Cover Picture: Cyclotetrabenzil Derivatives for Electrochemical Lithium-Ion Storage (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 29/2023)
Graphical Abstract
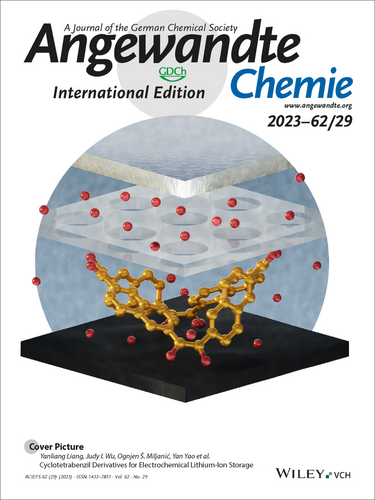
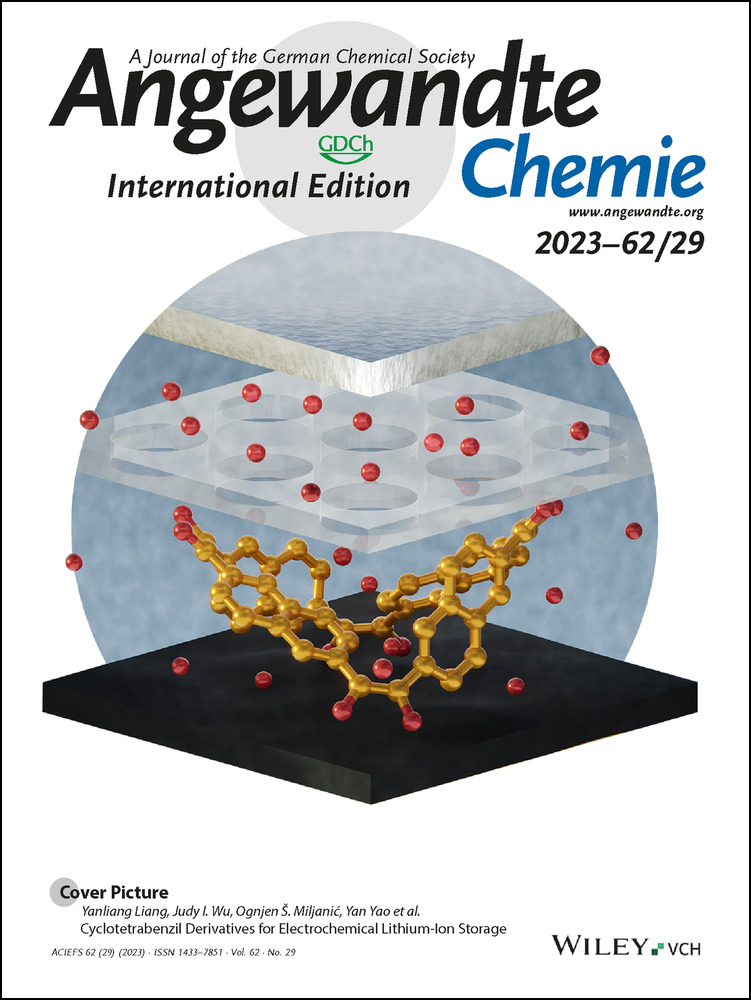
Organic electrode materials could break the dependency of lithium-ion batteries on minerals that are scarce and mined in conflict zones. In their Communication (e202300892), Yanliang Liang, Judy I. Wu, Ognjen Š. Miljanić, Yan Yao et al. report a naphthalene-based cyclotetrabenzil macrocycle as a promising organic electrode candidate. Its eight redox-active groups bring about a high specific capacity of 279 mAh g−1, while the low solubility—a consequence of the shape-persistent structure—results in stable cycling performance. Cover art: Ella Maru Studio.
Organic electrode materials could break the dependency of lithium-ion batteries on minerals that are scarce and mined in conflict zones. In their Communication (e202300892), Yanliang Liang, Judy I. Wu, Ognjen Š. Miljanić, Yan Yao et al. report a naphthalene-based cyclotetrabenzil macrocycle as a promising organic electrode candidate. Its eight redox-active groups bring about a high specific capacity of 279 mAh g−1, while the low solubility—a consequence of the shape-persistent structure—results in stable cycling performance. Cover art: Ella Maru Studio.
Chalcogen Bond
Polymers
CO2 Valorization
Metal–Organic Frameworks