ChemInform Abstract: Electron Transfer Processes. Part 64. Homolytic Base-Promoted Aromatic Alkylations by Alkylmercury Halides.
Abstract
ChemInform is a weekly Abstracting Service, delivering concise information at a glance that was extracted from about 100 leading journals. To access a ChemInform Abstract of an article which was published elsewhere, please select a “Full Text” option. The original article is trackable via the “References” option.
ChemInform Abstract
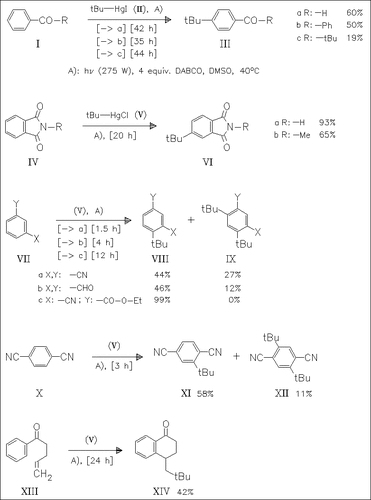
Electron transfer chain reactions leading to substitution in electronegatively substituted benzene derivatives can be observed with alkylmercury halides in the presence of proton acceptors such as DABCO. Such processes occur in the photolysis of tBuHg-halides with benzaldehyde, phenones, phthalimides and other disubstituted benzenes as well as in the homolytic cyclization to α-tetralone. A mechanism involving radical adducts and radical anions is discussed.