Precision Sequence-Defined Polymers: From Sequencing to Biological Functions
Dr. Qiangqiang Shi
Department of Pharmacy, The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, and Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, 96 Jinzhai Road, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Zhengbiao Zhang
State and Local Joint Engineering Laboratory for Novel Functional Polymeric Materials, College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, State Key Laboratory of Radiation Medicine and Protection, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Shiyong Liu
Department of Pharmacy, The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, and Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, 96 Jinzhai Road, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Qiangqiang Shi
Department of Pharmacy, The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, and Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, 96 Jinzhai Road, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Zhengbiao Zhang
State and Local Joint Engineering Laboratory for Novel Functional Polymeric Materials, College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, State Key Laboratory of Radiation Medicine and Protection, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Shiyong Liu
Department of Pharmacy, The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, and Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, 96 Jinzhai Road, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
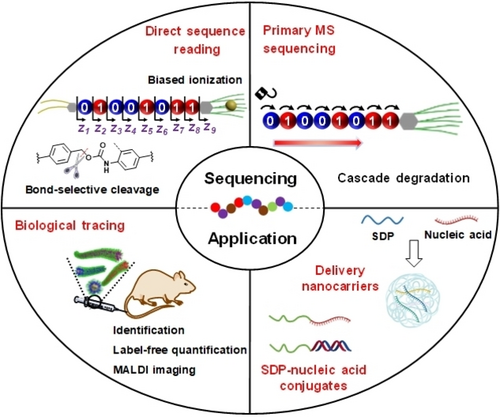
This Minireview summarizes recent advances in sequence-defined synthetic polymers (SDPs), focusing on newly developed sequencing methods including tandem mass spectrometry (MS) based on bond-selective cleavage and biased ionization, and primary MS based on cascade degradation. Their biological functions are also highlighted, and future perspectives of SDPs outlined.
Abstract
Precise sequence-defined polymers (SDPs) with uniform chain-to-chain structure including chain length, unit sequence, and end functionalities represent the pinnacle of sophistication in the realm of polymer science. For example, the absolute control over the unit sequence of SDPs allows for the bottom-up design of polymers with hierarchical microstructures and functions. Accompanied with the development of synthetic techniques towards precision SDPs, the decoding of SDP sequences and construction of advanced functions irreplaceable by other synthetic materials is of central importance. In this Minireview, we focus on recent advances in SDP sequencing techniques including tandem mass spectrometry (MS), chemically assisted primary MS, as well as other non-destructive sequencing methods such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, circular dichroism (CD), and nanopore sequencing. Additionally, we delve into the promising prospects of SDP functions in the area of cutting-edge biological research. Topics of exploration include gene delivery systems, the development of hybrid materials combining SDPs and nucleic acids, protein recognition and regulation, as well as the interplay between chirality and biological functions. A brief outlook towards the future directions of SDPs is also presented.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
References
- 1J.-F. Lutz, Polym. Chem. 2010, 1, 55–62.
- 2
- 2aQ. Shi, Z. Deng, M. Hou, X. Hu, S. Liu, Prog. Polym. Sci. 2023, 141, 101677;
- 2bJ.-F. Lutz, M. Ouchi, D. R. Liu, M. Sawamoto, Science 2013, 341, 1238149;
- 2cJ. K. Szymanski, Y. M. Abul-Haija, L. Cronin, Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 649–658;
- 2dY. Brudno, D. R. Liu, Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 265–276;
- 2eH. Yamauchi, S. Inayama, M. Nakabayashi, S. Hayashi, ACS Macro Lett. 2023, 12, 1264–1271;
- 2fW. He, S. Wang, M. Li, X. Wang, Y. Tao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112439.
- 3
- 3aL. Hartmann, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2011, 212, 8–13;
- 3bA. M. Rosales, R. A. Segalman, R. N. Zuckermann, Soft Matter 2013, 9, 8400–8414;
- 3cS. Lecommandoux, É. Garanger, C. R. Chim. 2016, 19, 143–147;
- 3dY. Wang, E. Wagner, Pharmaceutica 2020, 12, 888;
- 3eA. Shen, L. Zhang, Y. Xie, X. Zhu, J. Hu, S. Liu, Nano Today 2023, 48, 101728;
- 3fS. Liu, Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 40, 1129–1130.
- 4
- 4aW.-B. Zhang, X.-L. Wu, G.-Z. Yin, Y. Shao, S. Z. D. Cheng, Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 117–132;
- 4bM. Vybornyi, Y. Vyborna, R. Häner, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 4347–4360;
- 4cA. J. DeStefano, R. A. Segalman, E. C. Davidson, JACS Au 2021, 1, 1556–1571.
- 5
- 5aH. Mutlu, J. F. Lutz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13010–13019;
- 5bM. Soete, C. Mertens, N. Badi, F. E. Du Prez, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 22378–22390.
- 6F. Sanger, H. Tuppy, Biochem. J. 1951, 49, 481–490.
- 7
- 7aA. L. Richards, A. E. Merrill, J. J. Coon, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 24, 11–17;
- 7bJ. J. Coon, J. E. P. Syka, J. Shabanowitz, D. F. Hunt, BioTechniques 2005, 38, 519–523;
- 7cP. Edman, E. Högfeldt, L. G. Sillén, P.-O. Kinell, Acta Chem. Scand. 1950, 4, 283–293.
- 8F. Sanger, S. Nicklen, A. R. Coulson, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5463–5467.
- 9
- 9aY. Wang, Y. Zhao, A. Bollas, Y. Wang, K. F. Au, Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1348–1365;
- 9bY. L. Ying, J. Zhang, R. Gao, Y. T. Long, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13154–13161.
- 10
- 10aM. G. T. A. Rutten, F. W. Vaandrager, J. A. A. W. Elemans, R. J. M. Nolte, Nat. Chem. Rev. 2018, 2, 365–381;
- 10bJ. Steinkoenig, R. Aksakal, F. Du Prez, Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 120, 109260;
- 10cU. S. Gunay, B. E. Petit, D. Karamessini, A. Al Ouahabi, J.-A. Amalian, C. Chendo, M. Bouquey, D. Gigmes, L. Charles, J.-F. Lutz, Chem 2016, 1, 114–126;
- 10dA. C. Boukis, K. Reiter, M. Frolich, D. Hofheinz, M. A. R. Meier, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1439;
- 10eJ. A. Amalian, G. Cavallo, A. Al Ouahabi, J. F. Lutz, L. Charles, Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7266–7272;
- 10fN. F. König, A. Al Ouahabi, L. Oswald, R. Szweda, L. Charles, J. F. Lutz, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3774;
- 10gJ. O. Holloway, F. Van Lijsebetten, N. Badi, H. A. Houck, F. E. Du Prez, Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903698.
- 11
- 11aG. L. Sternhagen, S. Gupta, Y. Zhang, V. John, G. J. Schneider, D. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 4100–4109;
- 11bF. Jiao, X. Wu, T. Jian, S. Zhang, H. Jin, P. He, C.-L. Chen, J. J. De Yoreo, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 12223–12230;
- 11cS. Xuan, R. N. Zuckermann, Polymer 2020, 202, 122691;
- 11dZ. Li, B. Cai, W. Yang, C. L. Chen, Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 14031–14087;
- 11eM. Wang, Y. Song, S. Zhang, X. Zhang, X. Cai, Y. Lin, J. J. De Yoreo, C. L. Chen, Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg1448;
- 11fB. A. G. Lamers, J. J. B. van der Tol, K. M. Vonk, B. F. M. de Waal, A. R. A. Palmans, E. W. Meijer, G. Vantomme, ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 9, 38–42;
- 11gX. Y. Yan, Z. Lin, W. Zhang, H. Xu, Q. Y. Guo, Y. Liu, J. Luo, X. Y. Liu, R. Zhang, J. Huang, T. Liu, Z. Su, R. Zhang, S. Zhang, T. Liu, S. Z. D. Cheng, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 5226–5234;
- 11hM. D. Dore, T. Trinh, M. Zorman, D. de Rochambeau, C. M. Platnich, P. Xu, X. Luo, J. M. Remington, V. Toader, G. Cosa, J. Li, H. F. Sleiman, Chem 2021, 7, 2395–2414;
- 11iY. Kwon, H. Ma, K. T. Kim, Macromolecules 2022, 55, 2768–2776;
- 11jF. J. Rizzuto, M. D. Dore, M. G. Rafique, X. Luo, H. F. Sleiman, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 12272–12279;
- 11kJ. Xu, C. Lv, Q. Shi, J. Zhang, N. Wang, G. Zhang, J. Hu, S. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202306119;
- 11lQ.-Q. Shi, X. Zhou, J. Xu, N. Wang, J.-L. Zhang, X.-L. Hu, S.-Y. Liu, Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 41, 768–777;
- 11mS. Han, P. Wen, H. Wang, Y. Zhou, Y. Gu, L. Zhang, Y. Shao-Horn, X. Lin, M. Chen, Nat. Mater. 2023, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-41023-01693-z.
- 12
- 12aP. Chandra, A. M. Jonas, A. E. Fernandes, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 5179–5184;
- 12bP. Chandra, A. M. Jonas, A. E. Fernandes, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 6006–6011;
- 12cP. Chandra, A. M. Jonas, A. E. Fernandes, RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14194–14197.
- 13
- 13aM. Porel, D. N. Thornlow, N. N. Phan, C. A. Alabi, Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 590–596;
- 13bE. Maron, J. H. Swisher, J. J. Haven, T. Y. Meyer, T. Junkers, H. G. Borner, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10747–10751;
- 13cS. Celasun, D. Remmler, T. Schwaar, M. G. Weller, F. Du Prez, H. G. Borner, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1960–1964.
- 14F. Sanger, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1988, 57, 1–28.
- 15J. Shendure, H. Ji, Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1135–1145.
- 16Q. Shi, H. Yin, R. Song, J. Xu, J. Tan, X. Zhou, J. Cen, Z. Deng, H. Tong, C. Cui, Y. Zhang, X. Li, Z. Zhang, S. Liu, Nat. Chem. 2023, 15, 257–270.
- 17
- 17aZ. Huang, Q. Shi, J. Guo, F. Meng, Y. Zhang, Y. Lu, Z. Qian, X. Li, N. Zhou, Z. Zhang, X. Zhu, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1918;
- 17bB. Song, D. Lu, A. Qin, B. Z. Tang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1672–1680;
- 17cQ. Shi, X. Zhou, J. Xu, J. Zhang, N. Wang, G. Zhang, J. Hu, S. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202214695.
- 18K. De Bruycker, A. Welle, S. Hirth, S. J. Blanksby, C. Barner-Kowollik, Nat. Chem. Rev. 2020, 4, 257–268.
- 19
- 19aZ. Huang, J. Zhao, Z. Wang, F. Meng, K. Ding, X. Pan, N. Zhou, X. Li, Z. Zhang and X. Zhu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13612–13617;
- 19bB. Liu, Q. Shi, L. Hu, Z. Huang, X. Zhu, Z. Zhang, Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 1702–1707;
- 19cK. Ding, Y. Zhang, Z. Huang, B. Liu, Q. Shi, L. Hu, N. Zhou, Z. Zhang, X. Zhu, Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 119, 421–425;
- 19dQ. Shi, X. Cao, Y. Zhang, S. Duan, L. Hu, Y. Xu, J. Lu, Z. Huang, Z. Zhang, X. Zhu, Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 5974–5980.
- 20
- 20aM. G. Paulick, K. M. Hart, K. M. Brinner, M. Tjandra, D. H. Charych, R. N. Zuckermann, J. Comb. Chem. 2006, 8, 417–426;
- 20bM. Soete, K. De Bruycker, F. Du Prez, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202116718.
- 21M. Frölich, D. Hofheinz, M. A. R. Meier, Commun. Chem. 2020, 3, 184.
- 22S. Martens, A. Landuyt, P. Espeel, B. Devreese, P. Dawyndt, F. Du Prez, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4451.
- 23A. Burel, C. Carapito, J.-F. Lutz, L. Charles, Macromolecules 2017, 50, 8290–8296.
- 24Q. Shi, T. Miao, Y. Liu, L. Hu, H. Yang, H. Shen, M. Piao, Z. Huang, Z. Zhang, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 43, e2200029.
- 25A. Thakkar, A. S. Cohen, M. D. Connolly, R. N. Zuckermann, D. Pei, J. Comb. Chem. 2009, 11, 294–302.
- 26C. Proulx, F. Noe, S. Yoo, M. D. Connolly, R. N. Zuckermann, Biopolymers 2016, 106, 726–736.
- 27O. Shelef, S. Gnaim, D. Shabat, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 21177–21188.
- 28
- 28aS. D. Dahlhauser, P. R. Escamilla, A. N. VandeWalle, J. T. York, R. M. Rapagnani, J. S. Shei, S. A. Glass, J. N. Coronado, S. R. Moor, D. P. Saunders, E. V. Anslyn, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2744–2749;
- 28bS. D. Dahlhauser, S. R. Moor, M. S. Vera, J. T. York, P. Ngo, A. J. Boley, J. N. Coronado, Z. B. Simpson, E. V. Anslyn, Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2021, 2, 100393.
- 29M. Soete, J. Van Hoorde, F. Du Prez, Polym. Chem. 2022, 13, 4178–4185.
- 30T. Mondal, L. Charles, J. F. Lutz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 20390–20393.
- 31M. Soete, F. E. Du Prez, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202819.
- 32Z. Zhu, C. J. Cardin, Y. Gan, H. M. Colquhoun, Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 653–660.
- 33J. M. Lee, H. Jang, S. W. Lee, K. T. Kim, JACS Au 2022, 2, 2108–2118.
- 34Y. Ren, R. Jamagne, D. J. Tetlow, D. A. Leigh, Nature 2022, 612, 78–82.
- 35C. Cao, L. F. Krapp, A. Al Ouahabi, N. F. Konig, N. Cirauqui, A. Radenovic, J. F. Lutz, M. D. Peraro, Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc2661.
- 36G. Cavallo, S. Poyer, J. A. Amalian, F. Dufour, A. Burel, C. Carapito, L. Charles, J. F. Lutz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6266–6269.
- 37S. D. Dahlhauser, C. D. Wight, S. R. Moor, R. A. Scanga, P. Ngo, J. T. York, M. S. Vera, K. J. Blake, I. M. Riddington, J. F. Reuther, E. V. Anslyn, ACS Cent. Sci. 2022, 8, 1125–1133.
- 38Q. Shi, T. Miao, J. Lu, L. Hu, X. Huang, Z. Wang, M. Piao, Z. Huang, Z. Zhang, Giant 2023, 15, 100172.
- 39M. Boukhet, N. F. Konig, A. A. Ouahabi, G. Baaken, J. F. Lutz, J. C. Behrends, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2017, 38, 1700680.
- 40D. Karamessini, T. Simon-Yarza, S. Poyer, E. Konishcheva, L. Charles, D. Letourneur, J.-F. Lutz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10574–10578.
- 41Q. Shi, C. Song, M. Chen, J. Xu, S. Zheng, J. Tan, J. Zhang, N. Wang, J. Hu, S. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1023c07577.
- 42
- 42aB. Leader, Q. J. Baca, D. E. Golan, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2008, 7, 21–39;
- 42bU. Sahin, K. Kariko, O. Tureci, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2014, 13, 759–780;
- 42cJ. A. Kulkarni, D. Witzigmann, S. B. Thomson, S. Chen, B. R. Leavitt, P. R. Cullis, R. van der Meel, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 630–643;
- 42dQ. Zhang, J. Zhang, J. Song, Y. Liu, X. Ren, Y. Zhao, ACS Nano 2021, 15, 8001–8038.
- 43
- 43aA. R. Kirtane, M. Verma, P. Karandikar, J. Furin, R. Langer, G. Traverso, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 369–384;
- 43bJ. Szebeni, G. Storm, J. Y. Ljubimova, M. Castells, E. J. Phillips, K. Turjeman, Y. Barenholz, D. J. A. Crommelin, M. A. Dobrovolskaia, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 337–346;
- 43cM. D. Shin, S. Shukla, Y. H. Chung, V. Beiss, S. K. Chan, O. A. Ortega-Rivera, D. M. Wirth, A. Chen, M. Sack, J. K. Pokorski, N. F. Steinmetz, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 646–655;
- 43dP. Qu, J. N. Faraone, J. P. Evans, Y. M. Zheng, L. Yu, Q. Ma, C. Carlin, G. Lozanski, L. J. Saif, E. M. Oltz, R. J. Gumina, S. L. Liu, N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1329–1331.
- 44
- 44aX. Hou, T. Zaks, R. Langer, Y. Dong, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1078–1094;
- 44bF. Freitag, E. Wagner, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2021, 168, 30–54;
- 44cK. A. Hajj, K. A. Whitehead, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17056.
- 45L. Li, J. Cen, W. Li, W. Pan, Y. Zhang, H. Yin, J. Hu, S. Liu, CCS Chem. 2022, 4, 3864–3877.
- 46
- 46aC. Plank, M. X. Tang, A. R. Wolfe, F. C. Szoka Jr., Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 319–332;
- 46bQ. Leng, A. J. Mixson, Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e40;
- 46cQ. R. Chen, L. Zhang, P. W. Luther, A. J. Mixson, Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 1338–1345.
- 47
- 47aX. L. Wang, S. Ramusovic, T. Nguyen, Z. R. Lu, Bioconjugate Chem. 2007, 18, 2169–2177;
- 47bX. L. Wang, R. Jensen, Z. R. Lu, J. Controlled Release 2007, 120, 250–258.
- 48
- 48aR. Xu, X. L. Wang, Z. R. Lu, Langmuir 2010, 26, 13874–13882;
- 48bA. M. Vaidya, Z. Sun, N. Ayat, A. Schilb, X. Liu, H. Jiang, D. Sun, J. Scheidt, V. Qian, S. He, H. Gilmore, W. P. Schiemann, Z. R. Lu, Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 907–919.
- 49
- 49aL. Hartmann, H. G. Borner, Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3425–3431;
- 49bL. Hartmann, E. Krause, M. Antonietti, H. G. Borner, Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1239–1244;
- 49cL. Hartmann, S. Hafele, R. Peschka-Suss, M. Antonietti, H. G. Borner, Chem 2008, 14, 2025–2033.
- 50D. Schaffert, C. Troiber, E. E. Salcher, T. Frohlich, I. Martin, N. Badgujar, C. Dohmen, D. Edinger, R. Klager, G. Maiwald, K. Farkasova, S. Seeber, K. Jahn-Hofmann, P. Hadwiger, E. Wagner, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8986–8989.
- 51
- 51aD. Zhang, E. N. Atochina-Vasserman, D. S. Maurya, N. Huang, Q. Xiao, N. Ona, M. Liu, H. Shahnawaz, H. Ni, K. Kim, M. M. Billingsley, D. J. Pochan, M. J. Mitchell, D. Weissman, V. Percec, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 12315–12327;
- 51bD. Zhang, E. N. Atochina-Vasserman, D. S. Maurya, M. Liu, Q. Xiao, J. Lu, G. Lauri, N. Ona, E. K. Reagan, H. Ni, D. Weissman, V. Percec, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 17975–17982;
- 51cD. Zhang, E. N. Atochina-Vasserman, J. Lu, D. S. Maurya, Q. Xiao, M. Liu, J. Adamson, N. Ona, E. K. Reagan, H. Ni, D. Weissman, V. Percec, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 4746–4753.
- 52C. Scholz, P. Kos, L. Leclercq, X. Jin, H. Cottet, E. Wagner, ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 2104–2110.
- 53
- 53aM. H. Teplensky, M. Evangelopoulos, J. W. Dittmar, C. M. Forsyth, A. J. Sinegra, S. Wang, C. A. Mirkin, Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 7, 911–927;
- 53bG. Yamankurt, R. J. Stawicki, D. M. Posadas, J. Q. Nguyen, R. W. Carthew, C. A. Mirkin, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 1312–1320;
- 53cJ. I. Cutler, E. Auyeung, C. A. Mirkin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1376–1391;
- 53dP. Kumthekar, C. H. Ko, T. Paunesku, K. Dixit, A. M. Sonabend, O. Bloch, M. Tate, M. Schwartz, L. Zuckerman, R. Lezon, R. V. Lukas, B. Jovanovic, K. McCortney, H. Colman, S. Chen, B. Lai, O. Antipova, J. Deng, L. Li, S. Tommasini-Ghelfi, L. A. Hurley, D. Unruh, N. V. Sharma, M. Kandpal, F. M. Kouri, R. V. Davuluri, D. J. Brat, M. Muzzio, M. Glass, V. Vijayakumar, J. Heidel, F. J. Giles, A. K. Adams, C. D. James, G. E. Woloschak, C. Horbinski, A. H. Stegh, Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabb3945.
- 54A. Jäschke, J. P. Fürste, D. Cech, V. A. Erdmann, Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 301–304.
- 55
- 55aT. Schnitzler, A. Herrmann, Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1419–1430;
- 55bM. Kwak, A. Herrmann, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5745–5755.
- 56K. Liu, L. Zheng, Q. Liu, J. W. de Vries, J. Y. Gerasimov, A. Herrmann, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14255–14262.
- 57
- 57aX. Lu, T. H. Tran, F. Jia, X. Tan, S. Davis, S. Krishnan, M. M. Amiji, K. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 12466–12469;
- 57bC. Zhang, L. Hao, C. M. Calabrese, Y. Zhou, C. H. Choi, H. Xing, C. A. Mirkin, Small 2015, 11, 5360–5368;
- 57cF. E. Alemdaroglu, A. Herrmann, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 1311–1320;
- 57dD. Wang, X. Lu, F. Jia, X. Tan, X. Sun, X. Cao, F. Wai, C. Zhang, K. Zhang, Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 9882–9886.
- 58J. O'Brien, S. H. Lee, S. Onogi, K. J. Shea, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16604–16607.
- 59J. Ren, N. Andrikopoulos, K. Velonia, H. Tang, R. Cai, F. Ding, P. C. Ke, C. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 9184–9205.
- 60M. Z. C. Hatit, C. N. Dobrowolski, M. P. Lokugamage, D. Loughrey, H. Ni, C. Zurla, A. J. Da Silva Sanchez, A. Radmand, S. G. Huayamares, R. Zenhausern, K. Paunovska, H. E. Peck, J. Kim, M. Sato, J. I. Feldman, M. A. Rivera, A. Cristian, Y. Kim, P. J. Santangelo, J. E. Dahlman, Nat. Chem. 2023, 15, 508–515.
- 61H. V. Nguyen, Y. Jiang, S. Mohapatra, W. Wang, J. C. Barnes, N. J. Oldenhuis, K. K. Chen, S. Axelrod, Z. Huang, Q. Chen, M. R. Golder, K. Young, D. Suvlu, Y. Shen, A. P. Willard, M. J. A. Hore, R. Gomez-Bombarelli, J. A. Johnson, Nat. Chem. 2022, 14, 85–93.
- 62R. Breslow, Z. L. Cheng, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9144–9146.
- 63R. Breslow, Science 1982, 218, 532–537.
- 64G. Maayan, M. D. Ward, K. Kirshenbaum, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13679–13684.
- 65C. M. Darapaneni, P. Ghosh, T. Ghosh, G. Maayan, Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 9573–9579.
- 66E. A. Hoff, R. K. Weigel, A. Rangamani, C. A. Alabi, ACS Polym. Au 2023, 3, 276–283.
- 67J. M. Mata, E. van der Nol, S. J. Pomplun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 19129–19139.
- 68E. Krieg, K. Gupta, A. Dahl, M. Lesche, S. Boye, A. Lederer, W. M. Shih, Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 369.
- 69M. Hebel, A. Riegger, M. M. Zegota, G. Kizilsavas, J. Gacanin, M. Pieszka, T. Luckerath, J. A. S. Coelho, M. Wagner, P. M. P. Gois, D. Y. W. Ng, T. Weil, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14026–14031.
- 70
- 70aJ. Louwsma, A. Carvalho, J.-F. Lutz, S. Joly, D. Chan-Seng, Polymer 2021, 217, 123465;
- 70bC. B. Cooper, Z. Bao, Acc. Mater. Res. 2022, 3, 948–959.