Thiolation of starch and other polysaccharides†
Presented at 164th National Meeting of American Chemical Society, New York, New York, August 27–September 1, 1972.
Abstract
Thiolated starches with a degree of substitution of 0.01–0.6 were obtained by pyrolysis of starch dithiobis(thioformates) followed by saponification. The pyrolytic decomposition of dithiobis(thioformates) followed two pathways: (1) to thionocarbonate 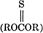 , carbon disulfide, and sulfur, and (2) to dithiocarbonate
, carbon disulfide, and sulfur, and (2) to dithiocarbonate 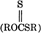 , carbonyl sulfide, and sulfur. Only the second pathway affords thiolation. Thiol groups were determined by Ellman's reagent, by sulfur analyses, and, following acetylation, by the ratio of O-acetyl versus S-acetyl absorption in nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. The poly-saccharides cellulose, dextran, and xylan were thiolated by the same procedure.
, carbonyl sulfide, and sulfur. Only the second pathway affords thiolation. Thiol groups were determined by Ellman's reagent, by sulfur analyses, and, following acetylation, by the ratio of O-acetyl versus S-acetyl absorption in nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. The poly-saccharides cellulose, dextran, and xylan were thiolated by the same procedure.




