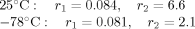The γ-ray-induced copolymerization of vinylphosphonic dichloride (VPDC) with methyl methacrylate (MMA) and styrene (St) was studied at 25°C (liquid phase) and −78°C (Solid phase). The reaction mechanisms are discussed. The reactivity ratios for the copolymerization of the VPDC–MMA system were determined as follows:
The difference between the reactivity between the liquid-phase (25°C) and solid-phase (−78°C) copolymerization is mainly attributable to the
r2 value. The behavior of the liquid-phase copolymerization of the VPDC–St system was anomalous, the
r1 value being negative in the range from 0 to 80 mole-% of VPDC monomer. In the solid-phase (−78°C) copolymerization for the VPDC–St system, the reactivity ratios
r1 and
r2 were 0.097 and 1.6, respectively. The rate of copolymerization (
Rp) at 25°C, for both the VPDC–MMA and VPDC–St systems, passes a maximum point at a certain monomer concentration, suggesting that the composition of copolymer is considerably affected by
Rp. This phenomenon was interpreted by the assumption that an energy transfer reaction from VPDC monomer to the other vinyl compound can easily occur.