Synthesis of Twisted [n]Cycloparaphenylene by Alkene Insertion
Graphical Abstract
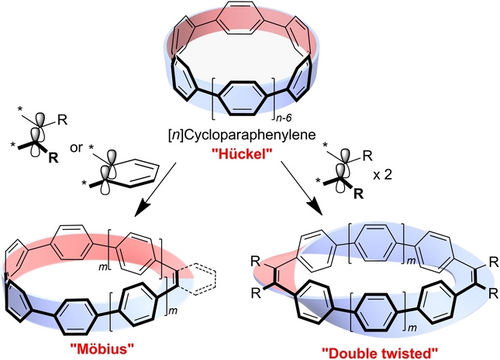
Mono-alkene-inserted [n]cycloparaphenylenes ([n]CPP) 1 with n=6, 8, and 10, mono-ortho-phenylene-inserted [6]CPP 2, and di-alkene-inserted [n]CPP with n=4, 6, and 8 were synthesized by inserting alkene or ortho-phenylene units into a CPP skeleton. 1 and 2 exhibited a Möbius topology only in the solid state, but mono-alkene-inserted [6]CPP with eight 1-pyrrolyl groups preserved the Möbius topology even in solution.
Abstract
Mono-alkene-inserted [n]cycloparaphenylenes 1 [(ene)-[n]CPP] with n=6, 8, and 10, mono-ortho-phenylene-inserted [6]CPP 2, and di-alkene-insertved [n]CPP 3 [(ene)2-[n]CPP] with n=4, 6, and 8 were synthesized by fusing CPP precursors and alkene or ortho- phenylene groups through coupling reactions. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction analyses reveal that the strips formed by the π-surfaces of 1 and 2 exhibited a Möbius topology in the solid state. While the Möbius topology in the parent 1 and 2 in solution was lost due to the free rotation of the paraphenylene unit even at low temperatures, ene-[6]CPP 4 with eight 1-pyrrolyl groups preserved the Möbius topology even in solution. Despite a twist, 1 has in-plane conjugation and possesses a unique size dependence of the electronic properties: namely, the opposite size dependency of the HOMO–LUMO energy relative to conventional π-conjugated molecules.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.