Inhibition of Alzheimer's Aβ1-42 Fibrillogenesis and Removal of Copper Ions by Polypeptides Modified Gold Nanoparticles
Binbin Zhou
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, 414006 China
Search for more papers by this authorXingxin Sheng
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, 414006 China
Search for more papers by this authorHao Xie
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, 414006 China
Search for more papers by this authorSisi Zhou
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, 414006 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ming Zhong
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, 414006 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
An Liu
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, 414006 China
Search for more papers by this authorBinbin Zhou
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, 414006 China
Search for more papers by this authorXingxin Sheng
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, 414006 China
Search for more papers by this authorHao Xie
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, 414006 China
Search for more papers by this authorSisi Zhou
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, 414006 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ming Zhong
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, 414006 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
An Liu
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, 414006 China
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
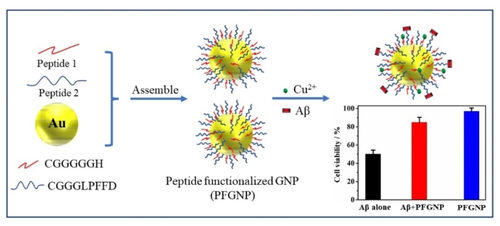
Aggregation and fibrillation of β-amyloid peptides (Aβ) as well as accumulation of toxic metal ions have been believed to be the central events to cause Alzheimer's disease (AD). Thus, an attractive therapeutic tactic for AD is to design and synthesize inhibitors and metal chelators to prevent Aβ aggregation and chelate toxic metal ions. In this study, the polypeptide functionalized gold nanoparticles (PFGNP) were obtained by modifying polypeptides Cys-Gly-Gly-Gly-Leu-Pro-Phe-Phe-Asp (CGGGLPFFD) and Cys-Gly-Gly-Gly-Gly-Gly-His (CGGGGGH) onto gold nanoparticles through gold-sulfur bond. The inhibitory properties of PFGNP toward Aβ1-42 fibril formation was assessed by thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence method and corroborated by atomic force microscopy analysis. The ability of PFGNP to complex copper ions was studied by electrochemical method. The experimental results reveal that PFGNP can effectively chelate copper ions and significantly inhibit the fibrillation of Aβ1-42. Moreover, PFGNP exhibits significantly protective effect on Aβ-induced cytotoxicity toward human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cbdv202200342-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf290 KB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1C. M. Henstridge, T. L. Spires-Jones, ‘Modeling Alzheimer's disease brains in vitro’, Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 899–900.
- 2P. Scheltens, B. De Strooper, M. Kivipelto, H. Holstege, G. Chetelat, C. E. Teunissen, J. Cummings, W. M. van der Flier, ‘Alzheimer's disease’, Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590.
- 3D. S. Knopman, H. Amieva, R. C. Petersen, G. Chetelat, D. M. Holtzman, B. T. Hyman, R. A. Nixon, D. T. Jones, ‘Alzheimer disease’, Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 33–38.
- 4L. Wang, Y. L. Yin, X. Z. Liu, P. Shen, Y. G. Zheng, X. R. Lan, C. B. Lu, J. Z. Wang, ‘Current understanding of metal ions in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease’, Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 10–23.
- 5F. Liu, Z. Zhang, L. Zhang, R. N. Meng, J. Gao, M. Jin, M. Li, X. P. Wang, ‘Effect of metal ions on Alzheimer's disease’, Brain. Behav. 2022, 12, 2527–2535.
- 6P. B. Allen, D. T. Chiu, ‘Alzheimer's disease protein Aβ1-42 does not disrupt isolated synaptic vesicles’, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1782, 326–334.
- 7H. Zhao, X. Huang, Z. J. C. Tong, ‘Formaldehyde-Crosslinked Nontoxic Aβ Monomers to Form Toxic Aβ Dimers and Aggregates: Pathogenicity and Therapeutic Perspectives’, ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 3376–3390.
- 8J. Han, Z. Du, M. H. Lim, ‘Mechanistic Insight into the Design of Chemical Tools to Control Multiple Pathogenic Features in Alzheimer's Disease’, Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 3930–3940.
- 9P. Zatta, D. Drago, S. Bolognin, S. L. Sensi, ‘Alzheimer's disease, metal ions and metal homeostatic therapy’, Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 346–355.
- 10J. A. Duce, A. I. Bush, ‘Biological metals and Alzheimer's disease: implications for therapeutics and diagnostics’, Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 92, 1–18.
- 11K. P. Kepp, ‘Alzheimer's disease: How metal ions define β-amyloid function’, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 351, 127–159.
- 12L. Iversen, ‘Amyloid diseases: small drugs lead the attack’, Nature 2002, 417, 231–233.
- 13Y. Sun, G. Zhang, C. A. Hawkes, J. E. Shaw, J. McLaurin, M. Nitz, ‘Synthesis of scyllo-inositol derivatives and their effects on amyloid beta peptide aggregation’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 7177–7184.
- 14A. Thapa, S. D. Jett, E. Y. Chi, ‘Curcumin Attenuates Amyloid-β Aggregate Toxicity and Modulates Amyloid-β Aggregation Pathway’, ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 56–68.
- 15J. W. Yan, Y. P. Li, W. J. Ye, S. B. Chen, J. Q. Hou, J. H. Tan, T. M. Ou, D. Li, L. Q. Gu, Z. S. Huang, ‘Design, synthesis and evaluation of isaindigotone derivatives as dual inhibitors for acetylcholinesterase and amyloid beta aggregation’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 2527–2534.
- 16M. Reches, Y. Porat, E. Gazit, ‘Amyloid fibril formation by pentapeptide and tetrapeptide fragments of human calcitonin’, J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35475–35480.
- 17C. Soto, E. M. Castano, B. Frangione, N. C. Inestrosa, ‘The alpha-helical to beta-strand transition in the amino-terminal fragment of the amyloid beta-peptide modulates amyloid formation’, J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 3063–3067.
- 18L. O. Tjernberg, J. Naslund, F. Lindqvist, J. Johansson, A. R. Karlstrom, J. Thyberg, L. Terenius, C. Nordstedt, ‘Arrest of β-amyloid fibril formation by a pentapeptide ligand’, J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8545–8548.
- 19J. S. Choi, J. J. Braymer, R. P. Nanga, A. Ramamoorthy, M. H. Lim, ‘Design of small molecules that target metal-Aβ species and regulate metal-induced Aβ aggregation and neurotoxicity’, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21990–21995.
- 20D. S. Folk, K. J. Franz, ‘A Prochelator Activated by β-Secretase Inhibits Aβ aggregation and Suppresses Copper-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species Formation’, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4994–4995.
- 21W. H. Wu, P. Lei, Q. Liu, J. Hu, A. P. Gunn, M. S. Chen, Y. F. Rui, X. Y. Su, Z. P. Xie, Y. F. Zhao, A. I. Bush, Y. M. Li, ‘Sequestration of copper from beta-amyloid promotes selective lysis by cyclen-hybrid cleavage agents’, J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31657–31664.
- 22K. Bourzac, ‘Nanotechnology: Carrying drugs’, Nature 2012, 491, 58–60.
- 23H. Jahangirian, K. Kalantari, Z. Izadiyan, R. Rafiee-Moghaddam, K. Shameli, T. J. Webster, ‘A review of small molecules and drug delivery applications using gold and iron nanoparticles’, Int. J. Nanomedic. 2019, 14, 1633–1657.
- 24F. Y. Kong, J. W. Zhang, R. F. Li, Z. X. Wang, W. J. Wang, W. Wang, ‘Unique Roles of Gold Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery, Targeting and Imaging Applications’, Molecules 2017, 22, 1445–1458.
- 25S. Palmal, A. R. Maity, B. K. Singh, S. Basu, N. R. Jana, N. R. Jana, ‘Inhibition of amyloid fibril growth and dissolution of amyloid fibrils by curcumin-gold nanoparticles’, Chemistry 2014, 20, 6184–6191.
- 26N. Gao, H. Sun, K. Dong, J. Ren, X. Qu, ‘Gold-Nanoparticle-Based Multifunctional Amyloid-β Inhibitor against Alzheimer's Disease’, Chemistry 2015, 21, 829–835.
- 27M. Samieegohar, F. Sha, A. Z. Clayborne, T. Wei, ‘ReaxFF MD Simulations of Peptide-Grafted Gold Nanoparticles’, Langmuir 2019, 35, 5029–5036.
- 28R. Levy, N. T. Thanh, R. C. Doty, I. Hussain, R. J. Nichols, D. J. Schiffrin, M. Brust, D. G. Fernig, ‘Rational and Combinatorial Design of Peptide Capping Ligands for Gold Nanoparticles’, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10076–10084.
- 29A. Nasrolahi Shirazi, D. Mandal, R. K. Tiwari, L. Guo, W. Lu, K. Parang, ‘Cyclic Peptide-Capped Gold Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems’, Mol. Pharmaceutics 2013, 10, 500–511.
- 30S. Parween, A. Ali, V. S. Chauhan, ‘Non-natural amino acids containing peptide-capped gold nanoparticles for drug delivery application’, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6484–6493.
- 31S. K. Tripathi, K. Kesharwani, G. Kaul, A. Akhir, D. Saxena, R. Singh, N. K. Mishra, A. Pandey, S. Chopra, K. B. Joshi, ‘Amyloid-β Inspired Short Peptide Amphiphile Facilitates Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antibacterial Agents’, ChemMedChem 2022.
- 32V. Kumar, K. V. Krishna, S. Khanna, K. B. Joshi, ‘Aggregation propensity of amyloidogenic and elastomeric dipeptides constituents’, Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 5369–5376.
- 33S. Li, L. Wang, Y. Hao, L. Zhang, B. Zhou, L. Deng, Y.-N. Liu, ‘An ultrasensitive colorimetric aptasensor for ATP based on peptide/Au nanocomposites and hemin–G-quadruplex DNAzyme’, RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 23185–23190.
- 34C. Soto, E. M. Sigurdsson, L. Morelli, R. A. Kumar, E. M. Castano, B. Frangione, ‘β-sheet breaker peptides inhibit fibrillogenesis in a rat brain model of amyloidosis: implications for Alzheimer's therapy’, Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 822–826.
- 35L. Liu, D. Jiang, A. McDonald, Y. Hao, G. L. Millhauser, F. Zhou, ‘Copper redox cycling in the prion protein depends critically on binding mode’, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12229–12237.
- 36U. E. Wawrzyniak, P. Ciosek, M. Zaborowski, G. Liu, J. J. Gooding, ‘Gly-Gly-His Immobilized On Monolayer Modified Back-Side Contact Miniaturized Sensors for Complexation of Copper Ions’, Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 1461–1471.
- 37B. Zhou, J. Li, B. J. Feng, Y. Ouyang, Y. N. Liu, F. Zhou, ‘Syntheses and in vitro antitumor activities of ferrocene-conjugated Arg-Gly-Asp peptides’, J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 116, 19–25.
- 38Z. Liu, B. Jia, J. Shi, X. Jin, H. Zhao, F. Li, S. Liu, F. Wang, ‘Tumor Uptake of the RGD Dimeric Probe 99mTc−G3-2P4-RGD2 is Correlated with Integrin αvβ3 Expressed on both Tumor Cells and Neovasculature’, Bioconjugate Chem. 2010, 21, 548–555.
- 39Z. Liu, S. Liu, F. Wang, S. Liu, X. Chen, ‘Noninvasive imaging of tumor integrin expression using (18)F-labeled RGD dimer peptide with PEG (4) linkers’, Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 36, 1296–1307.
- 40Y. Zheng, X. Cao, J. Orbulescu, V. Konka, F. M. Andreopoulos, S. M. Pham, R. M. Leblanc, ‘Peptidyl fluorescent chemosensors for the detection of divalent copper’, Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 1706–1712.
- 41Y. Hao, W. Chen, L. Wang, X. Zhu, Y. Zhang, P. Qu, L. Liu, B. Zhou, Y. N. Liu, M. Xu, ‘A retrievable, water-soluble and biocompatible fluorescent probe for recognition of Cu(II) and sulfide based on a peptide receptor’, Talanta 2015, 143, 307–314.
- 42W. Yang, E. Chow, G. D. Willett, D. B. Hibbert, J. J. Gooding, ‘Exploring the use of the tripeptide Gly-Gly-his as a selective recognition element for the fabrication of electrochemical copper sensors’, Analyst 2003, 128, 712–718.
- 43X. Hu, Q. Zhang, W. Wang, Z. Yuan, X. Zhu, B. Chen, X. Chen, ‘Tripeptide GGH as the Inhibitor of Copper-Amyloid-β-Mediated Redox Reaction and Toxicity’, ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 1255–1263.
- 44P. Frid, S. V. Anisimov, N. Popovic, ‘Congo red and protein aggregation in neurodegenerative diseases’, Brain Res. Rev. 2007, 53, 135–160.
- 45N. Gour, V. Kshtriya, S. Gupta, B. Koshti, R. Singh, D. Patel, K. B. Joshi, ‘Synthesis and Aggregation Studies of a Pyridothiazole-Based AIEE Probe and Its Application in Sensing Amyloid Fibrillation’, ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 4442–4455.
- 46H. LeVine, 3rd, ‘Quantification of β-sheet amyloid fibril structures with thioflavin T’, Methods Enzymol. 1999, 309, 274–284.
- 47B. Zhou, C. L. Li, Y. Q. Hao, M. C. Johnny, Y. N. Liu, J. Li, ‘Ferrocene tripeptide Gly-Pro-Arg conjugates: Synthesis and inhibitory effects on Alzheimer's Aβ1-42 fibrillogenesis and Aβ-induced cytotoxicity in vitro’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 395–402.
- 48C. W. Wei, Y. Peng, L. Zhang, Q. Huang, M. Cheng, Y. N. Liu, J. Li, ‘Synthesis and evaluation of ferrocenoyl pentapeptide (Fc-KLVFF) as an inhibitor of Alzheimer's Aβ1-42 fibril formation in vitro’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 5818–5821.
- 49B. M. Austen, K. E. Paleologou, S. A. Ali, M. M. Qureshi, D. Allsop, O. M. El-Agnaf, ‘Designing peptide inhibitors for oligomerization and toxicity of Alzheimer's β-amyloid peptide’, Biochemistry 2008, 47, 1984–1992.