Flavonoids From the Whole Plants of Leptopus clarkei and Their In Vitro Anti-inflammatory Activities
Funding: This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2023QH153) and the Research Foundation of Binzhou Medical University (BY2021KYQD30).
ABSTRACT
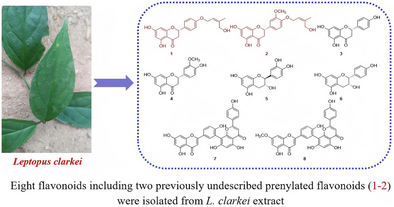
Our previous research has confirmed that the Leptopus genus plants possess significant anti-tumor and hepatoprotective effects, and over 50 triterpenoids were isolated from these plants. In the present work, the anti-inflammatory activities of four Leptopus genus plants were evaluated before phytochemical experiments. Subsequently, eight flavonoids (1–8) including two previously undescribed prenylated flavonoids (1–2) were isolated from the whole plants of Leptopus clarkei. The structures of these new compounds were unequivocally elucidated by high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and one-/two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance data. Additionally, all isolates were evaluated for their anti-inflammatory activities. Among these compounds, 1 exhibited moderate anti-inflammatory activity with a minimum inhibitory concentration value of 26.5 ± 1.2 µM on nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells.
Graphical Abstract
In this study, we isolated two undescribed prenylated flavonoids, along with six known compounds from the whole plants of Leptopus clarkei. All isolates were evaluated for their anti-inflammatory activities. Our findings demonstrated the 3-hydroxymethyl-2-butenyl moiety might be responsible for the increased anti-inflammatory activity of flavonoid.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the Supporting Information of this article.