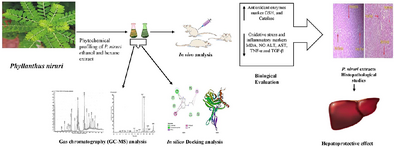
Hepatoprotective Potential of Phyllanthus niruri Extracts Against CCl4-Induced Liver Injury in Rats: Insight From Phytochemical Profiling, Molecular Docking, and Oxidative Stress Studies
Fatima Arshad
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Awais Altaf
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorAli Raza Arshad
Aziz Bhatti Shaheed Teaching Hospital, Gujrat, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorMuhammad Sarwar
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorTahir Maqbool
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorAsia kiran
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorSara Zahid
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tariq Aziz
Department of Agriculture, Laboratory of Animal Health, Food Hygiene and Quality, University of Ioannina, Arta, Greece
Search for more papers by this authorKhairiah Mubarak Alwutayd
Department of Biology, College of Science, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Search for more papers by this authorAshwag Shami
Department of Biology, College of Science, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Search for more papers by this authorFakhria A. Al-Joufi
Department of Pharmacology, College of Pharmacy, Jouf University, Aljouf, Saudi Arabia
Search for more papers by this authorMaher S. Alwethaynani
Department of Clinical Laboratory Sciences, College of Applied Medical Sciences, Shaqra University, Alquwayiyah, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Search for more papers by this authorFatima Arshad
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Awais Altaf
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorAli Raza Arshad
Aziz Bhatti Shaheed Teaching Hospital, Gujrat, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorMuhammad Sarwar
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorTahir Maqbool
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorAsia kiran
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorSara Zahid
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tariq Aziz
Department of Agriculture, Laboratory of Animal Health, Food Hygiene and Quality, University of Ioannina, Arta, Greece
Search for more papers by this authorKhairiah Mubarak Alwutayd
Department of Biology, College of Science, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Search for more papers by this authorAshwag Shami
Department of Biology, College of Science, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Search for more papers by this authorFakhria A. Al-Joufi
Department of Pharmacology, College of Pharmacy, Jouf University, Aljouf, Saudi Arabia
Search for more papers by this authorMaher S. Alwethaynani
Department of Clinical Laboratory Sciences, College of Applied Medical Sciences, Shaqra University, Alquwayiyah, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Search for more papers by this authorABSTRACT
Phyllanthus niruri, a well-known medicinal plant, has been widely recognized for its hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. In the present study, the hepatoprotective potential of ethanol extract of P. niruri (EPN) and hexane extract of P. niruri (HPN) were evaluated against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Oral administration of both EPN and HPN extracts at the dose of 200 mg/kg body weight and silymarin (50 mg/kg) was assessed for their therapeutic effect on liver function, oxidative stress markers, and inflammatory biomarkers. The results demonstrated that standard drug and P. niruri extracts significantly reduced elevated levels of liver enzymes (ALT and AST), oxidative stress (MDA and NO) markers, and inflammatory markers (TNF-α and TGF-β), along with remarkable restoration of antioxidants (GSH and CAT). Furthermore, histopathological outcomes suggested that the hepatic architecture of liver tissues normalized on extract treatment in comparison to the CCl4-treated group. The in silico study revealed that 1H-indole, 4-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)- and α-Amyrin from EPN extract, while phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) and Stigmast-4-en-3-one from HPN extract exhibited high binding affinities against selected proteins, TNF-α and TGF-β. These findings highlight P. niruri L. as a valuable source for the development of natural hepatoprotective drugs, as evidenced by its ability to mitigate CCl4-induced liver toxicity in rats primarily by enhancing antioxidant status and stabilizing liver cell integrity.
Graphical Abstract
-
Phyllanthus niruri extracts exhibit promising hepatoprotective effects and play a significant role in the prevention and management of liver diseases.
-
Administration of CCl4 markedly increased oxidative stress (MDA, NO), liver injury markers (ALT, AST), and inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, TGF-β) while significantly reducing the activities of antioxidant enzymes (GSH, CAT), indicating severe hepatic injury and inflammation.
-
The P. niruri (EPN and HPN) extracts significantly reduce oxidative stress markers, such as MDA and NO, by enhancing antioxidant enzymes (GSH and CAT) and lower liver injury and inflammatory markers, including ALT, AST, TNF-α, and TGF-β, thereby exerting strong hepatoprotective effects.
-
GC-MS analysis was employed to identify and characterize the phytochemicals present in the plant extracts, thereby providing a comprehensive phytochemical profile.
-
In silico docking analysis predicted that selected phytochemicals 1H-Indole, 4-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-, Alpha-Amyrin (from the EPN extract), as well as Stigmast-4-en-3-one, and Phenol, 2,4-bis (1,1-dimethyl ethyl)- (from HPN extract) exhibit high binding affinities for TNF-α and TGF-β, highlighting their potential as hepatoprotective agents.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
All the data generated in this research work has been included in this manuscript.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cbdv70054-sup-0001-TableS1.docx28.1 KB | Supporting Information |
| cbdv70054-sup-0002-TableS2.docx30.2 KB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1L. Conde de la Rosa, L. Goicoechea, S. Torres, and C. Garcia-Ruiz, “Role of Oxidative Stress in Liver Disorders,” Livers 2, no. 4 (2022): 283–314.
10.3390/livers2040023 Google Scholar
- 2A. A. Mokdad, A. D. Lopez, S. Shahraz, et al., “Liver Cirrhosis Mortality in 187 Countries Between 1980 and 2010: A Systematic Analysis,” BMC Medicine 12 (2014): 145.
- 3M. Stepanova, L. De Avila, M. Afendy, et al., “Direct and Indirect Economic Burden of Chronic Liver Disease in the United States,” Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 15, no. 5 (2017): 759–766.e5.
- 4H. Hirao, K. J. Dery, S. Kageyama, K. Nakamura, and J. W. Kupiec-Weglinski, “Heme Oxygenase-1 in Liver Transplant Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: From Bench-to-Bedside,” Free Radical Biology and Medicine 157 (2020): 75–82.
- 5H. Lyu, H. Wang, L Li, et al., “Hepatocyte-Specific Deficiency of Nrf2 Exacerbates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis via Aggravated Hepatocyte Injury and Subsequent Inflammatory and Fibrogenic Responses,” Free Radical Biology and Medicine 150 (2020): 136–147.
- 6A. M. AlSaad, M. Mohany, M. S. Almalki, I. Almutham, et al., “Baicalein Neutralizes Hypercholesterolemia-Induced Aggravation of Oxidative Injury in Rats,” International Journal of Medical Sciences 17, no. 9 (2020): 1156–1166.
- 7Y. Du, B. Qian, L. Gao, et al., “Aloin Preconditioning Attenuates Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Inhibiting TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signal Pathway In Vivo and In Vitro,” Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2019, no. 1 (2019): 3765898.
- 8L. Zhao and Y. Wang, “The Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications of Exosomes in Drug-Induced Liver Injury,” Toxicology Letters 337 (2021): 68–77.
- 9C. Brenner, L. Galluzzi, O. Kepp, and G. Kroemer, “Decoding Cell Death Signals in Liver Inflammation,” Journal of Hepatology 59, no. 3 (2013): 583–594.
- 10C. D. Klaassen and S. A. Reisman, “Nrf2 the Rescue: Effects of the Antioxidative/Electrophilic Response on the Liver,” Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 244, no. 1 (2010): 57–65.
- 11R. Li, P. Zhang, C. Li, W. Yang, Y. Yin, and K. Tao, “Tert-Butylhydroquinone Mitigates Carbon Tetrachloride Induced Hepatic Injury in Mice,” International Journal of Medical Sciences 17, no. 14 (2020): 2095–2103.
- 12V. Unsal and M. Cicek, “Toxicity of Carbon Tetrachloride, Free Radicals and Role of Antioxidants,” Reviews on Environmental Health 36, no. 2 (2021): 279–295.
- 13X. Li, X. Liu, Y. Zhang, et al., “Hepatoprotective Effect of Apolipoprotein A4 Against Carbon Tetrachloride Induced Acute Liver Injury Through Mediating Hepatic Antioxidant and Inflammation Response in Mice,” Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 534 (2021): 659–665.
- 14L. W. Weber and M. Boll, “Hepatotoxicity and Mechanism of Action of Haloalkanes: Carbon Tetrachloride as a Toxicological Model,” Critical Reviews in Toxicology 33, no. 2 (2003): 105–136.
- 15F. C. Kull Jr and P. Cuatrecasas, “Possible Requirement of Internalization in the Mechanism of In Vitro Cytotoxicity in Tumor Necrosis Serum,” Cancer Research 41, no. 121 (1981): 4885–4890.
- 16Y. Tahashi, K. Matsuzaki, M. Date, et al., “Differential Regulation of TGF-β Signal in Hepatic Stellate Cells between Acute and Chronic Rat Liver Injury,” Hepatology 35, no. 1 (2002): 49–61.
- 17K. Sabry, Z. Jamshidi, S. A. Emami, and A. Sahebka, “Potential Therapeutic Effects of Baicalin and Baicalein,” Avicenna Journal of Phytomedicine 14, no. 1 (2024): 23.
- 18R. A. Zaghloul, A. M. Zaghloul, and D. H. El-Kashef, “Hepatoprotective Effect of Baicalin Against Thioacetamide-Induced Cirrhosis in Rats: Targeting NOX4/NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Pathways,” Life Sciences 295 (2022): 120410.
- 19Q. Liu, Y. Sun, Y. Zhu, S. Qiao, J. Cai, and Z. Zhang, “Melatonin Relieves Liver Fibrosis Induced by Txnrd3 Knockdown and Nickel Exposure via IRE1/NF-kB/NLRP3 and PERK/TGF-β1 Axis Activation,” Life Sciences 301 (2022): 120622.
- 20Z. Zhu, R. Hu, J. Li, et al., “Alpinetin Exerts Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Angiogenic Effects Through Activating the Nrf2 Pathway and Inhibiting NLRP3 Pathway in Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis,” International Immunopharmacology 96 (2021): 107660.
- 21L. Sun, Y. Zhang, S. Wen, et al., “Extract of Jasminum grandiflorum L. Alleviates CCl4-Induced Liver Injury by Decreasing Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Hepatic CYP2E1 Expression in Mice,” Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 152 (2022): 113255.
- 22 World Health Organization, General Guidelines for Methodologies on Research and Evaluation of Traditional Medicine (No. WHO/EDM/TRM/2000.1) (World Health Organization, 2000).
- 23S. Kumar, S. Paul, Y. K. Walia, A. Kumar, and P. Singhal, “Therapeutic Potential of Medicinal Plants: A Review,” Journal of Biological and Chemical Chronicles 1, no. 1 (2015): 46–54.
- 24A. Zhang, H. Sun, and X. Wang, “Recent Advances in Natural Products from Plants for Treatment of Liver Diseases,” European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 63 (2013): 570–577.
- 25J. Xiao, K. F. So, E. C. Liong, and G. L. Tipoe, “Recent Advances in the Herbal Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease,” Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine 3, no. 2 (2013): 88–94.
- 26M. H. Farzaei, M. Zobeiri, F. Parvizi, et al., “Curcumin in Liver Diseases: A Systematic Review of the Cellular Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress and Clinical Perspective,” Nutrients 10, no. 7 (2018): 855.
- 27A. Federico, M. Dallio, and C. Loguercio, “Silymarin/Silybin and Chronic Liver Disease: A Marriage of Many Years,” Molecules 22, no. 2 (2017): 191.
- 28S. Li, H. Y. Tan, N. Wang, et al., “The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases,” International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 11 (2015): 26087–26124.
- 29Z. Samadi-Noshahr, M. A. R. Hadjzadeh, and R. Moradi-Marjaneh, “The Hepatoprotective Effects of Fennel Seeds Extract and Trans-Anethole in Streptozotocin-Induced Liver Injury in Rats,” Food Science & Nutrition 9, no. 2 (2021): 1121–1131.
- 30R. I. Kashkooli, S. S. Najafi, F. Sharif, et al., “The Effect of Berberis vulgaris Extract on Transaminase Activities in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease,” Hepatitis Monthly 15, no. 2 (2015): e25067.
- 31G.-Y. Li, “Hepatoprotective Effect of Cichorium intybus L., a Traditional Uighur Medicine, Against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis in Rats,” World Journal of Gastroenterology 20, no. 16 (2014): 4753.
- 32I. O. Pfingstgraf, M. Taulescu, R. M. Pop, et al., “Protective Effects of Taraxacum officinale L. (Dandelion) Root Extract in Experimental Acute on Chronic Liver Failure,” Antioxidants 10, no. 4 (2021): 504.
- 33R. Harish and T. Shivanandappa, “Antioxidant Activity and Hepatoprotective Potential of Phyllanthus niruri,” Food Chemistry 95, no. 2 (2006): 180–185.
- 34S. A. Almatroodi, S. Anwar, A. Almatroudi, et al., “Hepatoprotective Effects of Garlic Extract Against Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4)-Induced Liver Injury via Modulation of Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory Activities and Hepatocyte Architecture,” Applied Sciences 10, no. 18 (2020): 6200.
- 35M. A. Ayanaw, J. S. Yesuf, and E. M. Birru, “Evaluation of Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Methanolic Leaf and Root Extracts of Gomphocarpus purpurascens A. Rich (Asclepiadaceae) in Mice,” Journal of Experimental Pharmacology 15 (2023): 1–11, https://doi.org/10.2147/JEP.S361194.
- 36H. Ohkawa, N. Ohishi, and K. Yagi, “Assay for Lipid Peroxides in Animal Tissues by Thiobarbituric Acid Reaction,” Analytical Biochemistry 95, no. 2 (1979): 351–358.
- 37W. R. Tracey, J. Tse, and G. Carter, “Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Changes in Plasma Nitrite and Nitrate Concentrations in Rats and Mice: Pharmacological Evaluation of Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitors,” Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 272, no. 3 (1995): 1011–1015.
- 38S. Bahrami, A. Shahriari, M. Tavalla, S. Azadmanesh, and H. Hamidinejat, “Blood Levels of Oxidant/Antioxidant Parameters in Rats Infected with Toxoplasma gondii,” Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2016, no. 1 (2016): 8045969.
- 39A. K. Sinha, “Colorimetric Assay of Catalase,” Analytical Biochemistry 47, no. 2 (1972): 389–394.
- 40L. Kaushal, K. Alka, and D. Chand, “An In-Silico Approach for the Determination of the Hepatoprotective Properties of Phytoconstituents from Thalictrum foliolosum a Traditionally Used Himalayan Medicinal Plant,” Biomedical Journal of Scientific Technical Research 52, no. 2 (2023): 43476–43490.
- 41L. I. Design, Pharmacophore and Ligand-Based Design With Biovia Discovery Studio® (BIOVIA, 2014).
- 42A. Daina, O. Michielin, and V. Zoete, “SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules,” Scientific Reports 7, no. 1 (2017): 42717.
- 43A. V. Singh, A. Kayal, A. Malik, et al., “Interfacial Water in the SARS Spike Protein: Investigating the Interaction With Human ACE2 Receptor and In Vitro Uptake in A549 Cells,” Langmuir 38, no. 26 (2022): 7976–7988.
- 44M. Rai, A. V. Singh, N. Paudel, et al., “Herbal Concoction Unveiled: A Computational Analysis of Phytochemicals' Pharmacokinetic and Toxicological Profiles Using Novel Approach Methodologies (NAMs),” Current Research in Toxicology 5 (2023): 100118.
- 45P. S. Kanthe, B. S. Patil, K. K. Das, and P. P. Parvatikar, “Structural Analysis and Prediction of Potent Bioactive Molecule for eNOS Protein Through Molecular Docking,” In Silico Pharmacology 9 (2021): 1–10.
- 46S. Salentin, S. Schreiber, V. J. Haupt, M. F. Adasme, and M. Schroeder, “PLIP: Fully Automated Protein–Ligand Interaction Profiler,” Nucleic Acids Research 43, no. 1 (2015): W443–W447.
- 47K. Yang, Z. Zou, Y. Wu, and G. Hu, “MiR-195 Suppression Alleviates Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress in CCl4-Induced ALI in Mice by Targeting Pim-1,” Experimental and Molecular Pathology 115 (2020): 104438.
- 48S. Dutta, A. K. Chakraborty, P. Dey, et al., “Amelioration of CCl4 Induced Liver Injury in Swiss Albino Mice by Antioxidant Rich Leaf Extract of Croton bonplandianus Baill,” PLoS One 13, no. 4 (2018): e0196411.
- 49X. Huang, L. Wang, M. Meng, et al., “Extract of Averrhoa carambola L.(Oxalidaceae) Roots Ameliorates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis in Rats,” Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 121 (2020): 109516.
- 50H. Y. Lee, G. H. Lee, Y. Yoon, and H. J. Chae, “R. verniciflua and E. ulmoides Extract (ILF-RE) Protects Against Chronic CCl4-Induced Liver Damage by Enhancing Antioxidation,” Nutrients 11, no. 2 (2019): 382.
- 51M. Ali, S. Afzal, A. Zia, et al., “A Systematic Review of Treatment Response Rates in Pakistani Hepatitis C Virus Patients; Current Prospects and Future Challenges,” Medicine 95, no. 50 (2016): e5327.
- 52P. Lam, F. Cheung, H. Y. Tan, N. Wang, M. F. Yuen, and Y. Feng, “Hepatoprotective Effects of Chinese Medicinal Herbs: A Focus on Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Activities,” International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 4 (2016): 465.
- 53K. A. Conklin, “Dietary Antioxidants During Cancer Chemotherapy: Impact on Chemotherapeutic Effectiveness and Development of Side Effects,” Nutrition and Cancer 37, no. 1 (2000): 1–18.
- 54X. Zhang, E. D. Yeung, J. Wang, et al., “Isoliquiritigenin, a Natural Anti-Oxidant, Selectively Inhibits the Proliferation of Prostate Cancer Cells,” Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology 37, no. 8 (2010): 841–847.
- 55L. Sun, Y. Zhang, S. Wen, et al., “Extract of Jasminum grandiflorum L. Alleviates CCl4-Induced Liver Injury by Decreasing Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Hepatic CYP2E1 Expression in Mice,” Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 152 (2022): 113255.
- 56F. Alhakmani, S. Kumar, and S. A. Khan, “Estimation of Total Phenolic Content, In-Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Flowers of Moringa oleifera,” Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine 3, no. 8 (2013): 623–627.
- 57J. Checa and J. M. Aran, “Reactive Oxygen Species: Drivers of Physiological and Pathological Processes,” Journal of Inflammation Research 2 (2020): 1057–1073.
10.2147/JIR.S275595 Google Scholar
- 58A. Dey and J. Lakshmanan, “The Role of Antioxidants and Other Agents in Alleviating Hyperglycemia Mediated Oxidative Stress and Injury in Liver,” Food & Function 4, no. 8 (2013): 1148–1184.
- 59F. T. Johra, S. Hossain, P. Jain, et al., “Amelioration of CCl4-Induced Oxidative Stress and Hepatotoxicity by Ganoderma lucidum in Long Evans Rats,” Scientific Reports 13, no. 1 (2023): 9909.
- 60S. Mistry, K. R. Dutt, and J. Jena, “Protective Effect of Sida cordata Leaf Extract Against CCl4 Induced Acute Liver Toxicity in Rats,” Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine 6, no. 4 (2013): 280–284.
- 61H. M. Eltahir, M. A. Fawzy, E. M. Mohamed, et al., “Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Antifibrotic Effects of Boswellia serrate Gum Resin in CCl4-Induced Hepatotoxicity,” Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 19, no. 2 (2020): 1313–1321.
- 62M. Fatima, M. R. Khan, L. A. Al-Keridis, et al., “Pleurospermum candollei Methanolic Extract Ameliorates CCl4-Induced Liver Injury by Modulating Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory, and Apoptotic Markers in Rats,” ACS Omega 8, no. 29 (2023): 25999–26011.
- 63X. Xia, “Bioinformatics and Drug Discovery,” Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 17, no. 15 (2017): 1709–1726.
- 64R. Medeiros, M. F. Otuki, M. C. Avellar, and J. B. Calixto, “Mechanisms Underlying the Inhibitory Actions of the Pentacyclic Triterpene α-Amyrin in the Mouse Skin Inflammation Induced by Phorbol Ester 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-Acetate,” European Journal of Pharmacology 559, no. 2–3 (2007): 227–235.
- 65H. K. Alsaedi, N. A. Alwan, and E. A. Al-Masoudi, “Physiological and Biochemical Effect of α-Amyrin: A Review,” Journal of Medical and Life Science 6, no. 3 (2024): 443–452.
10.21608/jmals.2024.383360 Google Scholar
- 66S. Wen, L. He, Z. Zhong, et al., “Stigmasterol Restores the Balance of Treg/Th17 Cells by Activating the Butyrate-PPARγ Axis in Colitis,” Frontiers in Immunology 12 (2021): 741934.
- 67D. He, S. Wang, G. Fang, et al., “LXRs/ABCA1 Activation Contribute to the Anti-Inflammatory Role of Phytosterols on LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury,” Journal of Functional Foods 89 (2022): 104966.