Correction to: Overexpression of amplified in breast cancer 1 (AIB1) gene promotes lung adenocarcinoma aggressiveness in vitro and in vivo by upregulating c-x-c motif chemokine receptor 4
Following publication of this article [1], the authors noticed incorrect use of images in Figure 4: Western blot for β-actin in Figure 4b, wound-healing assays of A549-vector and A549-AIB1+CXCR4-siRNA-1 cells in Figure 4c, and transwell assays of A549 cells in Figure 4d and H1993 cells in Figure 4f. These images were chosen mistakenly during the figure typesetting process. The corrected Figure 4 is provided below.
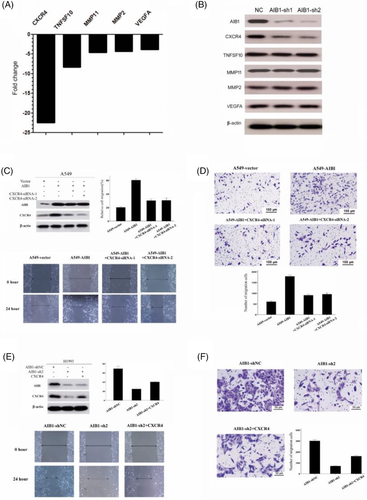
The original data has been submitted to the editorial board of Cancer Communications and has been approved. The corrections do not change the results and conclusions drawn in this paper.
Author information
Liru He and Haixia Deng contributed equally to this work.
Affiliations
1The State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, No. 651, Dongfeng Road East, Guangzhou, 510060, China.
Liru He, Haixia Deng, Shiliang Liu, Jiewei Chen, Binkui Li, Chenyuan Wang, Xin Wang, Mengzhong Liu & Dan Xie
2Department of Radiation Oncology, Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China.
Liru He, Shiliang Liu & Mengzhong Liu
3Department of Thoracic Oncology, Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China.
Xin Wang
4The State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
Yiguo Jiang
5Key Laboratory of Protein Modification and Degradation, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Affiliated Cancer Hospital & Institute of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
Ningfang Ma
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Menzhong Liu and Dan Xie.




