Phytochemical Analysis, and Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Activities of Chamaerops humilis L. Leaves; A Focus on Xanthine Oxidase
Shimaa A. Ahmed
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Seuf, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Data curation (equal), Investigation (lead), Methodology (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Emadeldin M. Kamel
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Seuf, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Conceptualization (equal), Data curation (equal), Formal analysis (equal), Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal), Validation (equal), Writing - original draft (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorAyman M. Mahmoud
Department of Life Sciences, Faculty of Science and Engineering, Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, M1 5GD UK
Contribution: Conceptualization (lead), Data curation (lead), Formal analysis (lead), Investigation (lead), Methodology (lead), Project administration (lead), Supervision (lead), Validation (lead), Visualization (lead), Writing - original draft (lead), Writing - review & editing (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorHamdi M. D. Nasr
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Al-Azhar University (Assiut), Assiut, 71524 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (supporting), Methodology (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorHossam M. Hassan
Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorMohammed M. Alanazi
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, College of Pharmacy, King Saud University, Riyadh 11451, Saudi Arabia
Contribution: Funding acquisition (lead), Investigation (supporting), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorMostafa E. Rateb
Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorWalaa G. Hozayen
Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Seuf, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorSayed A. Ahmed
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Seuf, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorShimaa A. Ahmed
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Seuf, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Data curation (equal), Investigation (lead), Methodology (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Emadeldin M. Kamel
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Seuf, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Conceptualization (equal), Data curation (equal), Formal analysis (equal), Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal), Validation (equal), Writing - original draft (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorAyman M. Mahmoud
Department of Life Sciences, Faculty of Science and Engineering, Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, M1 5GD UK
Contribution: Conceptualization (lead), Data curation (lead), Formal analysis (lead), Investigation (lead), Methodology (lead), Project administration (lead), Supervision (lead), Validation (lead), Visualization (lead), Writing - original draft (lead), Writing - review & editing (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorHamdi M. D. Nasr
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Al-Azhar University (Assiut), Assiut, 71524 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (supporting), Methodology (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorHossam M. Hassan
Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorMohammed M. Alanazi
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, College of Pharmacy, King Saud University, Riyadh 11451, Saudi Arabia
Contribution: Funding acquisition (lead), Investigation (supporting), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorMostafa E. Rateb
Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorWalaa G. Hozayen
Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Seuf, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorSayed A. Ahmed
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Seuf, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
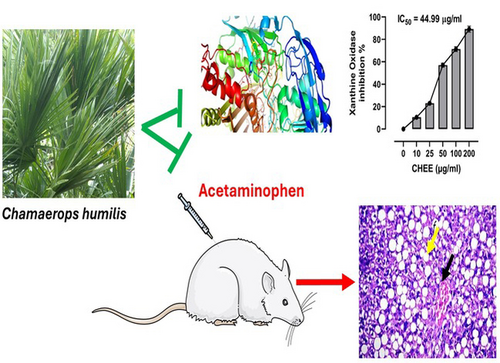
Chamaerops humilis L. is clumping palm of the family Arecaceae with promising health-promoting effects. Parts of this species are utilized as food and employed in folk medicine to treat several disorders. This study investigated the phytochemical constituents of C. humilis leaves and their antioxidant and xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitory activities in vitro and in vivo in acetaminophen (APAP)-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. The chemical structure of the isolated phytochemicals was determined using data obtained from UV, MS, IR, and 1H-, 13C-NMR spectroscopic tools as well as comparison with authentic markers. Eleven compounds, including tricin 7-O-β-rutinoside, vicenin, tricin, astragalin, borassoside D, pregnane-3,5,6,16-tetrol, oleanolic acid, β-sitosterol and campesterol were isolated from C. humilis ethanolic extract (CHEE). CHEE and the butanol, n-hexane, and dichloromethane fractions exhibited in vitro radical scavenging and XO inhibitory efficacies. The computational findings revealed the tendency of the isolated compounds towards the active site of XO. In vivo, CHEE ameliorated liver function markers and prevented tissue injury induced by APAP in rats. CHEE suppressed hepatic XO, decreased serum uric acid and liver malondialdehyde (MDA), and enhanced reduced glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase in APAP-treated rats. CHEE ameliorated serum tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin (IL)-1β in APAP-treated rats. Thus, C. humilis is rich in beneficial phytochemicals that possess binding affinity towards XO. C. humilis exhibited potent in vitro antioxidant and XO inhibitory activities, and prevented APAP hepatotoxicity by attenuating tissue injury, oxidative stress and inflammation.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cbdv202400865-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2.2 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aJ. Kang, K. M. Thakali, C. Xie, M. Kondo, Y. Tong, B. Ou, G. Jensen, M. B. Medina, A. G. Schauss, X. Wu, Food Chem. 2012, 133, 671–677;
- 1bW. Kchaou, F. Abbès, R. B. Mansour, C. Blecker, H. Attia, S. Besbes, Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1048–1055;
- 1cS. Gonçalves, J. Medronho, E. Moreira, C. Grosso, P. B. Andrade, P. Valentão, A. Romano, 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 88.
- 2
- 2aH. N. Gad El-Hak, H. S. Mahmoud, E. A. Ahmed, H. M. Elnegris, T. S. Aldayel, H. M. A. Abdelrazek, M. T. A. Soliman, M. A. I. El-Menyawy, Nutrients 2022, 14;
- 2bA. I. Hamed, R. Ben Said, A. S. Al-Ayed, J. Moldoch, U. A. Mahalel, A. M. Mahmoud, H. A. Elgebaly, A. J. Perez, A. Stochmal, Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 2024–2031.
- 3J. M. Fedriani, M. J. E. Delibes, Ecology 2011, 92, 304–315.
- 4A. Giovino, S. Scibetta, S. Saia, C. Guarino, Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 176, 66–81.
- 5I. Hinad, Y. S′Hih, A. Elhessni, A. Mesfioui, M. L. Ouahidi, Pan Afr. Med. J. 2022, 42, 319.
- 6
- 6aJ. C. Caissard, A. Meekijjironenroj, S. Baudino, M-C. Anstett, Am. J. Bot. 2004, 91, 1190–1199;
- 6bA. Bouhafsoun, M. A. Yilmaz, A. Boukeloua, H. Temel, M. K.. HARCHE, Food Sci Technol. 2018, 38, 242–247;
- 6cY. Hirai, S. SANADA, Y. IDA, J. SHOJI, Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 82–87.
- 7M. Miguel, S. Aazza, F. Gaamoussi, N. Bouchmaa, B. Lyoussi, Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2014, 23, 1375–1388.
- 8
- 8aR. S. Alruhaimi, G. Mostafa-Hedeab, M. S. Abduh, A. Bin-Ammar, E. H. M. Hassanein, E. M. Kamel, A. M. Mahmoud, Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1204641;
- 8bM. O. Germoush, A. M. Mahmoud, J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 1103–1109;
- 8cA. M. Mahmoud, O. A. M. Abd El-Ghafar, M. A. Alzoghaibi, E. H. M. Hassanein, Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119600;
- 8dA. M. Mahmoud, W. G. Hozayen, I. H. Hasan, E. Shaban, M. Bin-Jumah, Inflammation 2019, 42, 1103–1116;
- 8eA. Fadel, A. M. Mahmoud, J. J. Ashworth, W. Li, Y. L. Ng, A. Plunkett, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 819–831;
- 8fA. Abdel-Moneim, B. M. Morsy, A. M. Mahmoud, M. A. Abo-Seif, M. I. Zanaty, EXCLI Journal 2013, 12, 943–955.
- 9K. Du, A. Ramachandran, H. Jaeschke, Redox Biol 2016, 10, 148–156.
- 10H. Jaeschke, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1990, 255, 935–941.
- 11M. Frisch, G. Trucks, H. Schlegel, G. Scuseria, M. Robb, J. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, B. Mennucci, G. J. G. I. Petersson, Wallingford, CT, 2009.
- 12
- 12aA. D. Becke, J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652;
- 12bC. Lee, W. Yang, R. G. Parr, Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785;
- 12cA. D. Becke, Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098.
- 13W. J. Hehre, L. Radom, P. v. R. Schleyer, J. A. Pople, Ab initio molecular orbital theory, Vol. 67, Wiley New York et al., 1986.
- 14E. F. Pettersen, T. D. Goddard, C. C. Huang, G. S. Couch, D. M. Greenblatt, E. C. Meng, T. E. Ferrin, J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612.
- 15O. Trott, A. J. Olson, J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461.
- 16E. M. Kamel, A. M. Lamsabhi, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 3334–3345.
- 17J. Cheel, C. Theoduloz, J. A. Rodríguez, P. D. Caligari, G. Schmeda-Hirschmann, Food Chem. 2007, 102, 36–44.
- 18M. Ozyürek, B. Bektaşoğlu, K. Güçlü, R. Apak, Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 636, 42–50.
- 19D. K. Chellappan, S. Ganasen, S. Batumalai, M. Candasamy, P. Krishnappa, K. Dua, J. Chellian, G. Gupta, Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul 2016, 10, 72–76.
- 20S. A. Mard, K. Jalalvand, M. Jafarinejad, H. Balochi, M. K. Naseri, Malays J Med Sci 2010, 17, 4–13.
- 21J. D. Bancroft, M. Gamble, Theory and practice of histological techniques, Elsevier health sciences, 2008.
- 22M. N. Islam, I. J. Ishita, H. A. Jung, J. S. Choi, Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 69, 55–62.
- 23J. Jiao, Y. Zhang, C. Liu, J. E. Liu, X. Wu, Y. J. J. O. A. Zhang, Chemistry 2007, 55, 10086–10092.
- 24
- 24aR. H. Elsayed, E. M. Kamel, A. M. Mahmoud, A. A. El-Bassuony, M. Bin-Jumah, A. M. Lamsabhi, S. A. J. F. Ahmed, Journal of food and chemical toxicology 2020, 138, 111202;
- 24bJ.-H. Yang, T. P. Kondratyuk, L. E. Marler, X. Qiu, Y. Choi, H. Cao, R. Yu, M. Sturdy, S. Pegan, Y. J. P. Liu, 2010, 71, 641–647.
- 25M. Yoshikawa, F. Xu, T. Morikawa, Y. Pongpiriyadacha, S. Nakamura, Y. Asao, A. Kumahara, H. J. C. Matsuda, Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 308–316.
- 26T. Nakanishi, M. Kobayashi, H. Murata, A. J. C. Inada, Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 4148–4152.
- 27I. Ahmad, F. Ahmad, S. J. P. Osman, Phytochem. 1977, 16, 1761–1763.
- 28J. U. Obaroakpo, L. Liu, S. Zhang, L. Jing, L. Liu, X. Pang, J. Lv, J. Funct. Foods 2020, 66, 103779.
- 29M. Prabakaran, S.-H. Kim, A. Sasireka, V. Hemapriya, I.-M. Chung, New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 3900–3907.
- 30J. M. Choi, E. O. Lee, H. J. Lee, K. H. Kim, K. S. Ahn, B. S. Shim, N. I. Kim, M. C. Song, N. I. Baek, S-H. Kim, Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 954–959.
- 31D. S. Budnitz, M. C. Lovegrove, A. E. Crosby, Am. J. Prev. Med. 2011, 40, 585–592.
- 32A. M. Mahmoud, M. Y. Alexander, Y. Tutar, F. L. Wilkinson, A. Venditti, Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017, 2017, 2508909.
- 33N. Malik, P. Dhiman, E. Sobarzo-Sanchez, A. Khatkar, Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 2154–2164.
- 34
- 34aO. Dangles, Curr. Org. Chem. 2012, 16, 692–714;
- 34bE. M. Kamel, A. Bin-Ammar, A. A. El-Bassuony, M. M. Alanazi, A. Altharawi, A. F. Ahmeda, A. S. Alanazi, A. M. Lamsabhi, A. M. Mahmoud, RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 12361–12374.
- 35
- 35aE. M. Kamel, A. M. Lamsabhi, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 9031–9042;
- 35bE. M. Kamel, A. M. Tawfeek, A. A. El-Bassuony, A. M. Lamsabhi, New J. Chem. 2023.
- 36
- 36aE. M. Kamel, N. A. Ahmed, A. A. El-Bassuony, O. E. Hussein, B. Alrashdi, S. A. Ahmed, A. M. Lamsabhi, H. H. Arab, A. M. Mahmoud, J Combinatorial Chemistry and High Throughput Screening 2022, 25, 1336–1344;
- 36bE. M. Kamel, A. M. Tawfeek, A. A. El-Bassuony, A. M. Lamsabhi, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2023.
- 37B. M. ALRashdi, H. A. Elgebaly, M. O. Germoush, M. M. Qarmush, M. S. Azab, R. S. Alruhaimi, A. F. Ahmeda, M. H. Abukhalil, E. M. Kamel, H. H. J. E. S. Arab, P. Research, Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2022, in press, 1–13.
- 38
- 38aİ. Ö. Aycan, A. Tüfek, O. Tokgöz, O. Evliyaoğlu, U. Fırat, G. Ö. Kavak, H. Turgut, M. U. Yüksel, International Journal of Surgery 2014, 12, 213–218;
- 38bA. Mohammadi, S. Kazemi, M. Hosseini, H. Najafzadeh Varzi, F. Feyzi, P. Morakabati, A. A. Moghadamnia, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 2329–2337;
- 38cP. Hasanein, M. Sharifi, Pharmaceutical Biology 2017, 55, 1809–1816;
- 38dA. Rajasekaran, M. Periyasamy, Chinese Medicine 2012, 7, 12.
- 39H. Jaeschke, M. R. McGill, A. Ramachandran, Drug Metab. Rev. 2012, 44, 88–106.
- 40M. S. Abduh, M. A. Alzoghaibi, A. M. Alzoghaibi, A. Bin-Ammar, M. F. Alotaibi, E. M. Kamel, A. M. Mahmoud, Life Sci. 2023, 121612.
- 41A. Wendel, S. Feuerstein, K. H. Konz, Biochem. Pharmacol. 1979, 28, 2051–2055.
- 42A. Wendel, S. Feuerstein, Biochem. Pharmacol. 1981, 30, 2513–2520.
- 43
- 43aM. S. Abduh, S. A. M. Saghir, A. M. Al Hroob, A. Bin-Ammar, A. H. Al-Tarawni, V. Murugaiyah, A. M. Mahmoud, Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1134812;
- 43bA. M. Abdul-Rahman, A. Elwekeel, R. S. Alruhaimi, E. M. Kamel, A. Bin-Ammar, A. M. Mahmoud, A. S. Moawad, M. A. Zaki, Saudi Pharm. J. 2023, 31, 101762.