Highly Stable Photo-Assisted Zinc-Ion Batteries via Regulated Photo-Induced Proton Transfer
Wenwen Zha
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 P. R. China
Both authors contribute equally.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qiushi Ruan
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 P. R. China
Both authors contribute equally.
Search for more papers by this authorLong Ma
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorMeng Liu
State Key Lab Mol React Dynamics, Dynamics Research Center Energy and Environmental Material, Dalian Institute Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHuiwen Lin
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorLitao Sun
Key Lab of MEMS of Ministry of Education, SEU-FEI Nano-Pico Center, Southeast University, Nanjing, 210096 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
ZhengMing Sun
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Li Tao
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorWenwen Zha
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 P. R. China
Both authors contribute equally.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qiushi Ruan
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 P. R. China
Both authors contribute equally.
Search for more papers by this authorLong Ma
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorMeng Liu
State Key Lab Mol React Dynamics, Dynamics Research Center Energy and Environmental Material, Dalian Institute Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHuiwen Lin
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorLitao Sun
Key Lab of MEMS of Ministry of Education, SEU-FEI Nano-Pico Center, Southeast University, Nanjing, 210096 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
ZhengMing Sun
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Li Tao
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallic Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
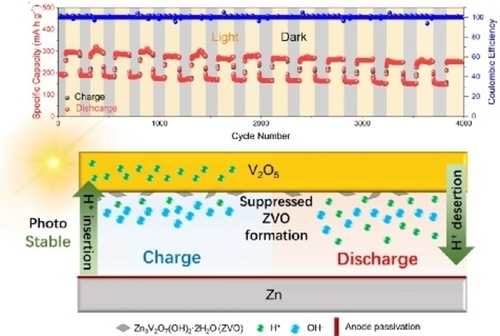
Light can significantly improve the performance of batteries. However, zinc ion battery often exhibits poor cycling life under illumination, which limits its application and the mechanism is still ambiguous. This work demonstrates integrated photo-assisted zinc-ion batteries with high cyclic stability of 4000 cycles, extending the previous record by one order of magnitude through the discovery and optimization of a photo-induced proton transfer.
Abstract
Photo-assisted ion batteries utilize light to boost capacity but face cycling instability due to complex charge/ion transfer under illumination. This study identified photo-induced proton transfer (photo-induced PT) as a significant process in photo-(dis)charging of widely-used V2O5-based zinc-ion batteries, contributing to enhanced capacity under illumination but jeopardizing photo-stability. Photo-induced PT occurs at 100 ps after photo-excitation, inducing rapid proton extraction into V2O5 photoelectrode. This process creates a proton-deficient microenvironment on surface, leading to repetitive cathode dissolution and anode corrosion in each cycle. Enabling the intercalated protons from photo-induced PT to be reversibly employed in charge-discharge processes via the anode-alloying strategy achieves high photo-stability for the battery. Consequently, a ~54 % capacity enhancement was achieved in a V2O5-based zinc-ion battery under illumination, with ~90 % capacity retention after 4000 cycles. This extends the photo-stability record by 10 times. This study offers promising advancements in energy storage by addressing instability issues in photo-assisted ion batteries.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202400621-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf3.2 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aM. A. Green, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 15015;
- 1bM. A. Green, Prog. Photovoltaics 2001, 9, 123–135.
- 2
- 2aP. Zhang, F. Wang, M. Yu, X. Zhuang, X. Feng, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 7426–7451;
- 2bV. Vega-Garita, L. Ramirez-Elizondo, N. Narayan, P. Bauer, Prog. Photovoltaics 2019, 27, 346–370;
- 2cR. Wang, H. Liu, Y. Zhang, K. Sun, W. Bao, Small 2022, 18, 2203014.
- 3
- 3aB. D. Boruah, B. Wen, M. De Volder, Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 3527–3532;
- 3bJ. Li, Y. Zhang, Y. Mao, Y. Zhao, D. Kan, K. Zhu, S. Chou, X. Zhang, C. Zhu, J. Ren, Y. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, e202303056-e202303056;
- 3cY.-X. Tan, X. Zhang, J. Lin, Y. Wang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 2432–2447.
- 4
- 4aB. Deka Boruah, A. Mathieson, S. K. Park, X. Zhang, B. Wen, L. Tan, A. Boies, M. De Volder, Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100115;
- 4bB. D. Boruah, A. Mathieson, B. Wen, S. Feldmann, W. M. Dose, M. De Volder, Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 2414–2421;
- 4cJ. Lv, J. Xie, A. G. A. Mohamed, X. Zhang, Y. Wang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 1511–1528.
- 5
- 5aA. Paolella, C. Faure, G. Bertoni, S. Marras, A. Guerfi, A. Darwiche, P. Hovington, B. Commarieu, Z. Wang, M. Prato, M. Colombo, S. Monaco, W. Zhu, Z. Feng, A. Vijh, C. George, G. P. Demopoulos, M. Armand, K. Zaghib, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14643;
- 5bJ. Lv, Y.-X. Tan, J. Xie, R. Yang, M. Yu, S. Sun, M.-D. Li, D. Yuan, Y. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12716–12720.
- 6A. Gouder, F. Podjaski, A. Jimenez-Solano, J. Kroeger, Y. Wang, B. V. Lotsch, Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 1520–1530.
- 7L. Ma, Q. Ruan, W. Zha, L. Kong, Z. Sun, Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 202303586.
- 8
- 8aB. D. Boruah, B. Wen, M. De Volder, ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16616–16624;
- 8bN.-F. Yan, X.-P. Gao, Energy Environ. 2022, 5, 439–451.
- 9
- 9aZ. Fang, X. Hu, D. Yu, ChemPlusChem 2020, 85, 600–612;
- 9bX. Yu, G. Liu, T. Wang, H. Gong, H. Qu, X. Meng, J. He, J. Ye, Chem. Eur. J. 2022, 28, e202202104.
- 10C. Rodriguez-Seco, Y.-S. Wang, K. Zaghib, D. Ma, Nat. Photonics 2022, 11, 1443–1484.
- 11
- 11aL. E. Blanc, D. Kundu, L. F. Nazar, Joule 2020, 4, 771–799;
- 11bF. Wan, L. Zhang, X. Dai, X. Wang, Z. Niu, J. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1656;
- 11cZ. Xing, S. Wang, A. Yu, Z. Chen, Nano Energy 2018, 50, 229–244.
- 12
- 12aF. Podjaski, B. V. Lotsch, Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003049;
- 12bL. Zhang, S. Wei, S. Shao, Q. Shi, J. Li, Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 16524–16537;
- 12cL. Jiao, X. Zhang, Y. Feng, J. Lin, D. Yuan, Y. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, e202306506-e202306506.
- 13
- 13aO. Savateev, Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2200352;
- 13bP. Wang, M. Xue, D. Jiang, Y. Yang, J. Zhang, H. Dong, G. Sun, Y. Yao, W. Luo, Z. Zou, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2544;
- 13cQ. Ruan, X. Xi, B. Yan, L. Kong, C. Jiang, J. Tang, Z. Sun, Chem 2023, 9, 1850–1864.
- 14
- 14aB. C. Westlake, M. K. Brennaman, J. J. Concepcion, J. J. Paul, S. E. Bettis, S. D. Hampton, S. A. Miller, N. V. Lebedeva, M. D. E. Forbes, A. M. Moran, T. J. Meyer, J. M. Papanikolas, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8554–8558;
- 14bN. Y. Shin, J. M. Ryss, X. Zhang, S. J. Miller, R. R. Knowles, Science 2019, 366, 364.
- 15J. Zhu, L. Cao, Y. Wu, Y. Gong, Z. Liu, H. E. Hoster, Y. Zhang, S. Zhang, S. Yang, Q. Yan, P. M. Ajayan, R. Vajtai, Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 5408–5413.
- 16
- 16aS. Chen, D. Ji, Q. Chen, J. Ma, S. Hou, J. Zhang, Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3526–3526;
- 16bF. Liu, Z. Chen, G. Fang, Z. Wang, Y. Cai, B. Tang, J. Zhou, S. Liang, Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 25.
- 17
- 17aY. Tao, D. Huang, H. Chen, Y. Luo, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 16576–16584;
- 17bR. Li, H. Zhang, Q. Zheng, X. Li, J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 5186–5193;
- 17cQ. Pan, R. Dong, H. Lv, X. Sun, Y. Song, X.-X. Liu, Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129491.
- 18Y. Li, Z. Huang, P. K. Kalambate, Y. Zhong, Z. Huang, M. Xie, Y. Shen, Y. Huang, Nano Energy 2019, 60, 752–759.
- 19S. N. Lou, N. Sharma, D. Goonetilleke, W. H. Saputera, T. M. Leoni, P. Brockbank, S. Lim, D.-W. Wang, J. Scott, R. Amal, Y. H. Ng, Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700545.
- 20Y. Kim, Y. Park, M. Kim, J. Lee, K. J. Kim, J. W. Choi, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2371.
- 21K. Zhu, T. Wu, K. Huang, Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 4089–4098.
- 22P. Oberholzer, E. Tervoort, A. Bouzid, A. Pasquarello, D. Kundu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 674–682.
- 23V. Mathew, B. Sambandam, S. Kim, S. Kim, S. Park, S. Lee, M. H. Alfaruqi, V. Soundharrajan, S. Islam, D. Y. Putro, J.-Y. Hwang, Y.-K. Sun, J. Kim, ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 2376–2400.
- 24L. Liu, T. Yuan, Z. Li, K. Chen, W. Huang, Electrochim. Acta 2023, 439, 141717.
- 25L. Wang, C. McCleese, A. Kovalsky, Y. Zhao, C. Burda, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12205–12208.
- 26
- 26aC. J. Gagliardi, L. Wang, P. Dongare, M. K. Brennaman, J. M. Papanikolas, T. J. Meyer, D. W. Thompson, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11106–11109;
- 26bZ. Zhang, W. Xie, J. Li, H. Zhang, Q. Wang, C. Zhang, G. Xu, J. Gao, A. A. Rogachev, H. Cao, Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2200883.
- 27S. Li, C. Huang, L. Gao, Q. Shen, P. Li, X. Qu, L. Jiao, Y. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202211478.
- 28C. Li, S. Jin, L. A. Archer, L. F. J. J. Nazar, 2022, 6, 1733–1738.
- 29
- 29aH. Liu, P. Wu, R. Wang, H. Meng, Y. Zhang, W. Bao, J. Li, ACS Nano 2023, 17, 1560–1569;
- 29bM. Wilhelm, R. Adam, A. Bhardwaj, I. Neumann, S. H. Cho, Y. Yamada, T. Sekino, J. Tao, Z. Hong, T. Fischer, S. Mathur, Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 2200765;
- 29cJ. Wang, Y. Wang, C. Zhu, B. Liu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 4071–4078;
- 29dJ. Li, C. Ren, L. Zhang, W. Jiang, H. Liu, J. Su, M. Li, J. Energy Chem. 2022, 65, 205–209;
- 29eY. Qu, X. He, J. Hu, L. Duan, J. Wang, S. Liao, F. Lu, J. Power Sources 2023, 555, 232374.
- 30L. M. Baugh, F. L. Tye, N. C. White, J. Appl. Electrochem. 1983, 13, 623–635.