From Polymerization Inhibition to Controlled Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization of Macromonomers with Tertiary Amine Groups: The Effect of Spacer Chain†
Tengda Zhao
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Composite and Functional Materials, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300350 China
Search for more papers by this authorKongying Zhu
Analysis and Measurement Center, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaoliang Yu
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Composite and Functional Materials, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300350 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaoyan Yuan
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Composite and Functional Materials, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300350 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Lixia Ren
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Composite and Functional Materials, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300350 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorTengda Zhao
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Composite and Functional Materials, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300350 China
Search for more papers by this authorKongying Zhu
Analysis and Measurement Center, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaoliang Yu
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Composite and Functional Materials, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300350 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaoyan Yuan
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Composite and Functional Materials, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300350 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Lixia Ren
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Composite and Functional Materials, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300350 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this author† Dedicated to the Special Issue of Polymer Synthesis.
Main observation and conclusion
Ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) is a powerful toolbox in preparation of bottlebrush polymers for its high activity. However, the ROMP of macromonomers with repeating tertiary amine groups, for example, poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) (PDMAEMA), is inhibited due to the coordination of nitrogen atom with ruthenium center ([Ru]) in the third generation Grubbs catalyst (G3). In this work, norbornenyl functionalized polystyrene-block-PDMAEMA (NB-PS-b-PDMAEMA) macromonomers with different length of polystyrene (PS) spacers are prepared. The PS spacers provide non-coordinating local environment to protect [Ru] in G3 from coordinating with tertiary amine groups. Kinetic studies show that the PS spacer with polymerization degree (DP) of 15 is enough to protect G3, and the polymerization is controlled. However, the PS spacer with DP of 5 is inhibited within 10 min. In situ proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies show that the [Ru] in G3 is active during the ROMP of NB-PS15-b-PDMAEMA39, which is inactive gradually for NB-PS5-b-PDMAEMA42. In comparison, the ROMP of NB-PDMAEMA macromonomer without spacer chain is inhibited and the G3 catalyst is inactive from the beginning. By introducing non-coordinating spacer chain with enough length, the ROMP of macromonomers with tertiary amine groups is controlled, which provides a new strategy for the preparation of bottlebrush polymers with functional amine groups.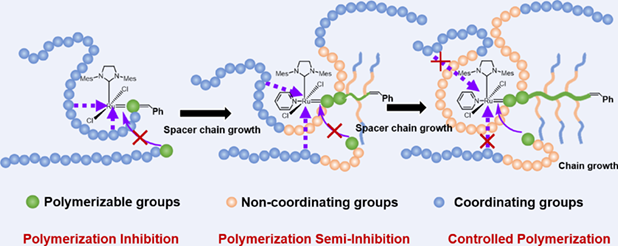
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202100152-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 717.7 KB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Georgios, C. V.; Grubbs, R. H. Ruthenium-Based Heterocyclic Carbene-Coordinated Olefin Metathesis Catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1746–1787.
- 2 Grubbs, R. H. Olefin Metathesis. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 7117–7140.
- 3 Zhao, Y.; Guo, T.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, L. Alcohols Responsive Photonic Crystals Prepared by Self-Assembly of Dendronized Block Copolymers. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 139, 162–169.
- 4 Guo, T.; Yu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Ren, L. Structure Memory Photonic Crystals Prepared by Hierarchical Self-Assembly of Semicrystalline Bottlebrush Block Copolymers. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 3602–3610.
- 5 Su, J. K.; Lee, S. Y.; Elling, B. R.; Xia, Y. Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization of 1,1-Disubstituted 1-Methylcyclopropenes. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 5833–5838.
- 6 Miyake, G. M.; Weitekamp, R. A.; Piunova, V. A.; Grubbs, R. H. Synthesis of Isocyanate-Based Brush Block Copolymers and Their Rapid Self-Assembly to Infrared-Reflecting Photonic Crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14249–14254.
- 7 Chae, C. G.; Yu, Y. G.; Seo, H. B.; Kim, M. J.; Kishore, M. Y. L. N.; Lee, J. S. Molecular and Kinetic Design for the Expanded Control of Molecular Weights in the Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization of Norbornene-Substituted Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 5179–5189.
- 8 Nicolas, C.; Fontaine, L.; Montembault, V. Nitroxide Radical-Containing Polynorbornenes by Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization as Stabilizing Agents for Polyolefins. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 5487–5497.
- 9 Yang, J.; Ren, L.; Li, Y. Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization of Cis-5-Norbornene-Endo-2,3-Dicarboxylic Anhydride Derivatives Using the Grubbs Third Generation Catalyst. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 35, 36–45.
- 10 Hou, X.; Chen, X.; Gao, X.; Xu, L.; Zou, H.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Z. Q. Synthesis of Cyclic Polyolefin: Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization by Binuclear Vanadium Complexes. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 1181–1187.
- 11 Nomura, K.; Chaimongkolkunasin, S. (Arylimido)vanadium(V)- Alkylidene Complexes as Catalysts for Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization (ROMP) of Cyclic Olefins: Ligand Design for Exhibiting the High Activity. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 37, 943–950.
- 12 Jiang, Z.-Q.; Xue, Y.-X.; Chen, J.-L.; Yu, Z.-P.; Liu, N.; Yin, J.; Zhu, Y.-Y.; Wu, Z.-Q. One-Pot Synthesis of Brush Copolymers Bearing Stereoregular Helical Polyisocyanides as Side Chains through Tandem Catalysis. Macromolecules 2014, 48, 81–89.
- 13 Choi, T. L.; Grubbs, R. H. Controlled Living Ring-Opening-Metathesis Polymerization by a Fast-Initiating Ruthenium Catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 1743–1746.
- 14 Grubbs, R. H. The Development of Functional Group Tolerant Romp Catalysts. J. Macromol. Sci. A 1994, 31, 1829–1933.
- 15 France, M. B.; Paciello, R. A.; Grubbs, R. H. Initiation of Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization in Protic Media. Extension of [Ru(H2O)6]2+ Catalyzed Polymerizations to Less-Strained Cyclic Monomers. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 4739–4741.
- 16 Nguyen, S. T.; Johnson, L. K.; Grubbs, R. H.; Ziller, J. W. Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization (ROMP) of Norbornene by a Group VIII Carbene Complex in Protic Media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 3974–3975.
- 17 Ogba, O. M.; Warner, N. C.; O'Leary, D. J.; Grubbs, R. H. Recent Advances in Ruthenium-Based Olefin Metathesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4510–4544.
- 18 Chae, C. G.; Yu, Y. G.; Seo, H. B.; Kim, M. J.; Grubbs, R. H.; Lee, J. S. Experimental Formulation of Photonic Crystal Properties for Hierarchically Self-Assembled POSS-Bottlebrush Block Copolymers. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 3458–3466.
- 19 Leitgeb, A.; Wappel, J.; Slugovc, C. The ROMP Toolbox Upgraded. Polymer 2010, 51, 2927–2946.
- 20 Scholl, M.; Ding, S.; Lee, C. W.; Grubbs, R. H. Synthesis and Activity of a New Generation of Ruthenium-Based Olefin Metathesis Catalysts Coordinated with 1,3-Dimesityl-4,5-Dihydroimidazol-2-Ylidene Ligands. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 953–956.
- 21 Frenzel, U.; Weskamp, T.; Kohl, F. J.; Schattenmann, W. C.; Nuyken, O.; Herrmann, W. A. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes: Application of Ruthenium-Alkylidene Complexes in Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization. J. Organomet. Chem. 1999, 586, 263–265.
- 22 Han, H.; Chen, F.; Yu, J.; Dang, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, M. Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization of Functionalized Cyclooctene by a Ruthenium-Based Catalyst in Ionic Liquid. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. 2007, 45, 3986–3993.
- 23 Herrmann, W. A.; Kocher, C. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997, 36, 2162–2187.
- 24 Guo, T.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, L. Thermal Property of Photonic Crystals (PCs) Prepared by Solvent Annealing Self-Assembly of Bottlebrush PS-b-PtBA. Polymer 2020, 194, 122389.
- 25 Yu, Y. G.; Chae, C. G.; Kim, M. J.; Seo, H. B.; Grubbs, R. H.; Lee, J. S. Precise Synthesis of Bottlebrush Block Copolymers from ω-End- Norbornyl Polystyrene and Poly(4-tert-butoxystyrene) via Living Anionic Polymerization and Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 447–455.
- 26 Sveinbjornsson, B. R.; Weitekamp, R. A.; Miyake, G. M.; Xia, Y.; Atwater, H. A.; Grubbs, R. H. Rapid Self-Assembly of Brush Block Copolymers to Photonic Crystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2012, 109, 14332–14336.
- 27 Radzinski, S. C.; Foster, J. C.; Matson, J. B. Preparation of Bottlebrush Polymers via a One-Pot Ring-Opening Polymerization (ROP) and Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization (ROMP) Grafting-Through Strategy. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 616–621.
- 28 Chen, M.; Chen, C. Controlling the Ring-Opening Polymerization Process Using External Stimuli. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 282–286.
- 29 Verduzco, R.; Li, X.; Pesek, S. L.; Stein, G. E. Structure, Function, Self-Assembly, and Applications of Bottlebrush Copolymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2405–2420.
- 30 Su, Y.-X.; Xu, L.; Xu, X.-H.; Hou, X.-H.; Liu, N.; Wu, Z.-Q. Controlled Synthesis of Densely Grafted Bottlebrushes That Bear Helical Polyisocyanide Side Chains on Polyisocyanide Backbones and Exhibit Greatly Increased Viscosity. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 3224–3233.
- 31 Walsh, D. J.; Lau, S. H.; Hyatt, M. G.; Guironnet, D. Kinetic Study of Living Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization with Third-Generation Grubbs Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13644–13647.
- 32 Wolf, W. J.; Lin, T. P.; Grubbs, R. H. Examining the Effects of Monomer and Catalyst Structure on the Mechanism of Ruthenium-Catalyzed Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17796–17808.
- 33 Cruz, T. R.; Silva, E. A.; Oliveira, D. P.; Martins, D. M.; Gois, P. D. S.; Machado, A. E. H.; Maia, P. I. S.; Goi, B. E.; Lima-Neto, B. S.; Carvalho-Jr, V. P. Dual Catalytic Performance of Arene-Ruthenium Amine Complexes for Norbornene Ring-Opening Metathesis and Methyl Methacrylate Atom Transfer Radical Polymerizations. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5602.
- 34 Silva Sá, J. L.; Nascimento, E. S. P.; Fonseca, L. R.; Lima-Neto, B. S. Ring-Opening Metathesis Copolymerization of Norbornene with Norbornadiene from Solutions with Different Mole Fractions of the Comonomers Catalyzed by Ru-Amine Complexes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 3578–3585.
- 35 Tomazett, V. K.; Santos, W. G.; Lima-Neto, B. S. Infrared Spectroscopy as an Effective Tool in Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization: Monitoring the Polymerization Kinetics of Norbornene with Amine- Based Ru Catalysts in Real Time. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2017, 120, 663–672.
- 36 Silva, T. B.; Camargo, R. S.; Lima-Neto, B. S. Electronic vs. Steric Hindrance Effects in Amine Ligands to Ru-Based Initiators for ROMP. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2014, 25, 2425–2432.
- 37 Liaw, D. J.; Tasi, C. H. Synthesis and Characterization of Polynorbornene Substituted with Phthalimide and Ammonium Groups via Living Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 1999, 147, 23–31.
- 38 Li, N.; Wang, H.; Qu, X.; Chen, Y. Synthesis of Poly(norbornene-methylamine), a Biomimetic of Chitosan, by Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization (ROMP). Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 223.
- 39 Xie, M.; Dang, J.; Han, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; He, X.; Zhang, Y. Well-Defined Brush Copolymers with High Grafting Density of Amphiphilic Side Chains by Combination of ROP, ROMP, and ATRP. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 9004–9010.
- 40 Wright, D. B.; Touve, M. A.; Thompson, M. P.; Gianneschi, N. C. Aqueous-Phase Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly. ACS Macro Lett. 2018, 7, 401–405.
- 41 Cui, J.; Nie, F.; Yang, J.; Pan, L.; Ma, Z.; Li, Y. Novel Imidazolium-Based Poly(ionic liquid)s with Different Counterions for Self-Healing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 25220–25229.
- 42 Wiesenauer, E. F.; Edwards, J. P.; Scalfani, V. F.; Bailey, T. S.; Gin, D. L. Synthesis and Ordered Phase Separation of Imidazolium-Based Alkyl- Ionic Diblock Copolymers Made via ROMP. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 5075–5078.
- 43 Suga, T.; Sakata, M.; Aoki, K.; Nishide, H. Synthesis of Pendant Radical- and Ion-Containing Block Copolymers via Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization for Organic Resistive Memory. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 703–707.
- 44 Senkum, H.; Gramlich, W. M. Cationic Bottlebrush Polymers from Quaternary Ammonium Macromonomers by Grafting-Through Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2020, 221, 1900476.
- 45 Yu, X.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, L. From Paramagnetic to Superparamagnetic Ionic Liquid/Poly(ionic liquid): The Effect of π-π Stacking Interaction. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 8, 1504–1510.
- 46 Qiao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, L. Ceiling Degree of Polymerization for Brush Polymers Prepared via ROMP of Poly(tert-butyl acrylate) Macromonomers. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2018, 34, 828–832.
- 47 Ireland, B. J.; Dobigny, B. T.; Fogg, D. E. Decomposition of a Phosphine-Free Metathesis Catalyst by Amines and Other Bronsted Bases: Metallacyclobutane Deprotonation as a Major Deactivation Pathway. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 4690–4698.
- 48 Liu, J.; Li, J.; Xie, M.; Ding, L.; Yang, D.; Zhang, L. A Novel Amphiphilic AB2 Star Copolymer Synthesized by The Combination of Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization and Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. Polymer 2009, 50, 5228–5235.
- 49 Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Gnanou, Y.; Hadjichristidis, N. Well-Defined Polyethylene-Based Random, Block, and Bilayered Molecular Cobrushes. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 3556–3562.




