Asymmetric C1 Extension of Aldehydes through Biocatalytic Cascades for Stereodivergent Synthesis of Mandelic Acids
Graphical Abstract
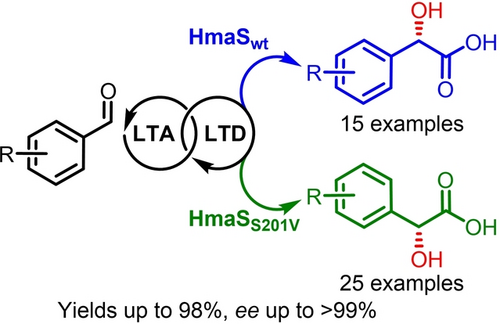
Biocatalytic cascades consisting of L-threonine aldolase (LTA), L-threonine dehydratase (LTD) and 4-hydroxymandelate synthase (HmaS) were developed for cyanide-free asymmetric C1-extension. Engineering of the central enzyme, HmaS, enabled the stereodivergent synthesis of mandelic acids from glycine and aromatic aldehydes.
Abstract
The development of mild, efficient, and enantioselective methods for preparing chiral building blocks from simple, renewable carbon units has been a long-term goal of the sustainable chemical industry. Mandelate derivatives are valuable pharmaceutical intermediates and chiral resolving agents, but their manufacture relies heavily on highly toxic cyanide. Herein, we report (S)-4-hydroxymandelate synthase (HmaS)-centered biocatalytic cascades for the synthesis of mandelates from benzaldehydes and glycine. We show that HmaS can be engineered to perform R-selective hydroxylation by single-point mutation, empowering the stereodivergent synthesis of both (S)- and (R)-mandelate derivatives. These biocatalytic cascades enabled the production of various mandelate derivatives with high atom economy as well as excellent yields (up to 98 %) and ee values (up to >99 %). This methodology offers an effective cyanide-free technology for greener and sustainable production of mandelate derivatives.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.