Synthesis, Docking Study and Biological Evaluation of Amide-Based Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors with Novel Secondary Pharmacophore of Pyrimidin-2-ol
Leila Hejazi
Personalized Medicine and Genometabolomics Research Center, Hope Generation Foundation, Tehran, Iran
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, No. 2660, Vali-e-Asr., Tehran, 1991953381 Iran
Search for more papers by this authorAbraham Ebadi
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, No. 2660, Vali-e-Asr., Tehran, 1991953381 Iran
Search for more papers by this authorZeynab Fakhar
Laboratory of Bioinformatics and Drug Design (LBD), Institute of Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran
Search for more papers by this authorMaryam Nazari
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, No. 2660, Vali-e-Asr., Tehran, 1991953381 Iran
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Elham Rezaee
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, No. 2660, Vali-e-Asr., Tehran, 1991953381 Iran
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Sayyed Abbas Tabatabai
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, No. 2660, Vali-e-Asr., Tehran, 1991953381 Iran
Search for more papers by this authorLeila Hejazi
Personalized Medicine and Genometabolomics Research Center, Hope Generation Foundation, Tehran, Iran
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, No. 2660, Vali-e-Asr., Tehran, 1991953381 Iran
Search for more papers by this authorAbraham Ebadi
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, No. 2660, Vali-e-Asr., Tehran, 1991953381 Iran
Search for more papers by this authorZeynab Fakhar
Laboratory of Bioinformatics and Drug Design (LBD), Institute of Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran
Search for more papers by this authorMaryam Nazari
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, No. 2660, Vali-e-Asr., Tehran, 1991953381 Iran
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Elham Rezaee
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, No. 2660, Vali-e-Asr., Tehran, 1991953381 Iran
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Sayyed Abbas Tabatabai
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, No. 2660, Vali-e-Asr., Tehran, 1991953381 Iran
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
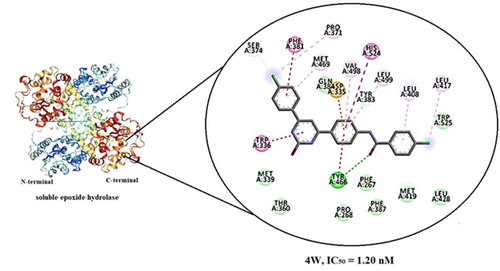
Soluble epoxide hydrolase enzyme (sEH) is one of the most promising and emerging targets to develop drugs for multiple disease indications, including hypertension, diabetes, stroke, dyslipidemia, pain, etc. Most inhibitor scaffolds have a urea or amide moiety to mimic the active-site transition state. In this regard, we developed a series of amide sEH inhibitors with a pyrimidin-2-ol ring as a new secondary pharmacophore, which was subjected to in vitro evaluation. Compound 4w (4-chloro-N-{4-[6-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-hydroxypyrimidin-4-yl]phenyl}benzamide), which contains 4-chloro substituent in both terminal phenyl rings, exhibited the most inhibitory activity against sEH with an IC50 value of 1.2 nM. Molecular docking analysis of the synthesized compounds revealed that the greater number of hydrogen bonding interactions of the amide group as the primary pharmacophore with Asp-353, Tyr-383, and Tyr-466 as the key catalytic residue triad of the enzyme played a critical role and led to a more favorable binding affinity. Pharmacokinetic properties of the synthesized compounds were calculated in silico, and all ADMET indices fell within acceptable ranges. Altogether, the results of this work could provide useful information on 4,6-diphenylpyrimidin-2-olas sEH inhibitors which can be utilized in further development in this area.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cbdv202200231-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf12.3 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1G. Curfman, H. Bauchner, P. Greenland, ‘Treatment and control of hypertension in 2020: The need for substantial improvement’, Jama 2020, 324, 1166–1167.
- 2D. Wan, J. Yang, C. B. McReynolds, B. Barnych, K. M. Wagner, C. Morisseau, S. H. Hwang, J. Sun, R. Blöcher, B. D. Hammock, ‘In vitro and in vivo metabolism of a potent inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase, 1-(1-propionylpiperidin-4-yl)-3-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)urea’, Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 464–482.
- 3N. Tripathi, S. Paliwal, S. Sharma, K. Verma, R. Gururani, A. Tiwari, A. Verma, M. Chauhan, A. Singh, D. Kumar, A. Pant, ‘Discovery of Novel Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors as Potent Vasodilators’, Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11.
- 4J. YANG, K. Wagner, D. Wan, S.-H. Hwang, C. B. McReynolds, B. D. Hammock, ‘Pharmacokinetics of a potent soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor in three formulations’, FASEB J. 2020, 34, 1–1.
- 5V. S. Hanna, E. A. A. Hafez, ‘Synopsis of arachidonic acid metabolism: A review’, J. Adv. Res. 2018, 11, 23–32.
- 6B. Zhou, S. He, X. Wang, X. Zhen, X. Su, W. Tan, ‘Metabolism of arachidonic acid by the cytochrome P450 enzyme in patients with chronic Keshan disease and dilated cardiomyopathy’, Biomed. Rep. 2016, 4, 251–255.
- 7J. D. Imig, ‘Epoxyeicosanoids in hypertension’, Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, 695–704.
- 8K. Hiesinger, K. M. Wagner, B. D. Hammock, E. Proschak, S. H. Hwang, ‘Development of multitarget agents possessing soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory activity’, Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediators 2019, 140, 31–39.
- 9J. Y. Liu, ‘Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase for renal health’, Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1551–1562.
- 10V. Burmistrov, C. Morisseau, D. Pitushkin, D. Karlov, R. R. Fayzullin, G. M. Butov, B. D. Hammock, ‘Adamantyl thioureas as soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 2302–2313.
- 11I. H. Kim, F. R. Heirtzler, C. Morisseau, K. Nishi, H. J. Tsai, B. D. Hammock, ‘Optimization of amide-based inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase with improved water solubility’, J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3621–3629.
- 12S. Codony, E. Pujol, J. Pizarro, F. Feixas, E. Valverde, M. I. Loza, J. M. Brea, E. Saez, J. Oyarzabal, A. Pineda-Lucena, B. Pérez, C. Pérez, M. I. Rodríguez-Franco, R. Leiva, S. Osuna, C. Morisseau, B. D. Hammock, M. Vázquez-Carrera, S. Vázquez, ‘2-Oxaadamant-1-yl Ureas as Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors: In Vivo Evaluation in a Murine Model of Acute Pancreatitis’, J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 9237–9257.
- 13I. A. Bukhari, B. I. Alorainey, A. A. Al-Motrefi, A. Mahmoud, W. B. Campbell, B. D. Hammock, ‘1-trifluoromethoxyphenyl-3-(1-propionylpiperidin-4-yl) urea (TPPU), a soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, lowers L-NAME-induced hypertension through suppression of angiotensin-converting enzyme in rats’, Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 8143–8150.
- 14A. G. P. Guedes, F. Aristizabal, A. Sole, A. Adedeji, R. Brosnan, H. Knych, J. Yang, S. H. Hwang, C. Morisseau, B. D. Hammock, ‘Pharmacokinetics and antinociceptive effects of the soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor t-TUCB in horses with experimentally induced radiocarpal synovitis’, J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 41, 230–238.
- 15A. Ulu, S. E. Appt, C. Morisseau, S. H. Hwang, P. D. Jones, T. E. Rose, H. Dong, J. Lango, J. Yang, H. J. Tsai, C. Miyabe, C. Fortenbach, M. R. Adams, B. D. Hammock, ‘Pharmacokinetics and in vivo potency of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors in cynomolgus monkeys’, Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 1401–1412.
- 16P. L. Podolin, B. J. Bolognese, J. F. Foley, E. Long, B. Peck, S. Umbrecht, X. Zhang, P. Zhu, B. Schwartz, W. Xie, C. Quinn, ‘In vitro and in vivo characterization of a novel soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor’, Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediators 2013, 104, 25–31.
- 17B. D. Hammock, C. B. McReynolds, K. Wagner, A. Buckpitt, I. Cortes-Puch, G. Croston, K. S. S. Lee, J. Yang, W. K. Schmidt, S. H. Hwang, ‘Movement to the Clinic of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor EC5026 as an Analgesic for Neuropathic Pain and for Use as a Nonaddictive Opioid Alternative’, J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1856–1872.
- 18M. Nazari, S. A. Tabatabai, E. Rezaee, ‘Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationships Study of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors Using MLR, ANN, CoMFA and CoMSIA Methods’, ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 6348–6353.
- 19E. Rezaee, S. M. Amrolah, M. Nazari, S. A. Tabatabai, ‘Novel amide derivatives of 3-phenylglutaric acid as potent soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors’, Mol. Diversity 2021, 25, 45–53.
- 20L. Hejazi, E. Rezaee, S. A. Tabatabai, ‘Quinazoline-4(3H)-one derivatives as novel and potent inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation’, Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 99, 103736–103744.
- 21I. Mahlooji, M. Shokri, R. Manoochehri, M. Mahboubi-Rabbani, E. Rezaee, S. A. Tabatabai, ‘Discovery of phthalimide derivatives as novel inhibitors of a soluble epoxide hydrolase’, Arch. Pharm. 2020, 353, 2000052–2000063.
- 22Z. Fakhar, L. Hejazi, S. A. Tabatabai, O. Q. Munro, ‘Discovery of novel heterocyclic amide-based inhibitors: an integrative in-silico approach to targeting soluble epoxide hydrolase’, J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 1–15.
- 23I. H. Kim, K. Nishi, H. J. Tsai, T. Bradford, Y. Koda, T. Watanabe, C. Morisseau, J. Blanchfield, I. Toth, B. D. Hammock, ‘Design of bioavailable derivatives of 12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido) dodecanoic acid, a potent inhibitor of the soluble epoxide hydrolase’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 312–323.
- 24D. Tanaka, Y. Tsuda, T. Shiyama, T. Nishimura, N. Chiyo, Y. Tominaga, N. Sawada, T. Mimoto, N. Kusunose, ‘A practical use of ligand efficiency indices out of the fragment-based approach: Ligand efficiency-guided lead identification of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors’, J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 851–857.
- 25Schrödinger Release 2020–3. QikProp, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2020.
- 26A. Daina, O. Michielin, V. Zoete, ‘SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules OPEN’, Nature Publishing Group 2017, DOI 10.1038/srep42717.
- 27D. S. Shihadih, T. R. Harris, S. D. Kodani, S.-H. Hwang, K. S. S. Lee, V. Mavangira, B. Hamamoto, A. Guedes, B. D. Hammock, C. Morisseau, ‘Selection of Potent Inhibitors of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase for Usage in Veterinary Medicine’, Front. vet. sci. 2020, 7, 580–588.
- 28A. K. Ghose, V. N. Viswanadhan, J. J. Wendoloski, ‘A knowledge-based approach in designing combinatorial or medicinal chemistry libraries for drug discovery. 1. A qualitative and quantitative characterization of known drug databases’, J. Comb. Chem. 1999, 1, 55–68.
- 29J. B. Baell, G. A. Holloway, ‘New substructure filters for removal of pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays’, J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2719–2740.
- 30J. B. Baell, J. W. M. Nissink, ‘Seven Year Itch: Pan-Assay Interference Compounds (PAINS) in 2017—Utility and Limitations’, ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 36–44.
- 31G. R. Bickerton, G. v. Paolini, J. Besnard, S. Muresan, A. L. Hopkins, ‘Quantifying the chemical beauty of drugs’, Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 90–98.
- 32G. Madhavi Sastry, M. Adzhigirey, T. Day, R. Annabhimoju, W. Sherman, ‘Protein and ligand preparation: Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments’, J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234.
- 33Schrödinger Release 2020–3: Protein Preparation Wizard; Epik, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2020; Impact, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY; Prime, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2020.
- 34E. Harder, W. Damm, J. Maple, C. Wu, M. Reboul, J. Y. Xiang, L. Wang, D. Lupyan, M. K. Dahlgren, J. L. Knight, J. W. Kaus, D. S. Cerutti, G. Krilov, W. L. Jorgensen, R. Abel, R. A. Friesner, ‘OPLS3: A Force Field Providing Broad Coverage of Drug-like Small Molecules and Proteins’, J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 281–296.
- 35W. L. Jorgensen, J. Tirado-Rives, ‘The OPLS Potential Functions for Proteins. Energy Minimizations for Crystals of Cyclic Peptides and Crambin’, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 1657–1666.
- 36Schrödinger Release 2020–3: LigPrep, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2020.
- 37Schrödinger Release 2020–3: Epik, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2020.
- 38R. A. Friesner, J. L. Banks, R. B. Murphy, T. A. Halgren, J. J. Klicic, D. T. Mainz, M. P. Repasky, E. H. Knoll, M. Shelley, J. K. Perry, D. E. Shaw, P. Francis, P. S. Shenkin, ‘Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 1. Method and Assessment of Docking Accuracy’, J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749.
- 39R. A. Friesner, R. B. Murphy, M. P. Repasky, L. L. Frye, J. R. Greenwood, T. A. Halgren, P. C. Sanschagrin, D. T. Mainz, ‘Extra precision glide: Docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes’, J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196.
- 40Schrödinger Release 2020–3: Maestro, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2020.
- 41Z. Fakhar, B. Faramarzi, S. Pacifico, S. Faramarzi, ‘Anthocyanin derivatives as potent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease: An in-silico perspective of therapeutic targets against COVID-19 pandemic’, J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 39, 6171–6183.
- 42H. van de Waterbeemd, E. Gifford, ‘ADMET in silico modelling: Towards prediction paradise’, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2003, 2, 192–204.
- 43C. A. Lipinski, ‘Lead- and drug-lik’ compounds: The rule-of-five revolution’, Drug Discovery Today Technol. 2004, 1, 337–341.
- 44C. A. Lipinski, F. Lombardo, B. W. Dominy, P. J. Feeney, ‘Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings’, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2012, 64, 4–17.