Halogen Modulation and Physical Property Variation in Two Novel Mixed-Cation Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Perovskites†
Xiaomei Fu
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Science and Applications of Molecular Ferroelectrics and School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211189 China
Search for more papers by this authorZining Zhou
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Science and Applications of Molecular Ferroelectrics and School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211189 China
Search for more papers by this authorYawen Yang
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Science and Applications of Molecular Ferroelectrics and School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211189 China
Search for more papers by this authorLei He
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Science and Applications of Molecular Ferroelectrics and School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211189 China
Search for more papers by this authorJie Mu
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Science and Applications of Molecular Ferroelectrics and School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211189 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qiong Ye
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Science and Applications of Molecular Ferroelectrics and School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211189 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorXiaomei Fu
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Science and Applications of Molecular Ferroelectrics and School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211189 China
Search for more papers by this authorZining Zhou
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Science and Applications of Molecular Ferroelectrics and School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211189 China
Search for more papers by this authorYawen Yang
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Science and Applications of Molecular Ferroelectrics and School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211189 China
Search for more papers by this authorLei He
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Science and Applications of Molecular Ferroelectrics and School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211189 China
Search for more papers by this authorJie Mu
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Science and Applications of Molecular Ferroelectrics and School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211189 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qiong Ye
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Science and Applications of Molecular Ferroelectrics and School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211189 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this author† Dedicated to the Special Issue of Emerging Investigators in 2024.
Comprehensive Summary
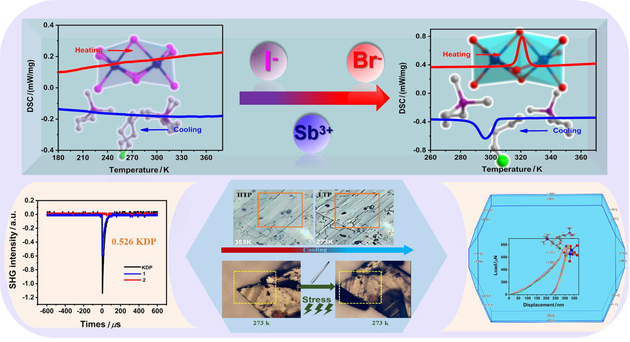
Organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites (OIHPs) offer precise control over material properties through the substitution of organic cations and halogens. In this study, two OIHPs, [(C6H10P)(n-BA)]Sb2X9 ([C6H10P]+ = [Me3PCH2CH2CH3]+, [n-BA]+ = n-butylamine cation, X = I (1), Br (2)), were synthesized by varying halogens within a mixed-cation system. The halogen substitution induced a shift from compound 1, which remains stable without phase transitions, to compound 2, which undergoes a ferroelastic phase transition (mmmF2/m). Compound 1 crystallizes in the non-centrosymmetric Pca21 space group and demonstrates a second harmonic generation (SHG) response, while compound 2 displays elasticity in nanoindentation tests. Halogen substitution alters Sb—X bond lengths, inducing structural distortions in the inorganic framework and influencing the spatial configuration of organic cations and inorganic anions. These changes lead to distinct crystallization behaviors, resulting in different physical properties for compounds 1 and 2. This work contributes to the development of multifunctional materials based on halogen regulation in mixed-cation OIHPs.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202401102-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 1.2 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Fan, C. C.; Han, X. B.; Liang, B. D.; Shi, C.; Miao, L. P.; Chai, C. Y.; Liu, C. D.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, W. Chiral Rashba Ferroelectrics for Circularly Polarized Light Detection. Adv Mater. 2022, 34, e2204119.
- 2 He, L.; Xu, K.; Shi, P. P.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, W. An Order-Disorder Type High-Temperature Multiaxial Supramolecular Ferroelectric. Adv. Electro. Mater. 2021, 8, 2100635.
- 3 Jiao, S.; Sun, X.; Zhao, M.; Chen, P.; Tang, Z.; Li, D.; Zhou, Z.; Li, T.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; et al. Halide Anions Tuning of Lead-Free Perovskite-Type Ferroelectric Semiconductors with Inverse High- Temperature Symmetry Breaking. Small 2024, 20, e2310768.
- 4 Zhang, Y.; Yu, G.; Xue, D.; Lu, J.; Meng, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; Chi, L. Construction of a High-Quality Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Heterostructure and Its Photo-response Performance. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 50–56.
- 5 Wan, M. Y.; Liu, W. F.; Luo, J. L.; Liao, J.; Wang, F. X.; Wang, L. J.; Tang, Y. Z.; Tan, Y. H. Silver/Antimony-Base Multifunctional Double Perovskite with H/F Substitution Enhance Properties. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 3083–3090.
- 6 Zhong, W. H.; Chen, H. R.; Li, Z. M.; Zhu, J. Y.; Shi, C. H.; Cao, Q. L.; Zhao, J. J.; Chen, L. Z. 1D Chiral Enantiomer Lead-Free Perovskites Induced Chiralopical Activity and Photoelectric Response. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 17985–17992.
- 7 Zhang, W.; Hong, M.; Luo, J. Centimeter-Sized Single Crystal of a One-Dimensional Lead-Free Mixed-Cation Perovskite Ferroelectric for Highly Polarization Sensitive Photodetection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 16758–16767.
- 8 Guan, Q.; You, S.; Zhu, Z. K.; Li, R.; Ye, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Ji, C.; Liu, X.; Luo, J. Three-Dimensional Polar Perovskites for Highly Sensitive Self-Driven X-Ray Detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202320180.
- 9 Li, B.; Li, H.; Wu, C.; Fu, L.; Boukhvalov, D. W.; Humphrey, M. G.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z. Unlocking Giant Third-Order Optical Nonlinearity in (MA)2CuX4 through Introducing Jahn-Teller Distortion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202406941.
- 10 Li, D.; Sun, X.; Jiao, S.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wu, Y.; Cai, H.-L.; Wu, X. A novel zero-dimensional organic–inorganic hybrid ferroelectric material. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 4267–4272.
- 11 Li, M.; Lin, J.; Wang, N.; Liu, K.; Fan, L.; Guo, Z.; Yuan, W.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Q. Synthetic-Method-Dependent Antimony Bromides and Their Photoluminescent Properties. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 15016–15022.
- 12 Mu, J.; Xu, K.; He, L.; Xu, Y.; Yin, T. J.; Men, J. T.; Ye, Q. Increasing the ferroelastic phase transition temperature of hybrid perovskites through a mixed phosphonium and ammonium cation strategy. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 1209–1212.
- 13 Wu, Y. Y.; Li, Z. Y.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Z. Y.; Cheng, H. M.; Su, H.; Hou, W. Q.; Yang, F. L.; Wu, S. Q.; Sato, O.; et al. Two-Dimensional Spin-Crossover Molecular Solid Solutions with Tunable Transition Temperatures across 90 K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 8206–8215.
- 14 Wu, Y.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Xu, G.; Dai, J.; Li, Z. Y.; Yamashita, M. Controlling Three-Step and Five-Step Spin Transitions by Polymorphism in an FeIII Spin Crossover Complex. Chin. J. Chem. 2024, 42, 879–886.
- 15 Zhang, T.; Xu, K.; Li, J.; He, L.; Fu, D.-W.; Ye, Q.; Xiong R.-G. Ferroelectric hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites and their structural and functional diversity. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwac240.
- 16 Liu, S. M.; He, L.; Wang, Y. Z.; Shi, P. P.; Ye, Q. Tunable phase transition, band gap and SHG properties by halogen replacement of hybrid perovskites [(thiomorpholinium)PbX3, X = Cl, Br, I]. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1032–1036.
- 17 Hua, X.-N.; Liao, W.-Q.; Tang, Y.-Y.; Li, P.-F.; Shi, P.-P.; Zhao, D.-W.; Xiong, R.-G. A Room-Temperature Hybrid Lead Iodide Perovskite Ferroelectric. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12296–12302.
- 18 Sun, C.; He, W. L.; Liu, M. J.; Pan, W. J.; Dong, L. F.; Chen, G.; Liu, G. D.; Lei, X. W. Zero-Dimensional Hybrid Cd-Based Perovskites with Broadband Bluish White-Light Emissions. Chem. Asian J. 2020, 15, 3050–3058.
- 19 LaFollette, D. K.; Hidalgo, J.; Allam, O.; Yang, J.; Shoemaker, A.; Li, R.; Lai, B.; Lawrie, B.; Kalinin, S.; Perini, C. A. R.; et al. Bromine Incorporation Affects Phase Transformations and Thermal Stability of Lead Halide Perovskites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 18576–18585.
- 20 Sun, Z.; Zeb, A.; Liu, S.; Ji, C.; Khan, T.; Li, L.; Hong, M.; Luo, J. Exploring a Lead-free Semiconducting Hybrid Ferroelectric with a Zero-Dimensional Perovskite-like Structure. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 11854–11858.
- 21 Zhou, Q. J.; Cao, P.; Zhou, Z. N.; Xu, K.; Yang, Y. W.; He, L.; Ye, Q. Phase Transition and Luminescent Property Change Induced by Different Organic Cations in One-Dimensional Double Perovskites. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 8846–8852.
- 22 Ju, T. Y.; Liu, C. D.; Fan, C. C.; Liang, B. D.; Chai, C. Y.; Zhang, W. Halogen Substitution Regulates High Temperature Dielectric Switch in Lead-Free Chiral Hybrid Perovskites. Chemistry 2024, 30, e202303415.
- 23 Liu, S.-X.; Han, Z.-X.; Tong, Y.-B.; Ren, X.-M. High dielectric permittivity and relaxation-induced dielectric pulsing effect-like in [1,3-bis(1-methylimidazolium) propane] [Pb2I6] crystal. J. Solid State Chem. 2024, 333, 124607.
- 24 Xu, K.; Zhou, Z. N.; Han, X. B.; Yang, Y. W.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Q. Shape Shifting and Locking in Mechanically Responsive Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Materials for Thermoelastic Actuators. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202408247.
- 25 Xu, Y.; Hu, J.; Xiao, X.; He, H.; Tong, G.; Chen, J.; He, Y. Evaporation crystallization of zero-dimensional guanidinium bismuth iodide perovskite single crystal for X-ray detection. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 494–500.
- 26 He, L.; Xu, K.; Shi, P.-P.; Liu, Z.-B.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Q. A rare 3D hybrid bimetal halide ferroelectric: (3-Hydroxypyrrolidinium)2RbBiBr6. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 2879–2883.
- 27 Luo, W.; Wu, L. K.; Shen, H. Y.; Li, H. K.; Xu, Z. J.; Shi, C.; Ye, H. Y.; Miao, L. P.; Wang, N. Halogen-Regulated Tc and X-ray Radiation Detection in 2D Hybrid Perovskite Ferroelastic Semiconductor. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 3913–3920.
- 28 Xu, K.; Zhou, Z.; Men, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ye, Q. A three-dimensional Mn(II) coordination polymer with ferroelasticity obtained by introducing coligands to form novel networks. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 5064–5070.
- 29 Xu, Y.; Xu, K.; He, L.; Yin, T. J.; Mu, J.; Men, J. T.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Q. Influence of Pd (II) Adsorption on High-Temperature Ferroelastic Phase Transition in (2-Amino-2-thiazolinium) PbBr3. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 1279–1285.
- 30 Cao, P.; Liu, Y. T.; Men, J. T.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, W.; He, L.; Ye, Q. Dimension-Dependent Phase Transitions, Ferroelasticity, and Photoluminescence in Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Materials. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 16898–16904.
- 31 Cao, Y. J.; Zhou, L.; Shi, P. P.; Ye, Q.; Fu, D. W. H/F substituted perovskite compounds with above-room-temperature ferroelasticity: [(CH3)4P] [Cd (SCN)3] and [(CH3)3PCH2F] [Cd (SCN)3]. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 8418–8421.
- 32 Huang, X. Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Gan, T.; Xu, Z. K.; Wang, Z. X. A Photoluminescent Lead Bromide Hybrid Perovskite Molecular Ferroelastic Semiconductor with Sequential High-Tc Phase Transitions. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 5221–5227.
- 33 He, L.; Zhou, L.; Shi, P.-P.; Ye, Q.; Fu, D.-W. One-Dimensional Cadmium Thiocyanate Perovskite Ferroelastics Tuned by Halogen Substitution. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 10236–10242.
- 34 Yin, T.-J.; Xu, K.; He, L.; Meng, X.; Xu, Y.; Men, J.-T.; Mu, J.; Ye, Q.; Shi, P.-P. Templating Influence of Regulated Inorganic Framework in Two-Dimensional Ferroelastic Perovskites: (C3H5CH2NH3)2[MCl4] (M = Mn and Cd). Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202203606.
- 35 Tu, Q.; Spanopoulos, I.; Hao, S.; Wolverton, C.; Kanatzidis, M. G.; Shekhawat, G. S.; Dravid, V. P. Out-of-Plane Mechanical Properties of 2D Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Perovskites by Nanoindentation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 22167–22173.
- 36 Umoh, G. V.; Gómez-Ovalle, A. E.; Cruz, M. P.; Leal-Pérez, J. E.; Obot, O. U.; Berrio, H. U.; Herrera-Basurto, R.; Mercader-Trejo, F.; Hurtado-Macias, A. Nanomechanical-ferroelastics behavior, and the low-temperature ferroelectric manifestation of BiMnO3 thin films. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 035962.
- 37 Varughese, S.; Kiran, M. S.; Ramamurty, U.; Desiraju, G. R. Nanoindentation in crystal engineering: quantifying mechanical properties of molecular crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2701–2712.
- 38 Liu, Y.; Varghese, S.; Ma, J.; Yoshino, M.; Lu, H.; Komanduri, R. Orientation effects in nanoindentation of single crystal copper. Int. J. Plasticity 2008, 24, 1990–2015.
- 39 Beake, B.-D.; Goel, S. Incipient plasticity in tungsten during nanoindentation: Dependence on surface roughness, probe radius and crystal orientation. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 75, 63–69.
- 40 Ji, L.-J.; Sun, S.-J.; Qin, Y.; Li, K.; Li, W. Mechanical properties of hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 391, 15–29.
- 41 Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Huang, J.; Wei, Y. Ferroelastic deformation mechanism and mechanical properties of [001]- oriented YSZ film by indentation. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 889, 161557.
- 42 Sun, S.; Fang, Y.; Kieslich, G.; White, T. J.; Cheetham, A. K. Mechanical properties of organic–inorganic halide perovskites, CH3NH3PbX3 (X = I, Br and Cl), by nanoindentation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 18450–18455.
- 43 Tan, J. C.; Jain, P.; Cheetham, A. K. Influence of ligand field stabilization energy on the elastic properties of multiferroic MOFs with the perovskite architecture. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 3949–3952.
- 44 Gao, H.; Wei, W.; Li, L.; Tan, Y.; Tang, Y. Mechanical Properties of a 2D Lead-Halide Perovskite, (C6H5CH2NH3)2PbCl4, by Nanoindentation and First-Principles Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 19204–19211.
- 45 Sun, D.-F.; Wang, D.-L.; Chen, H.-Z.; Hou, R.-X.; Dang, Y.-Y.; Wu, K.; Wang, J.-Y.; Shen, C.-Y. New Low-Dimensional Lead-Free Perovskite (2-AMP)2BiX7·H2O (X = Cl, Br) Crystals: Synthesis, Stability, and Nonlinear Optical Properties. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 15247–15255.
- 46 He, W.-X.; Chen, C.-J.; Wu, S.-Y.; Wong, W.-P.-D.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Chang, K.; Wang, J.; Gao, H.; Loh, P.-K. Dion–Jacobson Perovskites with a Ferroelectrically Switchable Chiral Nonlinear Optical Response. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024.




