Controlled Deformation Mode and Amplitude of Liquid Crystal Actuators Through Orthogonal Light and Heat-Induced Exchanges
Jian Ding
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tuan Liu
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorJinwen Zhang
School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, Composite Materials and Engineering Center, Washington State University, Pullman, WA, 99164 USA
Search for more papers by this authorYuzhan Li
School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, 100083 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXuepei Miao
School of Chemical Engineering and Materials, Changzhou Institute of Technology, Changzhou, 213032 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCaicai Li
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorWanqi Chen
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorBaihang Chen
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXinyi Huang
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorLiangdong Zhang
SINOPEC Beijing Research Institute of Chemical Industry, Beijing, 100013 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorKun Wang
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, 200234 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorZhixiang Dong
School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, 100083 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorBingkun Bao
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorLinyong Zhu
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qiuning Lin
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorJian Ding
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tuan Liu
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorJinwen Zhang
School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, Composite Materials and Engineering Center, Washington State University, Pullman, WA, 99164 USA
Search for more papers by this authorYuzhan Li
School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, 100083 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXuepei Miao
School of Chemical Engineering and Materials, Changzhou Institute of Technology, Changzhou, 213032 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCaicai Li
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorWanqi Chen
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorBaihang Chen
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXinyi Huang
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorLiangdong Zhang
SINOPEC Beijing Research Institute of Chemical Industry, Beijing, 100013 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorKun Wang
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, 200234 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorZhixiang Dong
School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, 100083 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorBingkun Bao
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorLinyong Zhu
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qiuning Lin
Department School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
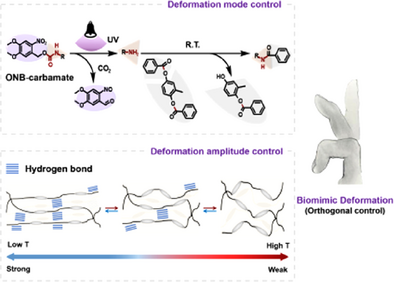
We introduce a structural design that enables independent control over both the mode and amplitude of deformation in liquid crystal elastomers (LCEs). This design incorporates photo-reactive o-nitrobenzyl moieties and temperature-dependent hydrogen bonds into the LCE structure, allowing for customizable, continuous, and precise deformations. This breakthrough is essential for bridging the gap between LCEs and biological motion systems.
Abstract
Liquid crystal elastomers (LCEs) are versatile soft actuators known for their flexible texture, low density, and ability to undergo reversible deformations that mimic the behavior of skeletal muscles. These properties make them highly attractive for applications in exoskeletons, soft robotics, and medical devices. However, their functionality is typically limited to simple and discontinuous deformations. This study introduces a novel structural design that enables precise control of both the mode and amplitude of deformation. This design integrates photo-reactive o-nitrobenzyl moieties and temperature-dependent hydrogen bonds into the LCE structure. The o-nitrobenzyl moieties enable irreversible reconfiguration of the LCE crosslinked network through photoreactions, allowing for easy alignment and reshaping of the material. Meanwhile, the hydrogen bonds act as “temperature-dependent locks”, regulating the mobility of polymer chains during thermal deformation. By adjusting the heating temperature, the deformation amplitude can be finely tuned across a wide range (0%–103%). The synergy of these two mechanisms—light-induced irreversible reconfiguration and temperature-induced reversible H-bond exchanges—empowers LCEs to achieve customizable and continuous deformations. This represents a significant advancement in bridging the gap between synthetic actuators and biological motion systems.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202505172-sup-0001-VideoS1.mp46.1 MB | Supplementary Information |
| anie202505172-sup-0002-VideoS2.mp47.6 MB | Supplementary Information |
| anie202505172-sup-0003-VideoS3.mp44.7 MB | Supplementary Information |
| anie202505172-sup-0004-VideoS4.mp46.6 MB | Supplementary Information |
| anie202505172-sup-0005-VideoS5.mp46.7 MB | Supplementary Information |
| anie202505172-sup-0006-VideoS6.mp45.6 MB | Supplementary Information |
| anie202505172-sup-0009-VideoS7.mp47.5 MB | Supplementary Information |
| anie202505172-sup-0008-VideoS8.mp48.2 MB | Supplementary Information |
| anie202505172-sup-0009-SuppMat.docx11.6 MB | Supplementary Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1Z. C. Jiang, Q. Liu, Y. Y. Xiao, Y. Zhao, Prog. Polym. Sci. 2024, 153, 101829.
- 2G. Long, Y. Deng, W. Zhao, G. Zhou, D. J. Broer, B. L. Feringa, J. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 13894–13902.
- 3S. H. Choi, J. H. Kim, J. Ahn, T. Kim, Y. Jung, D. Won, J. Bang, K. R. Pyun, S. Jeong, H. Kim, Y. G. Kim, S. H. Ko, Nat. Mater. 2024, 23, 834–843.
- 4Z. Zhang, X. Yang, Y. Zhao, F. Ye, L. Shang, Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2300220.
- 5I. H. Kim, S. Choi, J. Lee, J. Jung, J. Yeo, J. T. Kin, S. Ryu, S. Ahn, J. Kang, P. Poulin, S. O. Kim, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 1198–1205.
- 6S. Tasmim, Z. Yousuf, F. S. Rahman, E. Seelig, A. J. Clevenger, S. N. VandenHeuvel, C. P. Ambulo, S. Raghavan, P. E. Zimmern, M. I. Romero-Ortega, T. H. Ware, Biomaterials 2023, 292, 121912.
- 7A. Pena-Francesch, H. Jung, M. C. Demirel, M. Sitti, Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 1230–1235.
- 8H. Liu, H. Tian, X. Li, X. Chen, K. Zhang, H. Shi, C. Wang, J. Shao, Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn5722.
- 9K. M. Herbert, H. E. Fowler, J. M. McCracken, K. R. Schlafmann, J. A. Koch, T. J. White, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 23–38.
- 10D. Thomas, M. Cardarelli, A. Sánchez-Ferrer, B. L. Mbanga, T. J. Atherton, P. Cebe, Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 112.
- 11T. Ohzono, K. Katoh, E. M. Terentjev, Macromolecules 2021, 54, 3678–3688.
- 12Z. C. Jiang, Y. Y. Xiao, L. Yin, L. Han, Y. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 4955–4961.
- 13Z. C. Jiang, Y. Y. Xiao, X. Tong, Y. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 131, 5386–5391.
- 14E. C. Davidson, A. Kotikian, S. Li, J. Aizenberg, J. A. Lewis, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905682.
- 15Y. Fan, T. Liu, Y. Li, X. Miao, B. Chen, J. Ding, Z. Dong, O. Rios, B. Bao, Q. Lin, L. Zhu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202308793.
- 16J. Ding, T. Liu, Y. Li, X. Miao, Z. Yang, C. Li, Z. Dong, L. Jiang, L. Wang, R. Cheng, B. Bao, Q. Lin, L. Zhu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2414510.
- 17S. J. D. Lugger, D. J. Mulder, A. P. H. J. Schenning, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 134, e202115166.
10.1002/ange.202115166 Google Scholar
- 18H. Guo, T. P. Ruoko, H. Zeng, A. Priimagi, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2312068.
- 19X. Zhou, B. Jin, Z. Zhu, J. Wu, Q. Zhao, G. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202409182.
- 20R. Liang, H. Yu, L. Wang, D. Shen, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2211914.
- 21Z. Yang, J. Li, X. Chen, Y. Fan, J. Huang, S. Yang, E.-Q. Chen, Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2211648.
- 22T. Xie, Nature 2010, 464, 267–20.
- 23T. Liu, B. Bao, Y. Li, Q. Lin, L. Zhu, Prog. Polym. Sci. 2023, 146, 101741.
- 24P. J. LeValley, R. Neelarapu, B. P. Sutherland, S. Dasgupta, C. J. Kloxin, A. M. Klixin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4671–4679.
- 25C. B. Cooper, S. Nikzad, H. Yan, Y. Ochiai, J. C. Lai, Z. Yu, G. Chen, J. Kang, Z. Bao, ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 1657.
- 26Y. Wang, X. Huang, X. Zhang, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1291.
- 27Y. Li, J. K. Keum, J. Wang, N. Jiang, W. Bras, M. R. Kessler, O. Rios, Macromolecules 2021, 54, 10574–10582.
- 28H. Kim, J. M. Boothby, S. Ramachandran, C. D. Lee, T. H. Ware, Macromolecules 2017, 50, 4267–4275.
- 29M. J. Hansen, W. A. Velema, M. M. Lerch, W. Szymanski, B. L. Feringa, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3358–3377.
- 30D. Montarnal, M. Capelot, F. Tournilhac, L. Leibler, Science 2011, 334, 965–968.
- 31T. Liu, C. Hao, L. Wang, Y. Li, W. Liu, J. Xin, J. Zhang, Macromolecules 2017, 50, 8588–8597.
- 32J. Han, T. Liu, C. Hao, S. Zhang, B. Guo, J. Zhang, Macromolecules 2018, 51, 6789–6799.
- 33W. M. Zhang, J. Zhang, Z. Qiao, H.-Y. Liu, Z.-Q. Wu, J. Yin, Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 4233–4242.
- 34C. A. DeForest, D. A. Tirrell, Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 523–531.
- 35R. Shanti, A. N. Hadi, Y. S. Salim, S. Y. Chee, S. Ramesh, K. Tamesh, RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 112.
- 36H. Li, S. Rathi, E. S. Sterner, H. Zhao, S. L. Hsu, P. Theato, Y. Zhang, E. B. Coughlin, J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 4309–4316.
- 37Z. Zhang, D. Lei, C. Zhang, Z. Wang, Y. Jin, W. Zhang, X. Liu, J. Sun, Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2208619.
- 38P. Song, H. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1901244.
- 39H. F. Lu, M. Wang, X. M. Chen, B. P. Lin, H. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14364–14369.
- 40I. H. Kim, S. Choi, J. Lee, J. Jung, J. Yeo, J. T. Kim, S. Ryu, S. Ahn, J. Kang, P. Poulin, S. O. Kim, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 1198–1205.
- 41S. Leanza, S. Wu, X. Sun, H. J. Qi, R. R. Zhao, Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2302066.
- 42F. Zhao, Y. Li, H. Gao, R. Tao, Y. Mao, Y. Chen, S. Zhou, J. Zhao, D. Wang, Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2303594.
- 43J. Lv, Y. Liu, J. Wei, E. Chen, L. Qin, Y. Yu, Nature 2016, 537, 179–184.
- 44W. Zou, X. Lin, E. M. Terentjev, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2101955.
- 45X. Qian, Q. Chen, Y. Yang, Y. Xu, Z. Li, Z. Wang, Y. Wu, Y. Wei, Y. Ji, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801103.