A Significant Two-Dimensional Structural Transformation in a Coordination Polymer that Changes Its Electronic and Protonic Behavior
Yao Jing
Division of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University Kitashirakawa-Oiwakecho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-8502 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Yukihiro Yoshida
Division of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University Kitashirakawa-Oiwakecho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-8502 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Tokutaro Komatsu
School of Medicine, Nihon University, 30-1 Oyaguchi-Kamicho, Itabashi-ku, Tokyo, 173-8610 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hiroshi Kitagawa
Division of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University Kitashirakawa-Oiwakecho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-8502 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorYao Jing
Division of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University Kitashirakawa-Oiwakecho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-8502 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Yukihiro Yoshida
Division of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University Kitashirakawa-Oiwakecho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-8502 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Tokutaro Komatsu
School of Medicine, Nihon University, 30-1 Oyaguchi-Kamicho, Itabashi-ku, Tokyo, 173-8610 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hiroshi Kitagawa
Division of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University Kitashirakawa-Oiwakecho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-8502 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
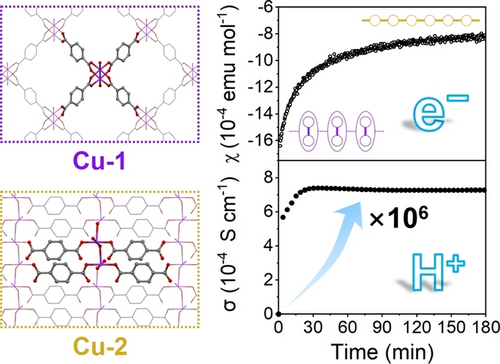
A 2D-to-2D structural transformation with a significant change in the coordination environment within the 2D layer was achieved in a copper-based coordination polymer in water at room temperature. The transformation led to large changes in the physical properties of the coordination polymers, such as proton conductivity and magnetism.
Abstract
A 2D-to-2D (2D: two-dimensional) structural transformation accompanying significant bond rearrangement and coordination environment change is demonstrated in a coordination polymer (CP) comprised of copper(II) ions and terephthalate (BDC2−) ligands for the first time. When immersed in water, a free-standing membrane of 2D Cu(BDC)(DMF) (Cu-1; DMF: N,N-dimethylformamide) transforms into 2D Cu(BDC)(H2O)2 (Cu-2) while maintaining its highly oriented layered structure. In the 2D sheet, paddlewheel-type CuII dimers coordinated with four bidentate BDC ligands in a square-planar array in Cu-1 were released to form uniform aqua-bridged CuII chains, which are cross-linked with each other by unidentate BDC ligands, in Cu-2. The present facile approach to implement the 2D-to-2D transformation accompanied by bond rearrangement, which is characteristic of CPs, leads to a marked increase in in-plane magnetic susceptibility and proton conductivity. In situ experiments in support of theoretical calculations unveiled the energy diagram that governs the unique structural transformation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202303778-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.6 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1K. S. Novoselov, A. K. Geim, S. V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S. V. Dubonos, I. V. Grigorieva, A. A. Firsov, Science 2004, 306, 666–669.
- 2
- 2aA. K. Geim, I. V. Grigorieva, Nature 2013, 499, 419–425;
- 2bC. Tan, X. Cao, X.-J. Wu, Q. He, J. Yang, X. Zhang, J. Chen, W. Zhao, S. Han, G.-H. Nam, M. Sindoro, H. Zhang, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6225–6331;
- 2cG. Chakraborty, I.-H. Park, R. Medishetty, J. J. Vittal, Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 3751–3891.
- 3
- 3aS. Latil, L. Henrard, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 036803;
- 3bB. Partoens, F. M. Peeters, Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 075404.
- 4
- 4aA. Splendiani, L. Sun, Y. Zhang, T. Li, J. Kim, C.-Y. Chim, G. Galli, F. Wang, Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1271–1275;
- 4bA. Kuc, N. Zibouche, T. Heine, Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 245213.
- 5
- 5aM. Naguib, V. N. Mochalin, M. W. Barsoum, Y. Gogotsi, Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 992–1005;
- 5bL. Jiang, D. Zhou, J. Yang, S. Zhou, H. Wang, X. Yuan, J. Liang, X. Li, Y. Chen, H. Li, J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 13651–13672.
- 6
- 6aM. Yankowitz, S. Chen, H. Polshyn, Y. Zhang, K. Watanabe, T. Taniguchi, D. Graf, A. F. Young, C. R. Dean, Science 2019, 363, 1059–1064;
- 6bL. Balents, C. R. Dean, D. K. Efetov, A. F. Young, Nat. Phys. 2020, 16, 725–733.
- 7
- 7aH.-L. Jiang, T. A. Makal, H.-C. Zhou, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 2232–2249;
- 7bS. R. Batten, R. Robson, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 1460–1494.
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980619)37:11<1460::AID-ANIE1460>3.0.CO;2-Z CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 8T. Kuila, S. Bose, A. K. Mishra, P. Khanra, N. H. Kim, J. H. Lee, Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 1061–1105.
- 9
- 9aX. Li, J. Shan, W. Zhang, S. Su, L. Yuwen, L. Wang, Small 2017, 13, 1602660;
- 9bA. Stergiou, N. Tagmatarchis, Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 18246–18257.
- 10
- 10aH. Yu, Y. Wang, Y. Jing, J. Ma, C.-F. Du, Q. Yan, Small 2019, 15, 1901503;
- 10bH. Huang, R. Jiang, Y. Feng, H. Ouyang, N. Zhou, X. Zhang, Y. Wei, Nanoscale 2020, 12, 1325–1338.
- 11
- 11aS. Kitagawa, M. Kondo, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1998, 71, 1739–1753;
- 11bW. Lu, Z. Wei, Z. Y. Gu, T. F. Liu, J. Park, J. Park, J. Tian, M. Zhang, Q. Zhang, T. Gentle, M. Bosch, H. C. Zhou, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5561–5593;
- 11cS.-Y. Ke, C.-C. Wang, CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 8776–8785;
- 11dA. Schoedel, M. Li, D. Li, M. O′Keeffe, O. M. Yaghi, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12466–12535;
- 11eR. E. Morris, L. Brammer, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 5444–5462;
- 11fL. S. Xie, G. Skorupskii, M. Dincă, Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8536–8580;
- 11gN. Behera, J. Duan, W. Jin, S. Kitagawa, EnergyChem 2021, 3, 100067.
- 12G. K. Kole, J. J. Vittal, Chem. Rev. 2013, 42, 1755–1775.
- 13H. Sato, R. Matsuda, M. H. Mir, S. Kitagawa, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7919–7921.
- 14
- 14aJ. Albalad, J. Aríñez-Soriano, J. Vidal-Gancedo, V. Lloveras, J. Juanhuix, I. Imaz, N. Aliaga-Alcalde, D. Maspoch, Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 13397–13400;
- 14bJ.-R. Zhang, J.-J. Lee, C.-H. Su, M.-J. Tsai, C.-Y. Li, J.-Y. Wu, Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 14201–14215;
- 14cY. Wu, M. I. Breeze, D. O'Hare, R. I. Walton, Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 254, 178–183;
- 14dX. Zhou, J. Dong, Y. Zhu, L. Liu, Y. Jiao, H. Li, Y. Han, K. Davey, Q. Xu, Y. Zheng, S.-Z. Qiao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 6681–6690.
- 15
- 15aC. G. Carson, K. Hardcastle, J. Schwartz, X. Liu, C. Hoffmann, R. A. Gerhardt, R. Tannenbaum, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2338–2343;
- 15bC. G. Carson, G. Brunnello, S. G. Lee, S. S. Jang, R. A. Gerhardt, R. Tannenbaum, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 2140–2145.
- 16Y. Jing, Y. Yoshida, P. Huang, H. Kitagawa, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202117417.
- 17
- 17aS. Cueto, V. Gramlich, W. Petter, F. S. Rys, P. Rys, Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 1991, 47, 75–78;
- 17bL. Deakin, A. M. Arif, J. S. Miller, Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 5072–5077.
- 18S. Zhao, Y. Wang, J. Dong, C. He, H. Yin, P. An, K. Zhao, X. Zhang, C. Gao, L. Zhang, J. Lv, J. Wang, J. Zhang, A. M. Khattak, N. A. Khan, Z. Wei, J. Zhang, S. Liu, H. Zhao, Z. Tang, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16184.
- 19
- 19aT. Rodenas, I. Luz, G. Prieto, B. Seoane, H. Miro, A. Corma, F. Kapteijn, F. X. Llabrés i Xamena, J. Gascon, Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 48–55;
- 19bG. Zhan, L. Fan, F. Zhao, Z. Huang, B. Chen, X. Yang, S.-f. Zhou, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806720.
- 20K. Tan, N. Nijem, P. Canepa, Q. Gong, J. Li, T. Thonhauser, Y. J. Chabal, Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 3153–3167.
- 21M. Nara, H. Torii, M. Tasumi, J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 19812–19817.
- 22
- 22aV. Paredes-García, R. C. Santana, R. Madrid, A. Vega, E. Spodine, D. Venegas-Yazigi, Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 8369–8377;
- 22bT. D. Smith, J. R. Pilbrow, Coord. Chem. Rev. 1974, 13, 173–278.
- 23R. Maurice, K. Sivalingam, D. Ganyushin, N. Guihery, C. de Graaf, F. Neese, Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 6229–6236.
- 24A. Ozarowski, Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 9760–9762.
- 25A. Abragam, B. Bleaney, Electron Paramagnetic Resonance of Transition Ions, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1970.
- 26
- 26aM. J. Van Vleet, T. Weng, X. Li, J. R. Schmidt, Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 3681–3721;
- 26bA. Khawam, D. R. Flanagan, J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 472–498;
- 26cM. Avrami, J. Chem. Phys. 1940, 8, 212–224;
- 26dB. V. Erofe'ev, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1946, 52, 511–514.
- 27J. D. Hancock, J. H. Sharp, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1972, 55, 74–77.
- 28
- 28aS. F. Hulbert, J. Br. Ceram. Soc. 1969, 6, 11–20;
- 28bF. Liu, S. J. Song, J. F. Xu, J. Wang, Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 6003–6012.
- 29S. S. Farvid, P. V. Radovanovic, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7015–7024.
- 30
- 30aP. Colomban, Proton Conductors: Solids, Membranes and Gels-Materials and Devices (Ed.: H. Baxter), Cambridge University Press, Oxford, 1992;
10.1017/CBO9780511524806 Google Scholar
- 30bK. D. Kreuer, Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 610–641;
- 30cD. W. Lim, H. Kitagawa, Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8416–8467.
- 31A. Bondi, J. Phys. Chem. 1964, 68, 441–451.