Tandem Synergistic Effect of Cu-In Dual Sites Confined on the Edge of Monolayer CuInP2S6 toward Selective Photoreduction of CO2 into Multi-Carbon Solar Fuels
Corresponding Author
Wa Gao
School of Physical Science and Technology, Tiangong University, Tianjin, 300387 P. R. China
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Li Shi
State Key Laboratory of Organic Electronics and Information Displays & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing, 210023 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWentao Hou
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCheng Ding
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Qi Liu
School of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, School of Materials and Engineering, Anhui Polytechnic University, Wuhu, 241000 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Ran Long
School of Chemistry and Materials Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230036 Anhui, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHaoqiang Chi
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yongcai Zhang
Chemistry Interdisciplinary Research Center, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, 225009 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaoyong Xu
Chemistry Interdisciplinary Research Center, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, 225009 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXueying Ma
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorZheng Tang
Key Laboratory of Soft Chemistry and Functional Materials (MOE), Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210094 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yong Yang
Key Laboratory of Soft Chemistry and Functional Materials (MOE), Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210094 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Xiaoyong Wang
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Qing Shen
Graduate School of Informatics and Engineering, University of Electrocommunication, 1-5-1 Chofugaoka, Chofu, Tokyo 1828585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yujie Xiong
School of Chemistry and Materials Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230036 Anhui, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jinlan Wang
School of Physics, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 Jiangsu, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhigang Zou
School of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, School of Materials and Engineering, Anhui Polytechnic University, Wuhu, 241000 P. R. China
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
School of Science and Engineering, The Chinese University of Hongkong (Shenzhen), Shenzhen, Guangdong 518172 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yong Zhou
School of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, School of Materials and Engineering, Anhui Polytechnic University, Wuhu, 241000 P. R. China
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
School of Science and Engineering, The Chinese University of Hongkong (Shenzhen), Shenzhen, Guangdong 518172 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wa Gao
School of Physical Science and Technology, Tiangong University, Tianjin, 300387 P. R. China
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Li Shi
State Key Laboratory of Organic Electronics and Information Displays & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing, 210023 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWentao Hou
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCheng Ding
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Qi Liu
School of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, School of Materials and Engineering, Anhui Polytechnic University, Wuhu, 241000 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Ran Long
School of Chemistry and Materials Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230036 Anhui, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHaoqiang Chi
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yongcai Zhang
Chemistry Interdisciplinary Research Center, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, 225009 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaoyong Xu
Chemistry Interdisciplinary Research Center, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, 225009 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXueying Ma
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorZheng Tang
Key Laboratory of Soft Chemistry and Functional Materials (MOE), Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210094 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yong Yang
Key Laboratory of Soft Chemistry and Functional Materials (MOE), Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210094 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Xiaoyong Wang
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Qing Shen
Graduate School of Informatics and Engineering, University of Electrocommunication, 1-5-1 Chofugaoka, Chofu, Tokyo 1828585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yujie Xiong
School of Chemistry and Materials Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230036 Anhui, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jinlan Wang
School of Physics, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189 Jiangsu, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhigang Zou
School of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, School of Materials and Engineering, Anhui Polytechnic University, Wuhu, 241000 P. R. China
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
School of Science and Engineering, The Chinese University of Hongkong (Shenzhen), Shenzhen, Guangdong 518172 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yong Zhou
School of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, School of Materials and Engineering, Anhui Polytechnic University, Wuhu, 241000 P. R. China
School of Physics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Eco-materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC), National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093 P. R. China
School of Science and Engineering, The Chinese University of Hongkong (Shenzhen), Shenzhen, Guangdong 518172 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
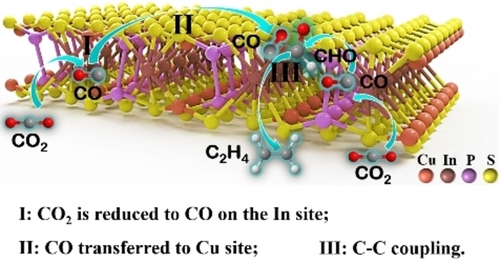
The tandem synergistic effect of charge-enriched Cu−In dual sites confined on the edge of CuInP2S6 ML triggers C−C coupling, facilitating the dominant generation of C2H4. The marginal In site of ML preeminently targets CO2 conversion to *CO under light illumination, and the *CO then migrate to the neighbor Cu sites for the subsequent C−C coupling reaction into C2H4 with thermodynamic and kinetic feasibility.
Abstract
One-unit-cell, single-crystal, hexagonal CuInP2S6 atomically thin sheets of≈0.81 nm in thickness was successfully synthesized for photocatalytic reduction of CO2. Exciting ethene (C2H4) as the main product was dominantly generated with the yield-based selectivity reaching ≈56.4 %, and the electron-based selectivity as high as ≈74.6 %. The tandem synergistic effect of charge-enriched Cu−In dual sites confined on the lateral edge of the CuInP2S6 monolayer (ML) is mainly responsible for efficient conversion and high selectivity of the C2H4 product as the basal surface site of the ML, exposing S atoms, can not derive the CO2 photoreduction due to the high energy barrier for the proton-coupled electron transfer of CO2 into *COOH. The marginal In site of the ML preeminently targets CO2 conversion to *CO under light illumination, and the *CO then migrates to the neighbor Cu sites for the subsequent C−C coupling reaction into C2H4 with thermodynamic and kinetic feasibility. Moreover, ultrathin structure of the ML also allows to shorten the transfer distance of charge carriers from the interior onto the surface, thus inhibiting electron-hole recombination and enabling more electrons to survive and accumulate on the exposed active sites for CO2 reduction.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202317852-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf4.6 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aH. Lin, S. Lou, H. Zhang, J. Ye, Joule 2022, 6, 294–314;
- 1bR. Das, R. Paul, A. Parui, A. Shrotri, C. Atzori, K. A. Lomachenko, A. K. Singh, J. Mondal, S. C. Peter, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 422;
- 1cE. Gong, S. Ali, C. B. Hiragond, H. S. Kim, N. S. Powar, D. Kim, H. Kim, S. -Il In, Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 880–937;
- 1dC. Feng, Z. P. Wu, K. W. Huang, J. Ye, H. Zhang, Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200180.
- 2
- 2aB. Ni, G. Zhang, H. Wang, Y. Min, K. Jiang, H. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202215574;
- 2bH. Ou, G. Li, W. Ren, B. Pan, G. Luo, Z. Hu, D. Wang, Y. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 22075–22082;
- 2cG. Wang, Z. Chen, T. Wang, D. Wang, J. Mao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202210789;
- 2dJ. Zhu, W. Shao, X. Li, X. Jiao, J. Zhu, Y. Sun, Y. Xie, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 18233–18241.
- 3
- 3aY. Zhao, K. Chang, Q. Gu, B. Yang, J. Xu, Y. Zhang, C. Pan, Z. Wang, Y. Lou, Y. Zhu, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 8986–8994;
- 3bY. Zhang, W. Zhou, Y. Tang, Y. Guo, Z. Geng, L. Liu, X. Tan, H. Wang, T. Yu, J. Ye, Appl. Catal. B 2022, 305, 121055;
- 3cM. Qorbani, A. Sabbah, Y. R. Lai, S. Kholimatussadiah, S. Quadir, C. Y. Huang, I. Shown, Y. F. Huang, M. Hayashi, K. H. Chen, L. C. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1256.
- 4C. Tsai, K. Chan, F. Abild-Pedersen, J. K. Nørskov, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 13156–13164.
- 5G. O. Larrazábal, A. J. Martín, S. Mitchell, R. Hauert, J. Pérez-Ramírez, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 6265.
- 6X. Li, Y. Sun, J. Xu, Y. Shao, J. Wu, X. Xu, Y. Pan, H. Ju, J. Zhu, Y. Xie, Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 690–699.
- 7H. Shi, H. Wang, Y. Zhou, J. Li, P. Zhai, X. Li, G. G. Gurzadyan, J. Hou, H. Yang, X. Guo, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202208904.
- 8
- 8aJ. Ran, H. Zhang, S. Fu, M. Jaroniec, J. Shan, B. Xia, Y. Qu, J. Qu, S. Chen, L. Song, J. M. Cairney, L. Jing, S. Z. Qiao, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4600;
- 8bZ. Cheng, T. A. Shifa, F. Wang, Y. Gao, P. He, K. Zhang, C. Jiang, Q. Liu, J. He, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1707433;
- 8cB. Xia, B. He, J. Zhang, L. Li, Y. Zhang, J. Yu, J. Ran, S. Z. Qiao, Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2201449;
- 8dL. mei Fang, Y. Zeng, M. Ekholm, C. feng Hu, Q. guo J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2021, 28, 3728–3736;
- 8eW. Gao, S. Li, H. He, X. Li, Z. Cheng, Y. Yang, Q. Shen, X. Wang, Y. Xiong, Y. Zhou, Z. Zou, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4747.
- 9
- 9aM. Si, A. K. Saha, P. Y. Liao, S. Gao, S. M. Neumayer, J. Jian, J. Qin, N. Balke Wisinger, H. Wang, P. Maksymovych, W. Wu, S. K. Gupta, P. D. Ye, ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8760–8765;
- 9bC. Chen, H. Liu, Q. Lai, X. Mao, J. Fu, Z. Fu, H. Zeng, Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 3275–3282;
- 9cS. Baek, H. H. Yoo, J. H. Ju, P. Sriboriboon, P. Singh, J. Niu, J. H. Park, C. Shin, Y. Kim, S. Lee, Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200566;
- 9dW. F. Io, M. C. Wong, S. Y. Pang, Y. Zhao, R. Ding, F. Guo, J. Hao, Nano Energy 2022, 99, 107371.
- 10M. A. Susner, A. Belianinov, A. Borisevich, Q. He, M. Chyasnavichyus, H. Demir, D. S. Sholl, P. Ganesh, D. L. Abernathy, M. A. McGuire, P. Maksymovych, ACS Nano 2015, 9, 12365.
- 11J. Zhou, J. Li, L. Kan, L. Zhang, Q. Huang, Y. Yan, Y. Chen, J. Liu, S. L. Li, Y. Q. Lan, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4681.
- 12M. P. Jiang, K. K. Huang, J. H. Liu, D. Wang, Y. Wang, X. Wang, Z. Da Li, X. Y. Wang, Z. Bin Geng, X. Y. Hou, S. H. Feng, Chem 2020, 6, 2335–2346.
- 13
- 13aK. Kähler, M. C. Holz, M. Rohe, J. Strunk, M. Muhler, ChemPhysChem 2010, 11, 2521–2529;
- 13bR. Zhang, H. Wang, S. Tang, C. Liu, F. Dong, H. Yue, B. Liang, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 9280–9286;
- 13cA. Yee, S. J. Morrison, H. Idriss, J. Catal. 1999, 186, 279–295.
- 14Q. Liu, H. Cheng, T. Chen, T. W. B. Lo, Z. Xiang, F. Wang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 225–233.
- 15X. Shi, X. Dong, Y. He, P. Yan, S. Zhang, F. Dong, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 3965–3973.