Protective Effects of Anthocyanins from Coreopsis tinctoria against Oxidative Stress Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide in MIN6 Cells
Correction(s) for this article
-
Corrigendum: Protective Effects of Anthocyanins from Coreopsis tinctoria against Oxidative Stress Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide in MIN6 Cells
- Volume 20Issue 1Chemistry & Biodiversity
- First Published online: December 8, 2022
Jianli Liu
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorSiqi Tian
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorMingyang Fu
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYin He
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hui Yu
Shenyang He Eye Hospital INC, Shenyang, 110034 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiangyu Cao
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYiyang Cao
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHanyuan Xu
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorJianli Liu
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorSiqi Tian
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorMingyang Fu
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYin He
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hui Yu
Shenyang He Eye Hospital INC, Shenyang, 110034 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiangyu Cao
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYiyang Cao
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHanyuan Xu
School of Life Sciences, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110036 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
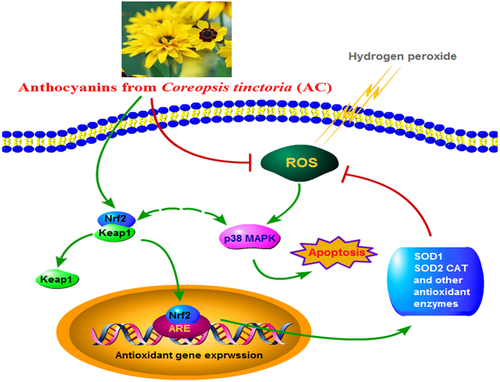
Anthocyanins (AC) from Coreopsis tinctoria possesses strong antioxidant properties, while the effects of AC on cells damage induced by reactive oxygen species (ROS) in diabetes mellitus diseases progression have not been reported. The present study was carried out to evaluate the protective property of AC against cellular oxidative stress with an experimental model, H2O2-exposed MIN6 cells. AC could reverse the decrease of cell viability induced by H2O2 and efficiently suppressed cellular ROS production and cell apoptosis. In addition, Real-time PCR and Western blot analyses indicated that AC could protect MIN6 cells against oxidative injury through increasing the translocation of Nrf2 into nuclear, decreasing the phosphorylation level of p38 and up-regulating the protein expression of antioxidant enzyme (SOD1, SOD2 and CAT). Thus, this study provides evidence to support the beneficial effect of AC in inhibiting MIN6 cells from H2O2-induced oxidative injury.
Graphical Abstract
References
- 1N. Katsiki, F. Purrello, C. Tsioufis, D. P. Mikhailidis, ‘Cardiovascular disease prevention strategies for type 2 diabetes mellitus’, Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2017, 18, 1243–1260.
- 2N. H. Cho, J. E. Shaw, S. Karuranga, Y. Huang, J. D. da Rocha Fernandes, A. W. Ohlrogge, B. Malanda, ‘IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045’, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281.
- 3R. Chen, L. Ji, L. Chen, L. Chen, D. Cai, B. Feng, H. Kuang, H. Li, Y. Li, J. Liu, Z. Shan, Z. Sun, H. Tian, Z. Xu, Y. Xu, Y. Yang, L. Yang, X. Yu, D. Zhu, D. Zou, ‘Glycemic control rate of T2DM outpatients in China: a multi-center survey’, Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 1440–1446.
- 4F. Giacco, M. Brownlee, A. M. Schmidt, ‘Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Complications’, Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1058–1070.
- 5A. Umeno, V. Biju, Y. Yoshida, ‘In vivo ROS production and use of oxidative stress-derived biomarkers to detect the onset of diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and diabetes’, Free Radical Res. 2017, 51, 413–427.
- 6H. Zhang, S. Zhang, J. Wang, B. Sun, ‘Wheat bran feruloyl oligosaccharides protect against AAPH-induced oxidative injury via p38mapk/PI3 K-Nrf2/Keap1-Mafk pathway’, J Funct. Foods 2017, 29, 53–59.
- 7W. Ma, C. Li, S. Yin, J. Liu, C. Gao, Z. Lin, R. Huang, J. Huang, Z. Li, ‘Novel role of TRPV2 in promoting the cytotoxicity of H2O2-mediated oxidative stress in human hepatoma cells’, Free Radical Biol. Med. 2015, 89, 1003–1013.
- 8Y. Pang, H. Zhu, J. Xu, L. Yang, L. Liu, J. Li, ‘β-Arrestin-2 is involved in irisin induced glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes via p38 MAPK signaling’, Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 360, 199–204.
- 9E. S. Chio, J. J. Yoon, B. H. Han, D. H. Jeong, Y. J. Lee, D. G. Kang, H. S. Lee, ‘Ligustilide attenuates vascular inflammation and activates Nrf2/HO-1 induction and, NO synthesis in HUVECs’, Phytomedicine 2018, 38, 12–23.
- 10Y. J. Surh, J. K. Kundu, H. K. Na, ‘Nrf2 as a master redox switch in turning on the cellular signaling involved in the induction of cytoprotective genes by some chemopreventive phytochemicals’, Planta Med. 2008, 74, 1526–1539.
- 11S. F. Nabavi, A. J. Barber, C. Spagnuolo, G. L. Russo, M. Daglia, S. M. Nabavi, E. Sobarzo-Sánchez, ‘Nrf2 as molecular target for polyphenols: A novel therapeutic strategy in diabetic retinopathy’, Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016, 53, 293–312.
- 12C. Chen, A. M. Pearson, J. I. Gray, ‘Effects of synthetic antioxidants (BHA, BHT and PG) on the mutagenicity of IQ-like compounds’, Food Chem. 1992, 43, 177–183.
- 13P. Anchi, A. Khurana, S. Bale, C. Godugu, ‘The role of plant-derived products in pancreatitis: experimental and clinical evidence’, Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 591–623.
- 14V. Gowd, Z. Jia, W. Chen, ‘Anthocyanins as promising molecules and dietary bioactive components against diabetes – A review of recent advances’, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 1–13.
- 15Q. L. Sun, H. Shu, J. H. Ye, H. Ye, X. Q. Zheng, Y. R. Liang, ‘Flavonoids and volatiles in Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat flower from Tongxiang County in China’, Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 925, 3817–3821.
- 16D. Du, L. Yao, R. Zhang, N. Shi, Y. Shen, X. Yang, X. Zhang, T. Jin, T. Liu, L. Hu, Z. Xing, D. N. Criddle, Q. Xia, W. Huang, R. Sutton, ‘Protective effects of flavonoids from Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. on experimental acute pancreatitis via Nrf-2/ARE-mediated antioxidant pathways’, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 224, 261–272.
- 17T. Dias, M. R. Bronze, P. J. Houghton, H. Mota-Filipe, A. Paulo, ‘The flavonoid-rich fraction of Coreopsis tinctoria promotes glucose tolerance regain through pancreatic function recovery in streptozotocin-induced glucose-intolerant rats’, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 132, 483–490.
- 18T. Wang, M. Xi, Q. Guo, L. Wang, Z. Shen, ‘Chemical components and antioxidant activity of volatile oil of a Compositae tea (Coreopsis tinctoria, Nutt.) from Mt. Kunlun’, Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 67, 318–323.
- 19T. Xia, J. Yao, J. Zhang, Y. Zheng, J. Song, M. Wang, ‘Protective effects of Shanxi aged vinegar against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in LO2 cells through Nrf2-mediated antioxidant responses’, RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17377–17386.
- 20Y. Jin, K. Liu, J. Peng, C. Wang, L. Kang, N. Chang, H. Sun, ‘Rhizoma Dioscoreae Nipponicae polysaccharides protect HUVECs from H2O2-induced injury by regulating PPARγ factor and the NADPH oxidase/ROS-NF-κB signal pathway’, Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 232, 149–158.
- 21Y. Jang, A. Y. Lee, S. H. Jeong, K. H. Park, M. H. Cho, ‘Chlorpyrifos induces NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis/apoptosis via mitochondrial oxidative stress in human keratinocyte HaCaT cells’, Toxicology 2015, 338, 37–46.
- 22Y. Wu, F. Wang, L. Fan, W. Zhang, T. Wang, Y. Du, X. Bai, ‘Baicalin alleviates atherosclerosis by relieving oxidative stress and inflammatory responses via inactivating the NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways’, Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1673–1679.
- 23D. P. Jones, ‘Redefining oxidative stress’, Antioxid. Redox Signaling 2006, 8, 1865–1879.
- 24T. Suzuki, H. Motothashi, M. Yamamoto, ‘Toward clinical application of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway’, Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 340–346.
- 25X. Wang, J. Liu, X. Zhang, S. Zhao, K. Zou, J. Xie, X. Wang, C. Liu, J. Wang, Y. Wang, ‘Seabuckthorn berry polysaccharide extracts protect against acetaminophen induced hepatotoxicity in mice via activating the Nrf-2/HO-1-SOD-2 signaling pathway’, Phytomedicine 2018, 38, 90–97.
- 26J. Wang, A. Shanugam, S. Markand, E. Zorrilla, V. Ganapathy, S. B. Smith, ‘Sigma 1 receptor regulates the oxidative stress response in primary retinal müller glial cells via Nrf2 signaling and system xc−, the Na+-independent glutamate-cystine exchanger’, Free Radical Biol. Med. 2015, 86, 25–36.
- 27G. Qi, Y. Mi, Y. Wang, R. Li, S. Huang, X. Li, X. Liu, ‘Neuroprotective action of tea polyphenols on oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through the activation of the Trkb/CREB/BDNF pathway and Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway in SH-SY5Y cells and mice brain’, Food Funct. 2017, 8, 4421–4432.
- 28H. Lian, Y. Cheng, X. Wu, ‘TMEM16 A exacerbates renal injury by activating P38/JNK signaling pathway to promote podocyte apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy mice’, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 487, 201–208.
- 29F. Jiang, Y. Zhang, G. J. Dusting, ‘NADPH oxidase-mediated redox signaling: roles in cellular stress response, stress tolerance, and tissue repair’, Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 218–242.
- 30L. Shi, H. Qin, X. Jin, X. Yang, X. Lu, H. Wang, R. Wang, D. Yu, B. Feng, ‘The natural phenolic peperobtusin a induces apoptosis of lymphoma u937 cells via the caspase dependent and p38 mapk signaling pathways’, Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 772–781.
- 31J. Guo, X. Qiu, L. Zhang, R. Wei, ‘Smurf1 regulates macrophage proliferation, apoptosis and migration via JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways’, Mol. Immunol. 2018, 97, 20–26.
- 32N. Kang, M. M. Wang, Y. H. Wang, Z. N. Zhang, H. R. Cao, Y. H. Lv, Y. Yang, P. H. Fan, F. Qiu, X. M. Gao, ‘Tetrahydrocurcumin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis involving p38 MAPK activation in human breast cancer cells’, Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 67, 193–200.
- 33Z. Ma, S. Zheng, H. Han, J. Meng, X. Yang, S. Zeng, H. Zhou, H. Jiang, ‘The bioactive components of Coreopsis tinctoria (Asteraceae) capitula: Antioxidant activity in vitro and profile in rat plasma’, J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 575–586.
- 34L. Xi, T. Mu, H. Sun, ‘Preparative purification of polyphenols from sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) leaves by AB-8 macroporous resins’, Food Chem. 2015, 172, 166–174.
- 35M. Rosales-Castro, R. F. González-Laredo, N. E. Rocha-Guzmán, J. Gallegos-Infante, J. Peralta-Cruz, J. Karchesy, ‘Evaluación química y capacidad antioxidante de extractos polifenólicos de cortezas’, Madera y Bosques 2016, 15, 87.
10.21829/myb.2009.1531187 Google Scholar
- 36N. A. Panat, D. K. Maurya, S. S. Ghaskadbi, S. K. Sandur, ‘Troxerutin, a plant flavonoid, protects cells against oxidative stress-induced cell death through radical scavenging mechanism’, Food Chem. 2016, 194, 32–45.
- 37W. Chen, J. Zhao, T. Ba, J. Xie, W. Liang, V. Gowd, ‘Comparative study on phenolics and antioxidant property of some new and common bayberry cultivars in China’, J. Funct. Foods 2016, 27, 472–482.
- 38R. Ferriero, E. Nusco, R. D. Cegli, A. Carissimo, G. Manco, N. Brunetti-Pierri, ‘Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and lactate dehydrogenase as targets for therapy of acute liver failure’, J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 325–335.
- 39L. Zuo, T. L. Clanton, ‘Detection of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in tissues using redox-sensitive fluorescent probes’, Methods Enzymol. 2002, 352, 307–325.
- 40K. C. Ha, H. J. Chae, C. S. Piao, S. H. Kim, H. R. Kim, S. W. Chae, ‘Dendroaspis natriuretic peptide induces the apoptosis of cardiac muscle cells’, Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2005, 27, 33–51.