Unlocking the Power of Lewis Basicity in Oxide Lattice Oxygens: A Regulating Force for Enhanced Oxygen Evolution Kinetics in Li-O2 Batteries
Graphical Abstract
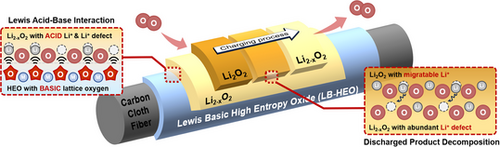
Lewis basicity of lattice oxygen is activated in our high entropy spinel oxide (LB-HEO). Through Lewis acid-base interaction, LB-HEO attracts acidic Li+, leading to more disorder and Li+ defects in the discharge product Li2O2 of lithium-oxygen batteries. This promotes Li+ diffusion in Li2O2 and interfacial electron transfer, eventually improving the decomposition kinetics during charging. It provides a new perspective on the regulation of Li+ behavior to achieve better electrochemical performance.
Abstract
Lithium-oxygen batteries (LOBs) require fast oxygen conversion kinetics to achieve good cycling performance and high energy efficiency. In the text of catalysts for LOBs, the Lewis basicity of lattice oxygens (OL) in common transition metal oxides is often underestimated due to the weak electron donor characteristic of OL. In this work, a new spinel-type high entropy oxide with Lewis basicity (LB-HEO) was synthesized through a Joule-heating method. OL was activated by regulating the tetrahedral site-OL-octahedral site (MTd-OL-MOh) units in the spinel-type HEO, enhancing the LB. Used as a cathode catalyst for LOBs, LB-HEO could attract Li+ and increase the disorder in discharge product, lithium peroxide (Li2O2), promoting the delithiation process and the interfacial charge transfer at the LB-HEO|Li2O2 interface. The activation energy of interfacial charge transfer was significantly reduced from 63.5 to 22.4 kJ mol−1. As a result, a low charging overpotential of 0.97 V and a long cycling lifespan of 135 cycles at 100 mA g−1 were achieved with a capacity limitation of 1000 mAh g−1. The strategy based on the regulation of Li+ behavior through its interaction with Lewis bases provides a promising prospect for the design of non-noble metal catalysts for high-performance LOBs.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.