Induced Absolute Configuration of Achiral Tetradentate Ligands in Metal–Organic Frameworks for Circularly Polarized Luminescence
Hong-Ru Fu
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Luoyang Normal University, Luoyang, Henan, 471934 China
State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350002 China
Search for more papers by this authorDan-Dan Ren
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Luoyang Normal University, Luoyang, Henan, 471934 China
College of Materials & Chemical Engineering, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, Hubei, 443002 China
Search for more papers by this authorKun Zhang
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Luoyang Normal University, Luoyang, Henan, 471934 China
College of Materials & Chemical Engineering, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, Hubei, 443002 China
Search for more papers by this authorHong Chen
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Luoyang Normal University, Luoyang, Henan, 471934 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaoyan Lu
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Luoyang Normal University, Luoyang, Henan, 471934 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qing-Rong Ding
State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350002 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Lu-Fang Ma
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Luoyang Normal University, Luoyang, Henan, 471934 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorHong-Ru Fu
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Luoyang Normal University, Luoyang, Henan, 471934 China
State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350002 China
Search for more papers by this authorDan-Dan Ren
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Luoyang Normal University, Luoyang, Henan, 471934 China
College of Materials & Chemical Engineering, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, Hubei, 443002 China
Search for more papers by this authorKun Zhang
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Luoyang Normal University, Luoyang, Henan, 471934 China
College of Materials & Chemical Engineering, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, Hubei, 443002 China
Search for more papers by this authorHong Chen
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Luoyang Normal University, Luoyang, Henan, 471934 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaoyan Lu
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Luoyang Normal University, Luoyang, Henan, 471934 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qing-Rong Ding
State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350002 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Lu-Fang Ma
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Luoyang Normal University, Luoyang, Henan, 471934 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
The crystallization of chiral molecules is of great significance to understand the origin and evolution of hierarchical chirality and reveal the relationships between structural chirality and circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) activity. Here, we report two pairs of chiral metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) (DCF-17/LCF-17, DCF-18/LCF-18) by utilizing tetradentate ligands tetra(3-imidazoylphenyl)ethylene (TIPE) and 4,4'-[4',5'-bis[4-(4-pyridinyl)phenyl][1,1':2',1”-terphenyl]-4,4”-diyl]bis[pyridine] (TPPP) as linkers. It can be observed that the spontaneous resolution of the achiral ligands is converted into the induced resolution, and the ligands form the absolute configuration by using enantiopure camphoric acid (cam) as chiral induced reagent (CIR). As a result, the racemate MOFs can be driven to generate absolute homochiral crystallization. Another two achiral MOFs [Cd(D-cam)(TPPP)0.5] (AF-1, AF = achiral framework) and [Cd(L-cam)(TPPP)0.5] (AF-2) were prepared. The position disorder of D/L-cam skeleton causes the generation of nonchiralization, further leading to disappearance of symmetry breaking of TPPP. For the perspective of structure, this is the first report which reveals the chiral transfer and nonchiralization between chiral induced agents and tetradentate ligands. Besides, DCF-17 and LCF-17 show CPL with luminescence dissymmetry factor (glum) of –1.0 × 10-2 and +9.2 × 10–3, respectively. This work provides the useful evidences to reveal the induced chiral crystallization and the construction of CPL-active crystalline materials.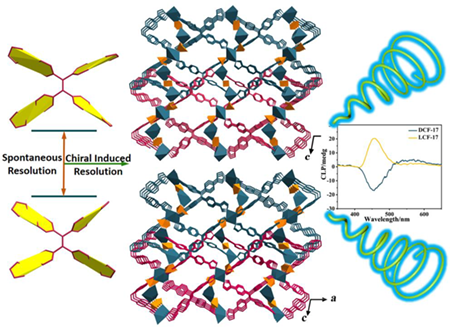
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300645-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 2.6 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1(a) Sharifzadeh, Z.; Berijani, K.; Morsali, A. Chiral metal–organic frameworks based on asymmetric synthetic strategies and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 214083; (b) Dybtsev, D. N.; Bryliakov, K. P. Asymmetric catalysis using metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 437, 213845; (c) Gong, W.; Chen, Z.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y. Chiral Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 9078–9144.
- 2(a) Gu, Z.; Zhan, C.; Zhang, J.; Bu, X. Chiral chemistry of metal–camphorate frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3122–3144; (b) Cheng, Q.; Ma, Q.; Pei, H.; Liang, H.; Zhang, X.; Jin, X.; Liu, N.; Guo, R.; Mo, Z. Chiral metal-organic frameworks materials for racemate resolution. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 484, 215120; (c) Liu, J.; Mukherjee, S.; Wang, F.; Fischer, R. A.; Zhang, J. Homochiral metal–organic frameworks for enantioseparation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5706–5745.
- 3(a) Zheng, A.; Zhao, T.; Jin, X.; Miao, W.; Duan, P. Circularly polarized luminescent porous crystalline nanomaterials. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 1123–1135;
(b) Gao, P.; Zhang, K.; Ren, D.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Fu, H.; Ma, L.; Li, D. Host-Guest Chemistry of Chiral MOFs for Multicolor Circularly Polarized Luminescence Including Room Temperature Phosphorescence. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 41, 2300105;
10.1002/adfm.202300105 Google Scholar(c) Wang, J. Y.; Si, Y.; Luo, X. M.; Wang, Z. Y.; Dong, X. Y.; Luo, P.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C.; Zang, S. Q. Stepwise Amplification of Circularly Polarized Luminescence in Chiral Metal Cluster Ensembles. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2207660.
- 4(a) Berijani, K.; Chang, L.; Gu, Z. G. Chiral templated synthesis of homochiral metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 474, 214852; (b) Cucinotta, A.; Kahlfuss, C.; Minoia, A.; Eyley, S.; Zwaenepoel, K.; Velpula, G.; Thielemans, W.; Lazzaroni, R.; Bulach, V.; Hosseini, W.; Mali, K. S.; De Feyter, S. Metal Ion and Guest-Mediated Spontaneous Resolution and Solvent-Induced Chiral Symmetry Breaking in Guanine-Based Metallosupramolecular Networks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 1194–1205; (c) Han, Z.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Z.; Ni, Y.; Xie, W.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, J.; Cheng, P.; Shi, W. High-Efficiency Lithium-Ion Transport in a Porous Coordination Chain-Based Hydrogen-Bonded Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 10149–10158;
- 5(a) Bisht, K. K.; Suresh, E. Spontaneous Resolution to Absolute Chiral Induction: Pseudo-Kagomé Type Homochiral Zn(II)/Co(II) Coordination Polymers with Achiral Precursors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15690–15693; (b) Wu, D.; Zhou, K.; Tian, J.; Liu, C.; Tian, J.; Jiang, F.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Hong, M. Induction of Chirality in a Metal–Organic Framework Built from Achiral Precursors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3087–3094; (c) Gao, X. J. Wu, T. T.; Ge, F. Y.; Lei, M. Y.; Zheng, H. G. Regulation of Chirality in Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) Based on Achiral Precursors through Substituent Modification. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 18335–18339.
- 6(a) Zhang, S. Y.; Li, D.; Guo, D.; Zhang, H.; Shi, W.; Cheng, P.; Wojtas, L.; Zaworotko, M. J. Synthesis of a Chiral Crystal Form of MOF-5, CMOF-5, by Chiral Induction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15406–15409; (b) Evans, J. D.; Coudert, F. X. Microscopic Mechanism of Chiral Induction in a Metal–Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6131–6134.
- 7(a) Tan, C.; Han, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y. Controlled exchange of achiral linkers with chiral linkers in Zr-based UiO-68 metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 16229–16236; (b) Han, Z.; Shi, W.; Cheng, P. Synthetic strategies for chiral metal-organic frameworks. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 819–822.
- 8(a) Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Zingiryan, A.; Bu, X. Integrated Molecular Chirality, Absolute Helicity, and Intrinsic Chiral Topology in Three-Dimensional Open-Framework Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 17246–17247; (b) Bi, M.; Hong, Q.; Liu, M.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. Chiral induction in boron imidazolate frameworks: the construction of cage-based absolute helices. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 5020–5023; (c) Luo, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Eddaoudi, M. Host–Guest Chirality Interplay: A Mutually Induced Formation of a Chiral ZMOF and Its Double-Helix Polymer Guests. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 786–789.
- 9 Buhse, T.; Cruz, J.; Noble-Terán, M. E.; Hochberg, D.; Ribó, J. M.; Crusats, J.; Micheau, J. Spontaneous Deracemizations. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 2147–2229.
- 10 Gong, Z. L.; Li, Z. Q.; Zhong, Y. W. Circularly polarized luminescence of coordination aggregates. Aggregate 2022, 3, e177.
- 11 Qu, L.; Zhou, X.; Song, J.; Zhang, B.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Xiang, H. Circularly Polarized Luminescence Switching, Chirality Self-Sorting, and Cell Imaging of Chiral Rhodamine Dyes. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2300779.
- 12 MacKenzie, L. E.; Pal, R. Circularly polarized lanthanide luminescence for advanced security inks. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 109–124.
- 13 Longhi, G.; Castiglioni, E.; Koshoubu, J.; Mazzeo, G.; Abbate, S. Circularly Polarized Luminescence: A Review of Experimental and Theoretical Aspects. Chirality 2016, 28, 696–707.
- 14(a) Sugimoto, M.; Liu, X. L.; Tsunega, S.; Nakajima, E.; Abe, S.; Nakashima, T.; Kawai, T.; Jin, R. H.Circularly polarized luminescence from inorganic materials: encapsulating guest lanthanide oxides in chiral silica hosts. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 6519–6524; (b) Deng, M.; Schley, N. D.; Ung, G. High circularly polarized luminescence brightness from analogues of Shibasaki's lanthanide complexes. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 14813–14816; (c) Carr, R.; Evans, N. H.; Parker, D. Lanthanide complexes as chiral probes exploiting circularly polarized luminescence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7673–7686; (d) Okayasu, Y.; Yuasa, J. Evaluation of circularly polarized luminescence in a chiral lanthanide ensemble. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2018, 3, 66–72; (e) Zhu, Q. Y.; Zhou, L. P.; Cai, L. X.; Li, X. Z.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Q. F. Chiral auxiliary and induced chiroptical sensing with 5d/4f lanthanide–organic macrocycles. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 2861–2864.
- 15(a) Yang, X.; Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Duan, P. Photon-upconverting chiral liquid crystal: significantly amplified upconverted circularly polarized luminescence. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 172–178; (b) Lu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Ni, B.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Tuning the circularly polarized luminescence of polymer-stabilized cholesteric liquid crystal films using chiral dopants. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 8246–8253; (c) Hou, J.; Toyoda, R.; Meskers, S. C. J.; Feringa, B. L. Programming and Dynamic Control of the Circular Polarization of Luminescence from an Achiral Fluorescent Dye in a Liquid Crystal Host by Molecular Motors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202206310; (d) Chen, H.; Guo, S.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, S.; Liao, Y.; Shen, J.; Hou. J. T. A stable NIR fluorescent probe for imaging lipid droplets in cells and tumors. Sensor Actuat. B-Chem. 2024, 398, 134740; (e) Chen, Y.; Lu, P.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, H. Preparation and property manipulation of high efficiency circularly polarized luminescent liquid crystal polypeptides. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 13632–13641.
- 16(a) Hong, J.; Kim, S.; Park, G.; Lee, Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, T.; Kim, C.; You, Y. Chiral polymer hosts for circularly polarized electroluminescence devices. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 8668–8681; (b) Kumar, J.; Marydasan, B.; Nakashima, T.; Kawai, T.; Yuasa, J. Chiral supramolecular polymerization leading to eye differentiable circular polarization in luminescence. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 9885–9888; (c) Ryu, N.; Harada, T.; Okazaki, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Shirosaki, T.; Oda, R.; Kuwahara, Y.; Takafuji, M.; Ihara, H.; Nagaoka, S. Co-assembling system that exhibits bright circularly polarized luminescence. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 3123–3127; (d) Kumar, J.; Marydasan, B.; Nakashima, T.; Kawai, T.; Yuasa, J. Chiral supramolecular polymerization leading to eye differentiable circular polarization in luminescence. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 9885–9888; (e) Xu, C.; Yin, C.; Wu, W.; Ma, X. Tunable room- temperature phosphorescence and circularly polarized luminescence encoding helical supramolecular polymer. Sci. Chi. Chem. 2022, 65, 75–81; (f) Greciano, E. E.; Rodríguez, R.; Maeda, K.; Sánchez, L. Disclosing chirality in consecutive supramolecular polymerizations: chiral induction by light in N-annulated perylenetetracarboxamides. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 2244–2247.
- 17 Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.; Han, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Tang, Z. Circularly polarized luminescence in chiral materials. Matter 2022, 5, 837–875.
- 18(a) Fu, H. R.; Jiang, Y. Y.; Luo, J. H.; Li, T. A Robust Heterometallic Cd(II)/Ba(II)-Organic Framework with Exposed Amino Group and Active Sites Exhibiting Excellent CO2/CH4 and C2H2/CH4 Separation. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2203287–2203292; (b) Fu, H. R.; Zhang, K.; Li, T.; Ren, D. D.; Zhu, X. L. Synthesis of isophthalic acid-carbazole coordination polymers with stacking-dependent ultralong room temperature phosphorescence and white-light emission. J. Solid State Chem. 2023, 326, 124216; (c) Mingabudinova, L. R.; Vinogradov, V. V.; Milichko, V. A.; Hey-Hawkins, E.; Vinogradov, A. V. Metal–organic frameworks as competitive materials for non-linear optics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5408–5431; (d) Cao, F. Y.; Liu, H. H.; Mu, Y.; Xue, Z. Z.; Li, J. H.; Wang, G. M. Enabling Dual Phosphorescence by Locating a Flexible Ligand in Zn-Based Hybrid Frameworks. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 6975–6980; (e) Jin, J.; Xue, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y. Y. Recent progresses in luminescent metal–organic frameworks (LMOFs) as sensors for the detection of anions and cations in aqueous solution. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 1950–1972.
- 19(a) Zhai, R.; Zhu, Y.; Chang, L.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, J. Layer-by-Layer Grafting Dye on Chiral MOF Thin Films for Circularly Polarized Luminescence. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2209074–2209079; (b) Zhang, C.; Yan, Z.; Dong, X.; Han, Z.; Li, S.; Fu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Niu, Y.; Zang, S. Enantiomeric MOF Crystals Using Helical Channels as Palettes with Bright White Circularly Polarized Luminescence. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002914; c Evans, J. D.; Coudert, F. X. Microscopic Mechanism of Chiral Induction in a Metal–Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6131–6134; d Shen, S. H.; Liu, Y. J.; Wang, S. T.; Fang, W. H.; Zhang, J. Chiral Induction in Aluminum Oxo Sulfate Helical Chains. Cryst. Growth Des. 2022, 22, 3954–3960; e Bi, M. Y.; Hong, Q.; L.; Liu, M.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H. X.; Zhang, J. Chiral induction in boron imidazolate frameworks: the construction of cage-based absolute helices. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 5020–5023; f Gheorghe, A.; Strudwick, B.; Dawson, D. M.; Ashbrook, S. E.; Woutersen, S.; Dubbeldam, D.; Tanase, S. Synthesis of Chiral MOF-74 Frameworks by Post-Synthetic Modification by Using an Amino Acid. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 13957–13965; g Han, Z.; Shi, W.; Cheng, P. Synthetic strategies for chiral metal-organic frameworks. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 819–822.
- 20 Wang, X.; Zhou, C.; Zheng, J.; Lian, Z.; Sun, M.; Huang, Y.; Luo, D.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X. Highly Boosting Circularly Polarized Luminescence of Chiral Metal–Imidazolate Frameworks. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2207333.
- 21 Gao, P.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, M.; Li, T.; Fu, H.; Ma, L.; Li, D. Pillar-Layer Chiral MOFs as a Crystalline Platform for Circularly Polarized Luminescence and Single-Phase White-Light Emission. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 16435–16444.
- 22(a) Sharifzadeh, Z.; Razavi, S. A. A.; Morsali, A. Construction of hierarchically chiral metal–organic frameworks for fast and mild asymmetric catalysis. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 8661–8678; (b) Tay, H. M.; Kyratzis, N.; Thoonen, S.; Boer, S. A.; Turner, D. R.; Hua, C. Synthetic strategies towards chiral coordination polymers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 435, 213763.
- 23(a) Bradshaw, D.; Prior, T. J.; Cussen, E. J.; Claridge, J. B.; Rosseinsky, M. J. Permanent microporosity and enantioselective sorption in a chiral open framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 6106–6114; (b) Gao, X. J.; Wu, T. T.; Ge, F. Y.; Lei, M. Y.; Zheng, H. G. Regulation of Chirality in Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) Based on Achiral Precursors through Substituent Modification. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 18335–18339; (c) Wu, D.; Zhou, K.; Tian, J.; Liu, C.; Tian, J.; Jiang, F.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Hong, M. Induction of Chirality in a Metal–Organic Framework Built from Achiral Precursors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3087−3094.
- 24(a) Hall, L. A.; D'Alessandro, D. M.; Lakhwani, G. Chiral metal–organic frameworks for photonics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 3567–3590; (b) Zhu, Y. Q.; Wang, X. H.; Wu, M. X. Intriguing Room Temperature Phosphorescence in Crystalline Porous Organic Frameworks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2308096.
- 25 Spek, A. L. PLATON SQUEEZE: A Tool for the Calculation of the Disordered Solvent Contribution to the Calculated Structure Factors. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C: Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 9−18.
- 26(a) Fu, H. R.; Wang, N.; Wu, X. X.; Li, F. F.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, L. F.; Du, M. Circularly Polarized Room-Temperature Phosphorescence and Encapsulation Engineering for MOF-Based Fluorescent/Phosphorescent White Light-Emitting Devices. Adv. Optical Mater. 2020, 8, 2000330; (b) Sinha, N.; Stegemann, L.; Tan, T.; Doltsinis, N.; Strassert, C.; Hahn, F. Turn-On Fluorescence in Tetra-NHC Ligands by Rigidification through Metal Complexation: An Alternative to Aggregation-Induced Emission. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2785−2789.
- 27 Riehl, J. P.; Richardson, F. S. Circularly Polarized Luminescence Spectroscopy. Chem. Rev. 1986, 86, 1−16.




