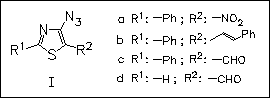ChemInform Abstract: Neighboring Group Effects on the Rates of Thermolysis of 4- Azidothiazoles.
Abstract
ChemInform is a weekly Abstracting Service, delivering concise information at a glance that was extracted from about 100 leading journals. To access a ChemInform Abstract of an article which was published elsewhere, please select a “Full Text” option. The original article is trackable via the “References” option.
ChemInform Abstract
Rate of thermolysis of a number of 4-azidothiazoles of type (I) leading to cyclized products is studied. The presence of nitro and phenyliminomethyl groups at position 5 causes significant rate enhancement, while the enhancement is quite small for formyl and acetyl groups. The 2-substituent, on the other hand, has little effect on the rate. The effects are very similar to those obtained for 3- azidothiophenes, but in azidobenzenes the rate increases are much larger.