Phytochemical Profiling and Biological Activity of Achillea sintenisii Hub.-Mor
Corresponding Author
Nuraniye Eruygur
Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Selcuk University, 42250 Konya, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorTugsen Buyukyildirim
Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Selcuk University, 42250 Konya, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorSeyma Tetik Rama
Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Selcuk University, 42250 Konya, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorFatma Ayaz
Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Selcuk University, 42250 Konya, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorMehmet Tekin
Department of Pharmaceutical Botany, Faculty of Pharmacy, Trakya University, 22030 Edirne, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorMehmet Tuzcu
Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Selcuk University, 42250 Konya, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorGokhan Akcakavak
Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Bozok University, Yozgat, 66900 Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorMustafa Abdullah Yilmaz
Department of Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Dicle University, 21280 Diyarbakir, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Nuraniye Eruygur
Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Selcuk University, 42250 Konya, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorTugsen Buyukyildirim
Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Selcuk University, 42250 Konya, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorSeyma Tetik Rama
Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Selcuk University, 42250 Konya, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorFatma Ayaz
Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Selcuk University, 42250 Konya, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorMehmet Tekin
Department of Pharmaceutical Botany, Faculty of Pharmacy, Trakya University, 22030 Edirne, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorMehmet Tuzcu
Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Selcuk University, 42250 Konya, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorGokhan Akcakavak
Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Bozok University, Yozgat, 66900 Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorMustafa Abdullah Yilmaz
Department of Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Dicle University, 21280 Diyarbakir, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
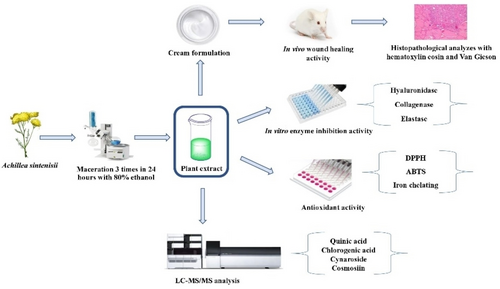
Achillea (Asteraceae) species have been traditionally used for their different therapeutical properties. In this study, phytochemical composition of aerial parts of A. sintenisii which is endemic in Turkey was determined with Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). To evaluate the wound healing potential, the cream formulation prepared from A. sintenisii was tested on the linear incision wound model in mice. In vitro enzyme inhibitory activity tests were performed on elastase, hyaluronidase, and collagenase. In the histopathological examination, angiogenesis and granulation tissue formation were significantly increased in A. sintenisii treatment groups compared to the negative control group. As a result of this study, it is thought that the enzyme inhibition and antioxidant activity of the plant may contribute to the wound healing process. According to LC/MS/MS analysis result, quinic acid (24.261 μg/mg extract) and chlorogenic acid (14.97 μg/mg extract) were identified as main constituents of the extract.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cbdv202201258-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf208.4 KB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1A. Budovsky, L. Yarmolinsky, S. Ben-Shabat, Wound Repair Regen. 2015, 23, 171.
- 2O. Yazarlu, M. Iranshahi, H. R. K. Kashani, S. Reshadat, S. Habtemariam, M. Iranshahy, M. Hasanpour, Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 174, 105841.
- 3A. Mensah, J. Sampson, P. Houghton, P. Hylands, J. Westbrook, M. Dunn, M. Hughes, G. Cherry, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 77, 219.
- 4I. Süntar, E. K. Akkol, L. Nahar, S. D. Sarker, Free Radic. Antioxid. 2012, 2, 1.
- 5M. P. Jorge, C. Madjarof, A. L. T. G. Ruiz, A. T. Fernandes, R. A. F. Rodrigues, I. M. de Oliveira Sousa, M. A. Foglio, J. E. de Carvalho, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 118, 361.
- 6S. Shetty, S. Udupa, L. Udupa, Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2008, 5, 95.
- 7D. G. Greenhalgh, J. Trauma 1996, 41, 159.
- 8S. Abhijit, D. Manjushree, Int. J. Bot. 2010, 6, 299.
10.3923/ijb.2010.299.303 Google Scholar
- 9N. B. Menke, K. R. Ward, T. M. Witten, D. G. Bonchev, R. F. Diegelmann, Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 19.
- 10E. Nemeth, J. Bernath, Cur. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 3151.
- 11S. Saeidnia, A. Gohari, N. Mokhber-Dezfuli, F. Kiuchi, DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 19, 173.
- 12M. Strzępek-Gomółka, K. Gaweł-Bęben, W. Kukula-Koch, Oxid. Met. 2021, 2021, 1.
- 13G. Cheers, Koln, Germany 1999.
- 14E. K. Akkol, U. Koca, I. Pesin, D. Yilmazer, Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 1.
- 15B. Dorjsembe, H. J. Lee, M. Kim, B. Dulamjav, T. Jigjid, C. W. Nho, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 206, 306.
- 16A. Hemmati, A. Arzi, M. Amin, J. Nat. Rem. 2002, 2, 164.
- 17A. G. Pirbalouti, A. Koohpayeh, I. Karimi, Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 107.
- 18T. F. Eissa, E. Gonzalez-Burgos, E. Carretero, M. P. Gomez-Serranillos, Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2018, 45, 897.
- 19M. Mohammadhosseini, S. D. Sarker, A. Akbarzadeh, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 199, 257.
- 20A. Ghorbani, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 102, 58.
- 21N. Eruygur, F. Ayaz, G. Bosdancı, D. Kırcı, T. Dogru, Research In Medicinal and Aromatic Plants 2020, p. 229.
- 22N. Karabay-Yavasoglu, C. Karamenderes, S. Baykan, S. Apaydin, Pharm. Biol. 2007, 45, 162.
- 23R. Re, N. Pellegrini, A. Proteggente, A. Pannala, M. Yang, C. Rice-Evans, Free Radical Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231.
- 24G. Clarke, K. N. Ting, C. Wiart, J. Fry, Antioxidants 2013, 2, 1.
- 25T. Chai, M. Mohan, H. Ong, F. Wong, Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 67.
- 26R. Boran, U. Aysel, N. Saraç, SDU J Nat Appl Sci. 2018, 22, 1182.
- 27A. Güvenç, E. K. Akkol, M. M. Hürkul, İ. Süntar, H. Keleş, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 401.
- 28B. A. Abeje, T. Bekele, K. A. Getahun, A. B. Asrie, J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2022, 14, 221.
- 29I. P. Süntar, E. K. Akkol, D. Yılmazer, T. Baykal, H. Kırmızıbekmez, M. Alper, E. Yeşilada, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 468.
- 30N. Eruygur, G. Yılmaz, O. Kutsal, G. Yücel, O. Üstün, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 185, 370.
- 31L. G. Luna, 1968.
- 32Z. Xu, S. Han, Z. Gu, J. Wu, Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 1901502.
- 33L. Deng, C. Du, P. Song, T. Chen, S. Rui, D. G. Armstrong, W. Deng, Oxid. Med. Cell. Longe. 2021, 2021, 1.
- 34M. A. Yilmaz, Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 149, 112347.
- 35O. T. Agar, M. Dikmen, N. Ozturk, M. A. Yilmaz, H. Temel, F. P. Turkmenoglu, Molecules 2015, 20, 17976.
- 36Z. Ghobadian, M. R. H. Ahmadi, L. Rezazadeh, E. Hosseini, T. Kokhazadeh, S. Ghavam, Med. Arch. 2015, 69, 212.
- 37G. Zengin, A. Aktumsek, R. Ceylan, S. Uysal, A. Mocan, G. O. Guler, M. F. Mahomoodally, J. Glamočlija, A. Ćirić, M. Soković, Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1152.
- 38M. Afshari, M. Rahimmalek, M. Miroliaei, Chem. Biodiversity 2018, 15, e1800075.
- 39L. Melguizo-Rodríguez, E. de Luna-Bertos, J. Ramos-Torrecillas, R. Illescas-Montesa, V. J. Costela-Ruiz, O. García-Martínez, Food 2021, 10, 1642.
- 40Y. Song, R. Zeng, L. Hu, K. G. Maffucci, X. Ren, Y. Qu, Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 451.
- 41E. Yadav, D. Singh, P. Yadav, A. Verma, Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1572.
- 42D. Bagdas, N. Y. Gul, A. Topal, S. Tas, M. O. Ozyigit, N. Cinkilic, Z. Gul, B. C. Etoz, S. Ziyanok, S. Inan, Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmakol. 2014, 387, 1101.
- 43D. Bagdas, B. C. Etoz, Z. Gul, S. Ziyanok, S. Inan, O. Turacozen, N. Y. Gul, A. Topal, N. Cinkilic, S. Tas, Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 81, 54.
- 44T. McClure, Am. J. Bot. 1960, 47, 277.
- 45S. E. Moghadam, S. N. Ebrahimi, P. Salehi, M. Moridi Farimani, M. Hamburger, E. Jabbarzadeh, Molecules 2017, 22, 1501.
- 46L. Song, H. Yang, D. Liang, D. Chu, L. Yang, M. Li, B. Yang, Y. Shi, Z. Chen, Z. Yu, J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 2022, 70, 103232.
- 47W.-C. Chen, S.-S. Liou, T.-F. Tzeng, S.-L. Lee, I.-M. Liu, Planta Med. 2013, 79, 616.
- 48F. C. Geller, M. R. Teixeira, A. B. D. Pereira, L. P. A. Dourado, D. G. Souza, F. C. Braga, C. M. O. Simões, Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1887.
- 49G. Sıdıka, Y. Yeşim, B. Cicek, A. Hacımüftüoğlu, Turkish J. Nat. Sci. 2022, 11, 63.
- 50S. I. Ali, B. Gopalakrishnan, V. Venkatesalu, Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 1140.
- 51R. Manivannan, J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 4, 54.
- 52I. Süntar, E. K. Akkol, H. Keles, E. Yesilada, S. D. Sarker, R. Arroo, T. Baykal, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 1058.
- 53D. Taşkın, T. Taşkın, E. Rayaman, Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 111, 555.
- 54C. Anlas, T. Bakirel, O. Ustuner, F. Ustun-Alkan, B. Diren-Sigirci, U. Koca-Caliskan, M. Mancak-Karakus, U. Dogan, S. Ak, H. A. Akpulat, Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104426.
- 55I. A. Ahmed, M. A. Mikail, N. H. Zamakshshari, M. R. Mustafa, N. M. Hashim, R. Othman, Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1.
- 56K. Madan, S. Nanda, Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 77, 159.
- 57P. Agarwal, A. Singh, K. Gaurav, S. Goel, H. Khanna, R. Goel, Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 47, 32.
- 58S. Enoch, D. J. Leaper, Surgery 2008, 26, 31.