Balancing and Therapeutic Roles of CXCR4-Inhibiting Nanomedicine via Synergetic Regulation of Hepatic Stellate Cells and Extracellular Matrix in Liver Injury†
Xu Huan
School of Pharmacy, Medical School, Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, 226001 China
Search for more papers by this authorYi Chen
School of Pharmacy, Medical School, Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, 226001 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaozhen Wu
School of Pharmacy, Medical School, Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, 226001 China
Search for more papers by this authorHui Wang
School of Pharmacy, Medical School, Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, 226001 China
Search for more papers by this authorYing Yang
School of Pharmacy, Medical School, Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, 226001 China
Search for more papers by this authorPengkai Wu
Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, 230022 China
Search for more papers by this authorTianqing Liu
NICM Health Research Institute, Western Sydney University, Sydney, NSW, 2145 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Kaikai Wang
School of Pharmacy, Medical School, Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, 226001 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dan Ding
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical Biology, Key Laboratory of Bioactive Materials, Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorXu Huan
School of Pharmacy, Medical School, Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, 226001 China
Search for more papers by this authorYi Chen
School of Pharmacy, Medical School, Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, 226001 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaozhen Wu
School of Pharmacy, Medical School, Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, 226001 China
Search for more papers by this authorHui Wang
School of Pharmacy, Medical School, Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, 226001 China
Search for more papers by this authorYing Yang
School of Pharmacy, Medical School, Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, 226001 China
Search for more papers by this authorPengkai Wu
Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, 230022 China
Search for more papers by this authorTianqing Liu
NICM Health Research Institute, Western Sydney University, Sydney, NSW, 2145 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Kaikai Wang
School of Pharmacy, Medical School, Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, 226001 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dan Ding
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical Biology, Key Laboratory of Bioactive Materials, Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the Special Issue of Emerging Themes in Polymer Science.
Comprehensive Summary
Inflammation is associated with different stages of liver disease, including acute injury, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatoma. During the progression of liver inflammation, activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition are critical pathologies, and thus the combined therapy using HSCs and ECM as targets represents a promising strategy in the treatment of liver injury. Here, a novel CXCR4-inhibiting nanomedicine that can simultaneously deliver AMD3100 (CXCR4 antagonist) and siPAI-1 (siRNA of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1) was designed and developed to reverse liver fibrosis by inhibiting HSCs activation and degrading ECM deposition. With this goal in mind, a Zn(II) coordinated polymeric AMD3100 named PAMD/Zn polymer with siRNA delivery and CXCR4 antagonism capabilities was synthesized. Overall, our results suggest that PAMD/Zn recruits pro-inflammatory cells for fibrogenesis and inhibits the activation of HSCs for fibrolysis at various stages of liver injury. Its use in conjunction with PAI-1 silencing achieved satisfactory therapeutic efficacy in liver injury and fibrosis. The derivative CXCR4-inhibiting nanomedicine is a versatile platform that offers valuable benefits for the treatment of liver diseases.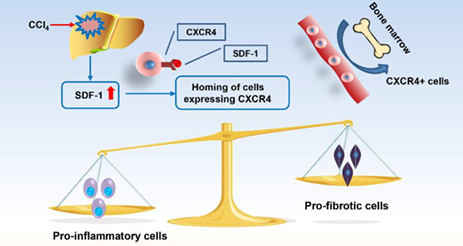
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300217-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 621.9 KB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Wang, J.; Tannous, B. A.; Poznansky, M. C.; Chen, H. CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 (plerixafor): From an impurity to a therapeutic agent, Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 105010.
- 2 Wilson, G. C.; Freeman, C. M.; Kuethe, J. W.; Rd, Q. R.; Nojima, H.; Schuster, R.; Blanchard, J.; Edwards, M. J.; Caldwell, C. C.; Lentsch, A. B. CXC Chemokine Receptor 4 Signaling Limits Hepatocyte Proliferation After Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion in Mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastr. L. 2015, 308, G702– G709.
- 3 Saiman, Y.; Jiao, J.; Fiel, M. I.; Friedman, S. L.; Aloman, C.; Bansal, M. B. Inhibition of the CXCL12/CXCR4 chemokine axis with AMD3100, a CXCR4 small molecule inhibitor, worsens murine hepatic injury. Hepatol. Res. 2015, 45, 794–803.
- 4 Wang, H.; Mehal, W.; Nagy, L. E.; Rotman, Y. Immunological mechanisms and therapeutic targets of fatty liver diseases, Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 73–91.
- 5 Chen, C.; Ni, X.; Jia, S.; Liang, Y.; Wu, X.; Kong, D.; Ding, D. Massively Evoking Immunogenic Cell Death by Focused Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress Using an AIE Luminogen with a Twisted Molecular Structure. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1904914.
- 6 Ma, J. Y.; Wang, Y. X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y. X.; Kong, D. M. Chemical–biological approaches for the direct regulation of cell–cell aggregation. Aggregate 2022, 3, e166.
- 7 Biasci, D.; Smoragiewicz, M. CXCR4 inhibition in human pancreatic and colorectal cancers induces an integrated immune response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2020, 117, 28960–28970.
- 8 Correia, A. L.; Guimaraes, J. C. Hepatic stellate cells suppress NK cell-sustained breast cancer dormancy. Nature 2021, 594, 566–571.
- 9 Shi, J.; Yang, Y.; Yin, N.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K. Engineering CXCL12 Biomimetic Decoy-Integrated Versatile Immunosuppressive Nanoparticle for Ischemic Stroke Therapy with Management of Overactivated Brain Immune Microenvironment. Small Methods 2022, 6, e2101158.
- 10 Liu, T.; Li, X.; You, S.; Bhuyan, S. S.; Dong, L. Effectiveness of AMD3100 in treatment of leukemia and solid tumors: from original discovery to use in current clinical practice. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 5, 1–11.
- 11 Grommes, J.; Soehnlein, O. Contribution of neutrophils to acute lung injury. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 293–307.
- 12 Maharjan, S.; Cecen, B.; Zhang, Y. S. 3D Immunocompetent Organ-on-a-Chip Models. Small Methods 2020, 4, 2000235.
- 13 Monteiro, M. V.; Gaspar, V. M.; Mendes, L.; Duarte, I. F.; Mano, J. F. Stratified 3D Microtumors as Organotypic Testing Platforms for Screening Pancreatic Cancer Therapies. Small Methods 2021, 5, e2001207.
- 14 Qi, J.; Ou, H.; Liu, Q.; Ding, D. Gathering brings strength: How organic aggregates boost disease phototheranostics. Aggregate 2021, 2, 95–113.
- 15 Wu, P.; Luo, X.; Sun, M.; Sun, B.; Sun, M. Synergetic regulation of kupffer cells, extracellular matrix and hepatic stellate cells with versatile CXCR4-inhibiting nanocomplex for magnified therapy in liver fibrosis. Biomaterials 2022, 284, 121492.
- 16 Zhou, T.; Liu, J. ESE3/EHF, a promising target of rosiglitazone, suppresses pancreatic cancer stemness by downregulating CXCR4. Gut 2022, 71, 357–371.
- 17 Li, Z.; Chen, G.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Sun, M.; Oupicky, D. Increased Survival by Pulmonary Treatment of Established Lung Metastases with Dual STAT3/CXCR4 Inhibition by siRNA Nanoemulsions. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 2100–2110.
- 18 Jin, G.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ou, H.; Xu, F.; Ding, D. Polymeric Nitric Oxide Delivery Nanoplatforms for Treating Cancer, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Infection. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2001550.
- 19 Sun, M.; Wang, K.; Oupický, D. Advances in Stimulus-Responsive Polymeric Materials for Systemic Delivery of Nucleic Acids. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701070.
- 20 Song, J.; Jia, X.; Ariga, K. Methods with Nanoarchitectonics for Small Molecules and Nanostructures to Regulate Living Cells. Small Methods 2020, 4, 2000500.
- 21 Cheng, Y. Design of Polymers for Intracellular Protein and Peptide Delivery. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 1443–1449.
- 22 Lv, J.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yu, H.; Tang, Z. A Novel Vascular Disrupting Agents Noncovalent Polymeric Nanomedicine: Significantly Increased Antitumor Therapeutic Efficiency. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 1447–1456.
- 23 Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Hazeldine, S. T.; Li, C.; Oupicky, D. Dual-function CXCR4 antagonist polyplexes to deliver gene therapy and inhibit cancer cell invasion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8740–8743.
- 24 Sun, J.; Yang, J.; Ding, J. Controlled Synthesis of Polymers. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 1235–1248.
- 25 Ming, Y.; Xia, Y.; Ma, G. Aggregating particles on the O/W interface: Tuning Pickering emulsion for the enhanced drug delivery systems. Aggregate 2022, 3, e162.
- 26 Zhang, L.; Ding, D. Recent advances of transition Ir(III) complexes as photosensitizers for improved photodynamic therapy. View 2021, 2, 20200179.
- 27 Zhang, Y. R.; Meng, B. W.; Hao, B.; Ma, P. C. Aggregation-induced demulsification triggered by the hydrophilic fabric for the separation of highly emulsified oil droplets from water. Aggregate 2022, 3, e131.
- 28 Pearce, H. A.; Kim, Y. S.; Watson, E.; Bahrami, K.; Smoak, M. M.; Jiang, E. Y.; Elder, M.; Shannon, T. A. G. Mikos, Development of a modular, bio-compatible thiolated gelatin microparticle platform for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications. Regen. Biomater. 2021, 8, rbab012.
- 29 Chen, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Chen, S.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Ding, D.; Tang, B. Z. Taming Reactive Oxygen Species: Mitochondria-Targeting Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen for Neuron Protection via Photosensitization-Triggered Autophagy. CCS Chem. 2022, 4, 2249–2257.
- 30 Chen, M.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Tang, Y.; Ding, D. Strategies in boosting photo-sensitization for biomedical applications. Sci. China Chem. 2022, 65, 647–649.
- 31 Duan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, X.; Yue, X.; Geng, Y.; Shen, J.; Ding, D. Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticles with Intramolecular Motion-Induced Photothermy for Tumor Phototheranostics and Tooth Root Canal Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2200179.
- 32 Qi, J.; Jia, S.; Kang, X.; Wu, X.; Hong, Y.; Shan, K.; Kong, X.; Wang, Z.; Ding, D. Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticles with Surface-Mimicking Protein Secondary Structure as Lysosome-Targeting Chimaeras for Self-Synergistic Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2203309.
- 33 Zhao, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, W.; Wang, F.; Du, L.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, Y.; He, X.; Cai, Y.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Gao, X.; Sun, P.; Phillips, D. L.; Ding, D.; Tang, B. Z. Highly efficient photothermal nanoagent achieved by harvesting energy via excited-state intramolecular motion within nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 768.
- 34 Cooksey, C. Quirks of dye nomenclature. 1. Evans blue. Biotech. Histochem. 2014, 89, 111–113.
- 35 Wang, C.; Ma, C.; Fu, K.; Gong, L. H.; Zhang, Y. F.; Zhou, H. L.; Li, Y. X. Phillygenin Attenuates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis via Modulating Inflammation and Gut Microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 756924.
- 36 Wu, X.; Qian, L.; Zhao, H.; Lei, W.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, R.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Y. CXCL12/CXCR4: an amazing challenge and opportunity in the fight against fibrosis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 83, 101809.
- 37 Gentilini, A.; Rombouts, K.; Galastri, S.; Caligiuri, A.; Mingarelli, E.; Mello, T.; Marra, F.; Mantero, S.; Roncalli, M.; Invernizzi, P.; Pinzani, M. Role of the stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)-CXCR4 axis in the interaction between hepatic stellate cells and cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 813–820.
- 38 Hong, F.; Tuyama, A.; Lee, T. F.; Loke, J.; Agarwal, R.; Cheng, X.; Garg, A.; Fiel, M. I.; Schwartz, M.; Walewski, J.; Branch, A.; Schecter, A. D.; Bansal, M. B. Hepatic stellate cells express functional CXCR4: role in stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha-mediated stellate cell activation. Hepatology 2009, 49, 2055–2067.
- 39 Zhang, W. S.; Zhang, R.; Ge, Y.; Wang, D.; Hu, Y.; Qin, X.; Kan, J.; Liu, Y. S100a16 deficiency prevents hepatic stellate cells activation and liver fibrosis via inhibiting CXCR4 expression. Metabolism 2022, 135, 155271.
- 40 Liepelt, A.; Tacke, F. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) as a target in liver diseases. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastr. L. 2016, 311, G203.
- 41 Xiang, Z. L.; Zeng, Z. C.; Tang, Z. Y.; Fan, J.; Zhuang, P. Y.; Liang, Y.; Tan, Y. S.; He, J. Chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma patients increases the risk of bone metastases and poor survival. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 176.
- 42 Luo, P.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, F.; Wong, Y. K.; Xia, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Tian, Y.; Yang, C.; Dai, L.; Shen, H. M.; Wang, J. Celastrol induces ferroptosis in activated HSCs to ameliorate hepatic fibrosis via targeting peroxiredoxins and HO-1. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2300–2314.
- 43 Yuan, S.; Wei, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Cai, S.; Fang, L. Sorafenib attenuates liver fibrosis by triggering hepatic stellate cell ferroptosis via HIF-1α/SLC7A11 pathway. Cell Prolif. 2022, 55, e13158.
- 44 Guo, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, S.; Jing, D.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, K.; Xu, J.-J. Construction of Nanocarriers Based on Endogenous Cell Membrane and Their Application in Nanomedicine. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 1623–1640.
- 45 Wang, Y.; Lei, C.; Lin, D. Environmental Behaviors and Biological Effects of Engineered Nanomaterials: Important Roles of Interfacial Interactions and Dissolved Organic Matter. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 232–242.
- 46 Gao, Z.; Jia, S.; Ou, H.; Hong, Y.; Shan, K.; Kong, X.; Wang, Z.; Feng, G.; Ding, D. An Activatable Near-Infrared Afterglow Theranostic Prodrug with Self-Sustainable Magnification Effect of Immunogenic Cell Death. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202209793.
- 47 Li, J.; Gao, H.; Liu, R.; Chen, C.; Zeng, S.; Liu, Q.; Ding, D. Endoplasmic reticulum targeted AIE bioprobe as a highly efficient inducer of immunogenic cell death. Sci. China Chem. 2020, 63, 1428–1434.
- 48 Ni, X.; Zhang, X.; Duan, X.; Zheng, H.L.; Xue, X. S.; Ding, D. Near-Infrared Afterglow Luminescent Aggregation-Induced Emission Dots with Ultrahigh Tumor-to-Liver Signal Ratio for Promoted Image- Guided Cancer Surgery. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 318–330.
- 49 Ren, F.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Zheng, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, C.; Guo, H.; Tong, B.; Xi, L.; Cai, Z.; Dong, Y. Donor strategy for promoting nonradiative decay to achieve an efficient photothermal therapy for treating cancer. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 1530–1539.
- 50 Ding B. S.; Cao, Z.; Lis, R.; Nolan, D. J.; Guo, P.; Simons, M.; Penfold, M. E.; Shido, K.; Rabbany, S. Y.; Rafii, S. Divergent angiocrine signals from vascular niche balance liver regeneration and fibrosis. Nature 2014, 505, 97–102.
- 51 Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Oupický, D. Balancing polymer hydrophobicity for ligand presentation and siRNA delivery in dual function CXCR4 inhibiting polyplexes. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 1114–1123.
- 52 Wang, Y.; Hazeldine, S. T.; Li, J.; Oupický, D. Development of Functional Poly(amido amine) CXCR4 Antagonists with the Ability to Mobilize Leukocytes and Deliver Nucleic Acids. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 729.
- 53 Zhou, Y.; Yu, F.; Zhang, F.; Chen, G.; Wang, K.; Sun, M.; Li, J.; Oupicky, D. Cyclam-modified PEI for combined VEGF siRNA silencing and CXCR4 inhibition to treat metastatic breast cancer. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 392–401.
- 54 Konrad, F. M.; Meichssner, N.; Bury, A.; Ngamsri, K. C.; Reutershan, J. Inhibition of SDF-1 receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 attenuates acute pulmonary inflammation via the adenosine A2B-receptor on blood cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2832.




