma, D. Highly Water-Soluble Cucurbit[8]uril Derivative as a Broad-Spectrum Neuromuscular Block Reversal Agent. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 16893–16901.
- 40 Jon, S. Y.; Selvapalam, N.; Oh, D. H.; Kang, J.-K.; Kim, S.-Y.; Jeon, Y. J.; Lee, J. W.; Kim, K. Facile Synthesis of Cucurbit[n]uril Derivatives via Direct Functionalization: Expanding Utilization of Cucurbit[n]uril. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 10186–10187.
- 41 Könczöl, Á.; Dargó, G. Brief overview of solubility methods: Recent trends in equilibrium solubility measurement and predictive models. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2018, 27, 3–10.
- 42 Young, B. M.; Hyatt, J. L.; Bouck, D. C.; Chen, T.; Hanumesh, P.; Price, J.; Boyd, V. A.; Potter, P. M.; Webb, T. R. Structure-activity relationships of substituted 1-pyridyl-2-phenyl-1,2-ethanediones: potent, selective carboxylesterase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8709–8715.
- 43 Jackson, S.; Agbana, P.; Kim, K. B.; Bae, Y. Effects of Organic Acids on Drug Release from Ternary Polypeptide Nanoparticles Entrapping Carfilzomib. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 1172–1177.
- 44 Bigler, L.; Spirli, C.; Fiorotto, R.; Pettenazzo, A.; Duner, E.; Baritussio, A.; Follath, F.; Ha, H. R. Synthesis and cytotoxicity properties of amiodarone analogues. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 42, 861–867.
- 45 Najlah, M.; Kadam, A.; Wan, K. W.; Ahmed, W.; Taylor, K. M.; Elhissi, A. M. Novel paclitaxel formulations solubilized by parenteral nutrition nanoemulsions for application against glioma cell lines. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 506, 102–109.
- 46 Schiller, D. S.; Fung, H. B. Posaconazole: an extended-spectrum triazole antifungal agent. Clin. Ther. 2007, 29, 1862–1886.
- 47 Eastman, R. T.; Roth, J. S.; Brimacombe, K. R.; Simeonov, A.; Shen, M.; Patnaik, S.; Hall, M. D. Remdesivir: A Review of Its Discovery and Development Leading to Emergency Use Authorization for Treatment of COVID-19. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 672–683.
- 48 Lamb, Y. N. Remdesivir: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 1355–1363.




